Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2022 Mar;26(2):87-94. 10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.2.87.
Peiminine inhibits myocardial injury and fibrosis after myocardial infarction in rats by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Vasculocardiology, Xiangyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, Hubei 441000, China
- KMID: 2526728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.2.87
Abstract
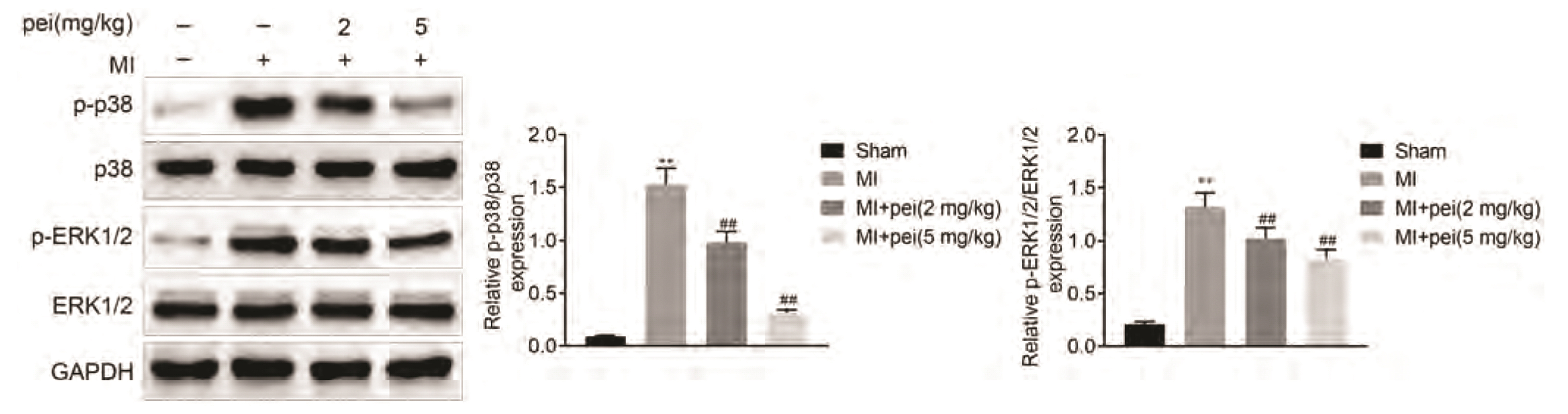
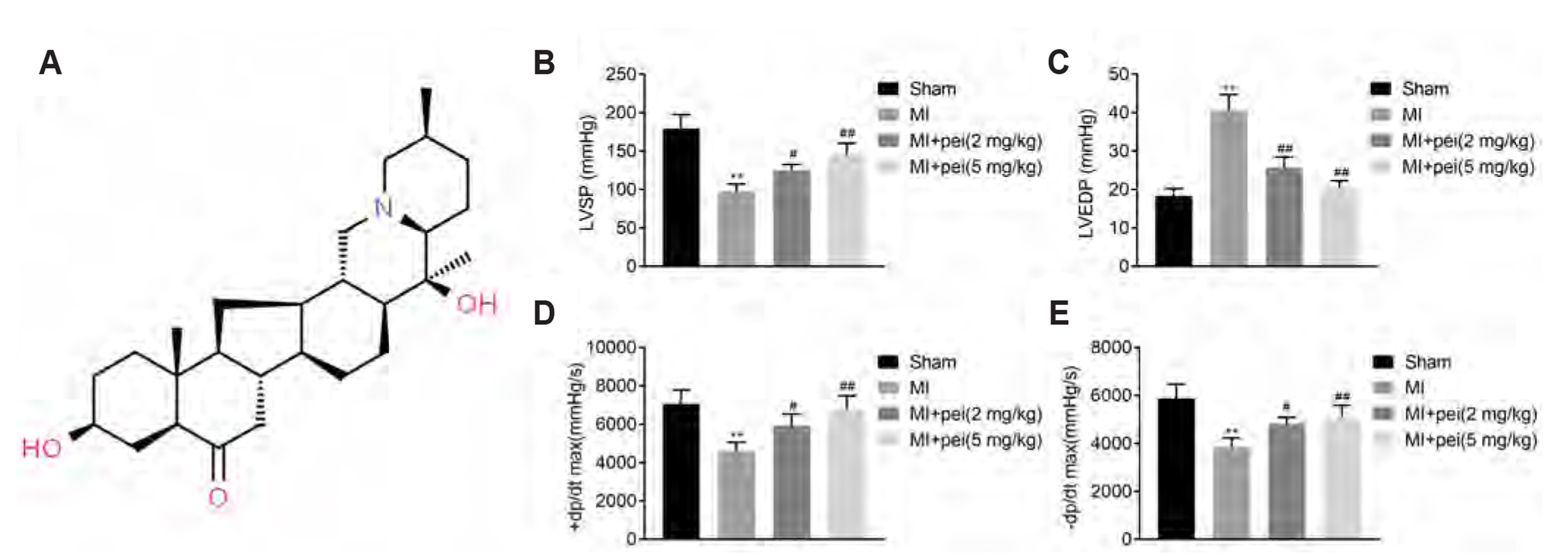
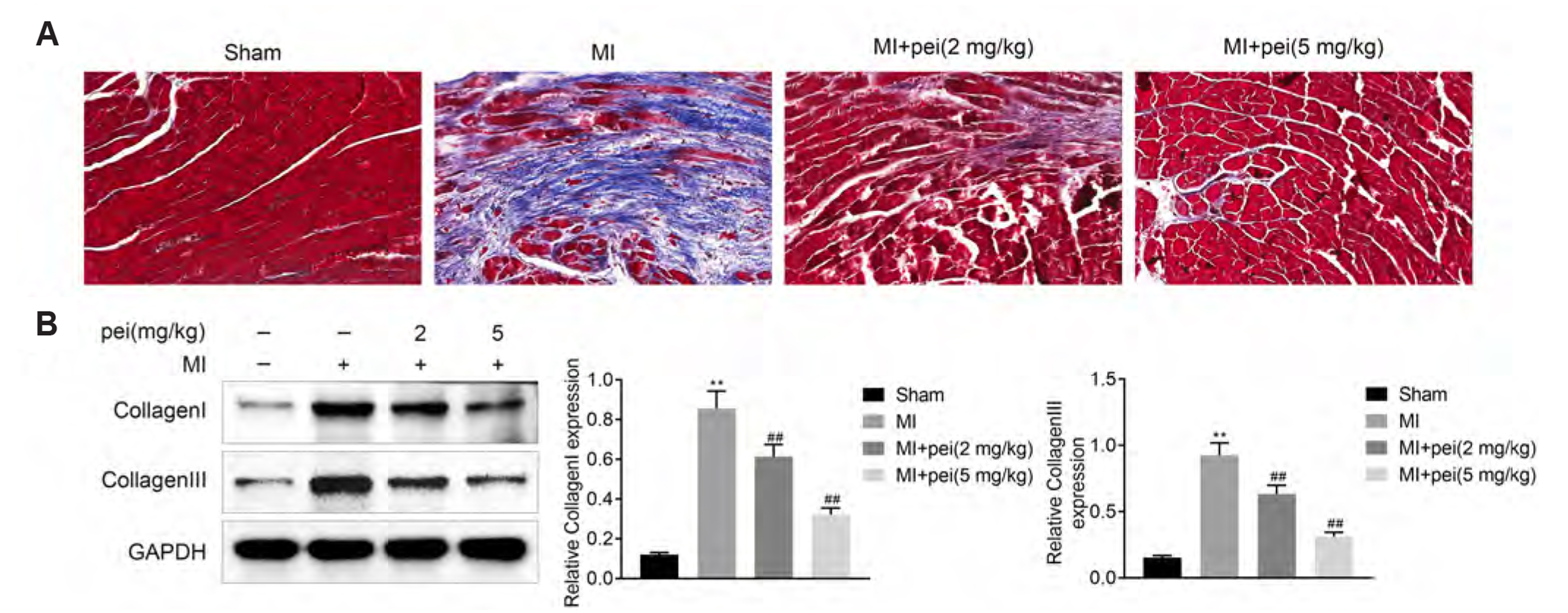
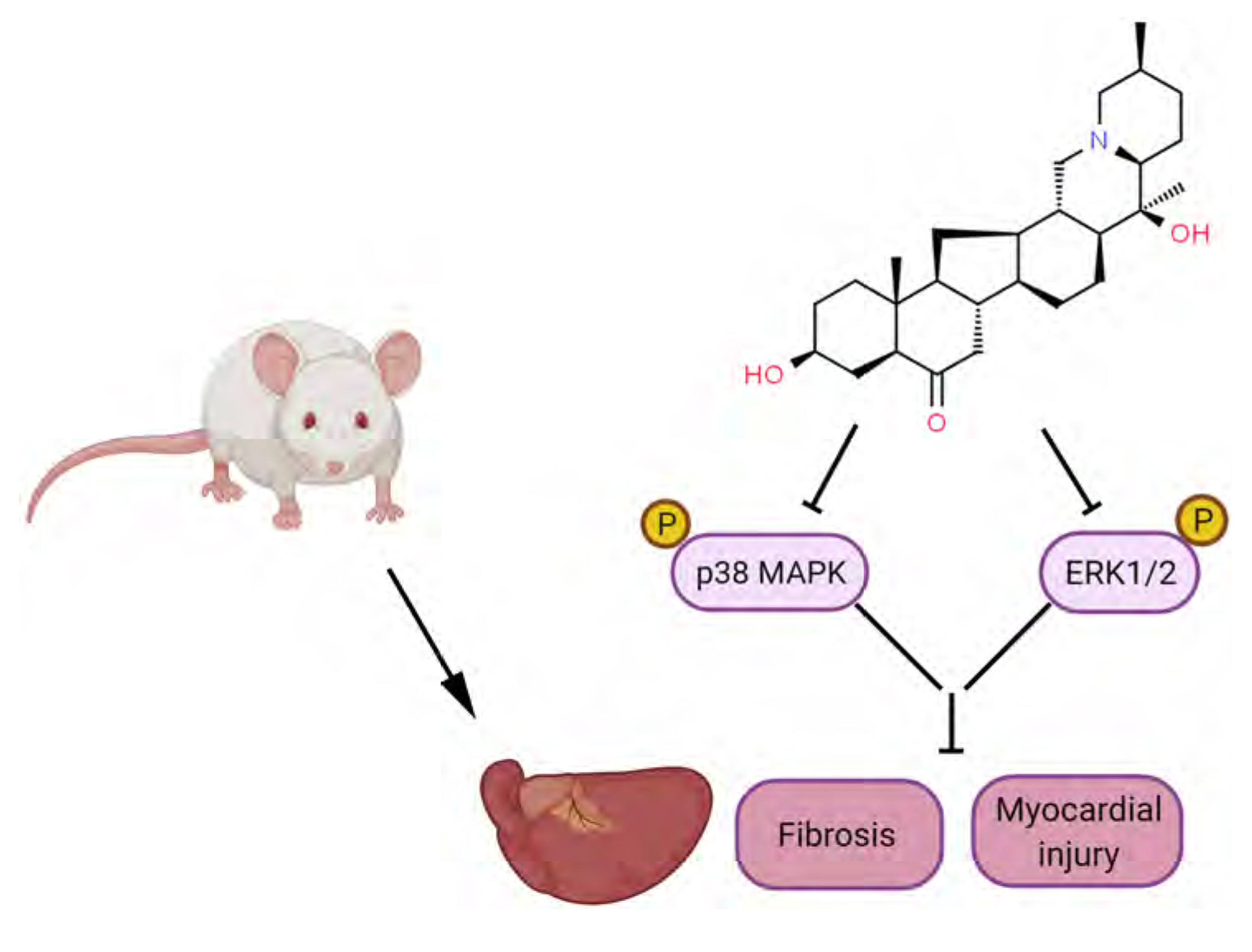
- Myocardial infarction promotes cardiac remodeling and myocardial fibrosis, thus leading to cardiac dysfunction or heart failure. Peiminine has been regarded as a traditional anti-fibrotic Chinese medicine in pulmonary fibrosis. However, the role of peiminine in myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and fibrosis remained elusive. Firstly, rat model of myocardial infarction was established using ligation of the left coronary artery, which were then intraperitoneally injected with 2 or 5 mg/kg peiminine once a day for 4 weeks. Echocardiography and haemodynamic evaluation results showed that peiminine treatment reduced left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, and enhanced maximum rate of increase/decrease of left ventricle pressure (± dP/dt max) and left ventricular systolic pressure, which ameliorate the cardiac function. Secondly, myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and infarct size were also attenuated by peiminine. Moreover, peiminine inhibited myocardial infarction-induced increase of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α production, as well as the myocardial cell apoptosis, in the rats. Thirdly, peiminine also decreased the myocardial fibrosis related protein expression including collagen I and collagen III. Lastly, peiminine reduced the expression of p38 and phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in rat model of myocardial infarction. In conclusion, peiminine has a cardioprotective effect against myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and fibrosis, which can be attributed to the inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jneid H, Alam M, Virani SS, Bozkurt B. 2013; Redefining myocardial infarction: what is new in the ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Third Universal Definition of myocardial infarction? Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 9:169–172. DOI: 10.14797/mdcj-9-3-169. PMID: 24066201. PMCID: PMC3782325.
