J Rheum Dis.
2023 Oct;30(4):234-242. 10.4078/jrd.2023.0030.
Changes in the cholesterol profile of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics or Janus kinase inhibitors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Center for Integrative Rheumatoid Transcriptomics and Dynamics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2546239
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2023.0030
Abstract
Objective
To assess the effects of biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) on lipid profiles in patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
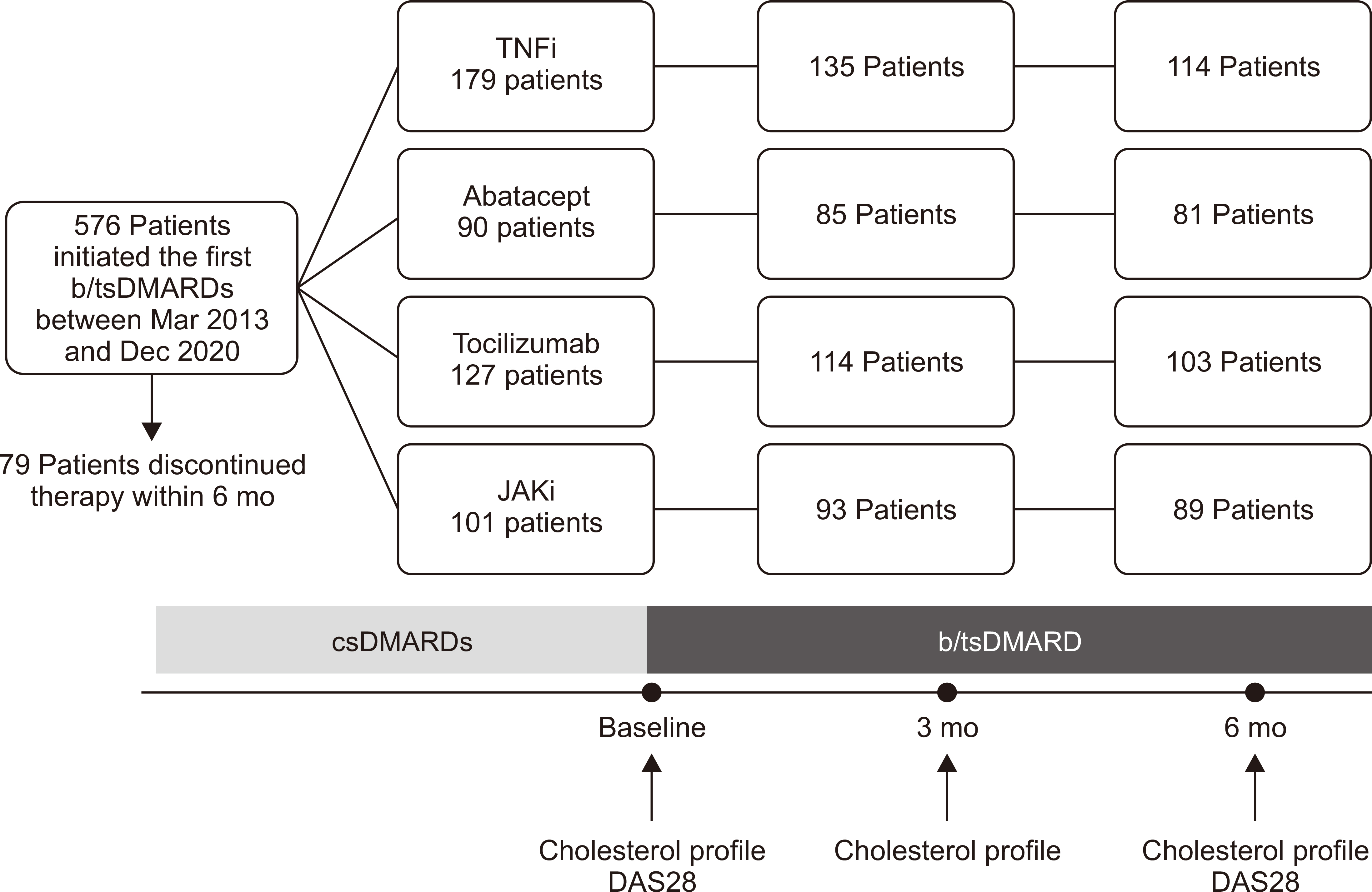
This retrospective single-center observational study included patients with RA taking a tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor (TNFi), abatacept, tocilizumab, or a Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) for at least 6 months. Changes in lipid profile were assessed at 6 months after the start of treatment, and associations between changes in lipid profiles and clinical efficacy, concomitant medications, and comorbidities were evaluated.
Results
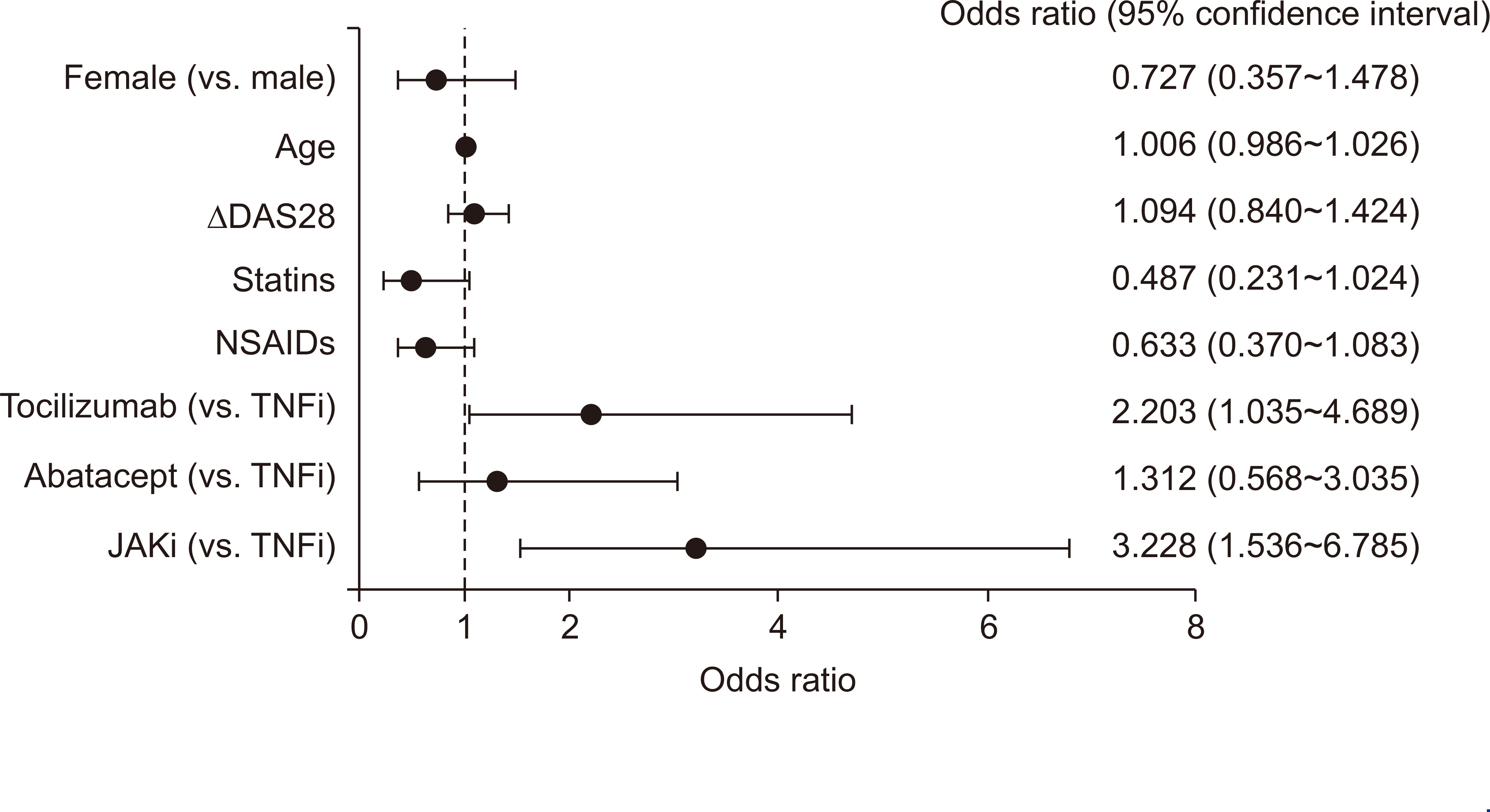
This study included 114 patients treated with TNFi, 81 with abatacept, 103 with tocilizumab, and 89 with JAKi. The mean percentage change (from baseline to 6 months) in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and non-HDL-C levels was higher in those taking tocilizumab and JAKi than in those taking TNFi and abatacept. A significant change in non-HDL-C was associated with JAKi (versus TNFi: odds ratio [OR], 3.228; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.536~6.785), tocilizumab (versus TNFi: OR, 2.203; 95% CI, 1.035~4.689), and statins (OR, 0.487; 95% CI, 0.231~1.024). However, changes in disease activity in 28 joints were not associated with a significant change in non-HDL-C.
Conclusion
Tocilizumab- and JAKi-associated increases in serum non-HDL-C levels were observed regardless of changes in disease activity. Statins are recommended for RA patients showing a significant increase in cholesterol levels after initiating biological and targeted synthetic DMARDs.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dadoun S, Zeboulon-Ktorza N, Combescure C, Elhai M, Rozenberg S, Gossec L, et al. 2013; Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis over the last fifty years: systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine. 80:29–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.02.005. PMID: 22459416.