Article2. Teringova E, Tousek P. 2017; Apoptosis in ischemic heart disease. . J Transl Med. 15:87. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1191-y. PMID: 28460644. PMCID: PMC5412049.
Article3. Roever L, Palandri Chagas AC. 2017; Editorial: Cardiac remodeling: new insights in physiological and pathological adaptations. Front Physiol. 8:751. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00751. PMID: 29018366. PMCID: PMC5622945.
Article4. Gajarsa JJ, Kloner RA. 2011; Left ventricular remodeling in the post-infarction heart: a review of cellular, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic modalities. Heart Fail Rev. 16:13–21. DOI: 10.1007/s10741-010-9181-7. PMID: 20623185.
Article5. Çakır B, Kılıçkaya O. 2015; Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in Vitis vinifera. Front Plant Sci. 6:556. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00556. PMID: 26257761. PMCID: PMC4511077.6. Qiu L, Liu X. 2019; Identification of key genes involved in myocardial infarction. Eur J Med Res. 24:22. DOI: 10.1186/s40001-019-0381-x. PMID: 31269974. PMCID: PMC6607516. PMID: 2998ee9e46864095bd464b854e02583e.
Article7. Zhang Q, Lu L, Liang T, Liu M, Wang ZL, Zhang PY. 2017; MAPK pathway regulated the cardiomyocyte apoptosis in mice with post-infarction heart failure. Bratisl Lek Listy. 118:339–346. DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2017_065. PMID: 28664743.
Article8. Matsumoto-Ida M, Takimoto Y, Aoyama T, Akao M, Takeda T, Kita T. 2006; Activation of TGF-β1-TAK1-p38 MAPK pathway in spared cardiomyocytes is involved in left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 290:H709–H715. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00186.2005. PMID: 16183734.
Article9. Kumphune S, Bassi R, Jacquet S, Sicard P, Clark JE, Verma S, Avkiran M, O'Keefe SJ, Marber MS. 2010; A chemical genetic approach reveals that p38alpha MAPK activation by diphosphorylation aggravates myocardial infarction and is prevented by the direct binding of SB203580. J Biol Chem. 285:2968–2975. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.079228. PMID: 19996096. PMCID: PMC2823430.
Article10. Zhang Z, Zhou S, Mei Z, Zhang M. 2017; Inhibition of p38MAPK potentiates mesenchymal stem cell therapy against myocardial infarction injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 16:3489–3493. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6973. PMID: 28713990.
Article11. Bassi R, Heads R, Marber MS, Clark JE. 2008; Targeting p38-MAPK in the ischaemic heart: kill or cure? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:141–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.01.002. PMID: 18289939.
Article12. Lyu Q, Tou F, Su H, Wu X, Chen X, Zheng Z. 2015; The natural product peiminine represses colorectal carcinoma tumor growth by inducing autophagic cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 462:38–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.102. PMID: 25935480.
Article13. Tang Q, Wang Y, Ma L, Ding M, Li T, Nie Y, Gu Z. 2018; Peiminine serves as an adriamycin chemosensitizer in gastric cancer by modulating the EGFR/FAK pathway. Oncol Rep. 39:1299–1305. DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6184. PMID: 29328433.
Article14. Lim JM, Lee B, Min JH, Kim EY, Kim JH, Hong S, Kim JJ, Sohn Y, Jung HS. 2018; Effect of peiminine on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine expression in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 56:135–142. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.01.025. PMID: 29414643.
Article15. Ruan X, Yang L, Cui WX, Zhang MX, Li ZH, Liu B, Wang Q. 2016; Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of total alkaloids, peimisine, peimine and peiminine from the bulb of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq, and evaluation of antioxidant activities of the extracts. Materials (Basel). 9:524. DOI: 10.3390/ma9070524. PMID: 28773648. PMCID: PMC5456939.
Article16. Lee B, Kim EY, Kim JH, Min JH, Jeong DW, Jun JY, Cho CY, Sohn Y, Jung HS. 2015; Antiallergic effects of peiminine through the regulation of inflammatory mediators in HMC-1 cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 37:351–358. DOI: 10.3109/08923973.2015.1059441. PMID: 26121924.