Article2. Widdifield J, Paterson JM, Huang A, Bernatsky S. 2018; Causes of death in rheumatoid arthritis: how do they compare to the general population? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 70:1748–55. DOI: 10.1002/acr.23548. PMID: 29512334.
Article3. Nurmohamed MT, Heslinga M, Kitas GD. 2015; Cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 11:693–704. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.112. PMID: 26282082.
Article4. Schwartz DM, Kanno Y, Villarino A, Ward M, Gadina M, O'Shea JJ. 2017; JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:843–62. Erratum in: Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017;17:78. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2017.201. PMID: 29104284. PMCID: PMC6168198.
Article5. Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, Koch GG, Fleischmann R, Rivas JL, et al. 2022; Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 386:316–26. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2109927. PMID: 35081280.
Article6. Robertson J, Peters MJ, McInnes IB, Sattar N. 2013; Changes in lipid levels with inflammation and therapy in RA: a maturing paradigm. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 9:513–23. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.91. PMID: 23774906.
Article7. Kremer JM, Genovese MC, Keystone E, Taylor PC, Zuckerman SH, Ruotolo G, et al. 2017; Effects of baricitinib on lipid, apolipoprotein, and lipoprotein particle profiles in a phase IIb study of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:943–52. DOI: 10.1002/art.40036. PMID: 28029752.
Article8. Lee EB, Fleischmann R, Hall S, Wilkinson B, Bradley JD, Gruben D, et al. 2014; Tofacitinib versus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 370:2377–86. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1310476. PMID: 24941177.
Article9. Pollono EN, Lopez-Olivo MA, Lopez JA, Suarez-Almazor ME. 2010; A systematic review of the effect of TNF-alpha antagonists on lipid profiles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 29:947–55. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-010-1405-7. PMID: 20383550.
Article10. van Vollenhoven RF, Fleischmann R, Cohen S, Lee EB, García Meijide JA, Wagner S, et al. 2012; Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 367:508–19. Erratum in: N Engl J Med 2013;369:293. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112072. PMID: 22873531.
Article11. Ference BA, Graham I, Tokgozoglu L, Catapano AL. 2018; Impact of lipids on cardiovascular health: JACC Health Promotion Series. J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:1141–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.06.046. PMID: 30165986.12. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. 2019; 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 139:e1082–143. Erratum in: Circulation 2019;139:e1182-6. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000624. PMID: 30586774. PMCID: PMC7403606.13. Langlois MR, Sniderman AD. 2020; Non-HDL cholesterol or apoB: which to prefer as a target for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease? Curr Cardiol Rep. 22:67. DOI: 10.1007/s11886-020-01323-z. PMID: 32562186.
Article14. Colantonio LD, Bittner V, Reynolds K, Levitan EB, Rosenson RS, Banach M, et al. 2016; Association of serum lipids and coronary heart disease in contemporary observational studies. Circulation. 133:256–64. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.011646. PMID: 26659948. PMCID: PMC4718875.
Article15. Brunner FJ, Waldeyer C, Ojeda F, Salomaa V, Kee F, Sans S, et al. 2019; Application of non-HDL cholesterol for population-based cardiovascular risk stratification: results from the Multinational Cardiovascular Risk Consortium. Lancet. 394:2173–83. Erratum in: Lancet 2019;394:2154. Erratum in: Lancet 2020;395:32. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32519-X. PMID: 31810609. PMCID: PMC6913519.
Article16. Nordestgaard BG, Langsted A, Mora S, Kolovou G, Baum H, Bruckert E, et al. 2016; Fasting is not routinely required for determination of a lipid profile: clinical and laboratory implications including flagging at desirable concentration cut-points-a joint consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society and European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Eur Heart J. 37:1944–58. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw152. PMID: 27122601. PMCID: PMC4929379.
Article17. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, et al. 2010; 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62:2569–81. DOI: 10.1002/art.27584. PMID: 20872595.
Article18. van Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, van 't Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. 1996; Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 39:34–40. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780390105. PMID: 8546736.
Article19. Rhee EJ, Kim HC, Kim JH, Lee EY, Kim BJ, Kim EM, et al. 2019; 2018 Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia in Korea. J Lipid Atheroscler. 8:78–131. DOI: 10.12997/jla.2019.8.2.78. PMID: 32821702. PMCID: PMC7379116.
Article20. Welsh C, Celis-Morales CA, Brown R, Mackay DF, Lewsey J, Mark PB, et al. 2019; Comparison of conventional lipoprotein tests and apolipoproteins in the prediction of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 140:542–52. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.041149. PMID: 31216866. PMCID: PMC6693929.
Article21. Gabay C, McInnes IB, Kavanaugh A, Tuckwell K, Klearman M, Pulley J, et al. 2016; Comparison of lipid and lipid-associated cardiovascular risk marker changes after treatment with tocilizumab or adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 75:1806–12. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207872. PMID: 26613768. PMCID: PMC5036214.
Article22. Lee J, Lee S, Zhang H, Hill MA, Zhang C, Park Y. 2017; Interaction of IL-6 and TNF-α contributes to endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mouse hearts. PLoS One. 12:e0187189. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187189. PMID: 29095915. PMCID: PMC5667841.
Article23. Hashizume M, Mihara M. 2012; Atherogenic effects of TNF-α and IL-6 via up-regulation of scavenger receptors. Cytokine. 58:424–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.02.010. PMID: 22436638.
Article24. Noack M, Miossec P. 2017; Selected cytokine pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 39:365–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-017-0619-z. PMID: 28213794.
Article25. Hunter CA, Jones SA. 2015; IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol. 16:448–57. Erratum in: Nat Immunol 2017; 18:1271. DOI: 10.1038/ni.3153. PMID: 25898198.
Article26. Hashizume M, Mihara M. 2012; Blockade of IL-6 and TNF-α inhibited oxLDL-induced production of MCP-1 via scavenger receptor induction. Eur J Pharmacol. 689:249–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.05.035. PMID: 22683409.
Article27. Bianconi V, Sahebkar A, Atkin SL, Pirro M. 2018; The regulation and importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Curr Opin Hematol. 25:44–51. DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000389. PMID: 28914666.
Article28. Richard AJ, Stephens JM. 2014; The role of JAK-STAT signaling in adipose tissue function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:431–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.030. PMID: 23735217. PMCID: PMC4029773.
Article29. Srivastava S, Rasool M. 2022; Underpinning IL-6 biology and emphasizing selective JAK blockade as the potential alternate therapeutic intervention for rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci. 298:120516. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120516. PMID: 35367240.
Article30. Cernkovich ER, Deng J, Bond MC, Combs TP, Harp JB. 2008; Adipose-specific disruption of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 increases body weight and adiposity. Endocrinology. 149:1581–90. DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1148. PMID: 18096662. PMCID: PMC2276706.
Article31. Verghese PB, Arrese EL, Soulages JL. 2007; Stimulation of lipolysis enhances the rate of cholesterol efflux to HDL in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 302:241–8. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-007-9447-0. PMID: 17390217.
Article32. Charles-Schoeman C, Fleischmann R, Davignon J, Schwartz H, Turner SM, Beysen C, et al. 2015; Potential mechanisms leading to the abnormal lipid profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus healthy volunteers and reversal by tofacitinib. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:616–25. DOI: 10.1002/art.38974. PMID: 25470338. PMCID: PMC5024065.
Article33. Charles-Schoeman C, Gugiu GB, Ge H, Shahbazian A, Lee YY, Wang X, et al. 2018; Remodeling of the HDL proteome with treatment response to abatacept or adalimumab in the AMPLE trial of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis. 275:107–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.04.003. PMID: 29886354. PMCID: PMC6113060.
Article34. Ozen G, Pedro S, Michaud K. 2021; The risk of cardiovascular events associated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 48:648–55. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.200265. PMID: 32801134.
Article35. Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, Roger VL, Fitz-Gibbon PD, Therneau TM, et al. 2011; Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:482–7. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.135871. PMID: 21216812. PMCID: PMC3058921.
Article36. Stary HC, Chandler AB, Glagov S, Guyton JR, Insull W Jr, Rosenfeld ME, et al. 1994; A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation. 89:2462–78. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.89.5.2462. PMID: 8181179.
Article37. Park JB, Kim DH, Lee H, Hwang IC, Yoon YE, Park HE, et al. 2020; Mildly abnormal lipid levels, but not high lipid variability, are associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in "statin-naive" young population a nationwide cohort study. Circ Res. 126:824–35. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315705. PMID: 31978313.
Article38. Bisoendial RJ, Stroes ES, Kastelein JJ, Tak PP. 2010; Targeting cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: a dual role for statins. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 6:157–64. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.277. PMID: 20142814.
Article39. Min HK, Kim HR, Lee SH, Shin K, Kim HA, Park SH, et al. 2021; Four-year follow-up of atherogenicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: from the nationwide Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics Registry. Clin Rheumatol. 40:3105–13. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-021-05613-x. PMID: 33576925.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Advantages and disadvantages of targeted therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Current concepts in the management of rheumatoid arthritis
- Effect of biologics in the level of cytokines in the synovial fluid of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- Biological Agent and Total Hip Arthroplasty in Rheumatoid Arthritis