Article17. Chen G, Liu J, Jiang L, Ran X, He D, Li Y, Huang B, Wang W, Liu D, Fu S. 2018; Peiminine protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced cell death by inhibiting the ERK1/2 and NF-κB signalling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 19:821. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030821. PMID: 29534526. PMCID: PMC5877682.
Article18. Gong Q, Li Y, Ma H, Guo W, Kan X, Xu D, Liu J, Fu S. 2018; Peiminine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by inhibiting the AKT/NF-κB, ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 19:2637. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092637. PMID: 30200569. PMCID: PMC6164606.
Article19. Guo H, Ji F, Liu B, Chen X, He J, Gong J. 2013; Peiminine ameliorates bleomycin-induced acute lung injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 7:1103–1110. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1312. PMID: 23404624.
Article20. Soriano FG, Guido MC, Barbeiro HV, Caldini EG, Lorigados CB, Nogueira AC. 2014; Endotoxemic myocardial dysfunction: subendocardial collagen deposition related to coronary driving pressure. Shock. 42:472–479. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000232. PMID: 25051283.21. Liu JJ, Huang N, Lu Y, Zhao M, Yu XJ, Yang Y, Yang YH, Zang WJ. 2015; Improving vagal activity ameliorates cardiac fibrosis induced by angiotensin II: in vivo and in vitro. Sci Rep. 5:17108. DOI: 10.1038/srep17108. PMID: 26596640. PMCID: PMC4656999.
Article22. Li C, Han R, Kang L, Wang J, Gao Y, Li Y, He J, Tian J. 2017; Pirfenidone controls the feedback loop of the AT1R/p38 MAPK/renin-angiotensin system axis by regulating liver X receptor-α in myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis. Sci Rep. 7:40523. DOI: 10.1038/srep40523. PMID: 28091615. PMCID: PMC5238375.
Article23. Reichert K, Colantuono B, McCormack I, Rodrigues F, Pavlov V, Abid MR. 2017; Murine left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation: an improved and simplified model for myocardial infarction. J Vis Exp. (122):55353. DOI: 10.3791/55353. PMID: 28448010. PMCID: PMC5564466.
Article24. Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW, Entman ML. 2002; The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 53:31–47. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00434-5. PMID: 11744011.
Article25. Wan N, Liu X, Zhang XJ, Zhao Y, Hu G, Wan F, Zhang R, Zhu X, Xia H, Li H. 2015; Toll-interacting protein contributes to mortality following myocardial infarction through promoting inflammation and apoptosis. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3383–3396. DOI: 10.1111/bph.13130. PMID: 25765712. PMCID: PMC4500373.
Article26. Ge J, Guo K, Zhang C, Talukder M, Lv MW, Li JY, Li JL. 2021; Comparison of nanoparticle-selenium, selenium-enriched yeast and sodium selenite on the alleviation of cadmium-induced inflammation via NF-κB/IκB pathway in heart. Sci Total Environ. 773:145442. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145442. PMID: 33940727.27. Fan D, Yang Z, Yuan Y, Wu QQ, Xu M, Jin YG, Tang QZ. 2017; Sesamin prevents apoptosis and inflammation after experimental myocardial infarction by JNK and NF-κB pathways. Food Funct. 8:2875–2885. DOI: 10.1039/C7FO00204A. PMID: 28726929.
Article28. Wang X, Guo Z, Ding Z, Mehta JL. 2018; Inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis after myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 7:e008024. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008024. PMID: 29680826. PMCID: PMC6015297.
Article29. Anzai T. 2018; Inflammatory mechanisms of cardiovascular remodeling. Circ J. 82:629–635. DOI: 10.1253/circj.CJ-18-0063. PMID: 29415911.
Article30. Zhang X, Hu W, Feng F, Xu J, Wu F. 2016; Apelin-13 protects against myocardial infarction-induced myocardial fibrosis. Mol Med Rep. 13:5262–5268. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5163. PMID: 27109054.
Article31. Ren J, Zhang S, Kovacs A, Wang Y, Muslin AJ. 2005; Role of p38alpha MAPK in cardiac apoptosis and remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 38:617–623. DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.01.012. PMID: 15808838.
Article32. Zhu J, Gu H, Lv X, Yuan C, Ni P, Liu F. 2018; LINC-PINT activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to promote acute myocardial infarction by regulating miR-208a-3p. Circ J. 82:2783–2792. DOI: 10.1253/circj.CJ-18-0396. PMID: 30249926.
Article33. Mitra A, Ray A, Datta R, Sengupta S, Sarkar S. 2014; Cardioprotective role of P38 MAPK during myocardial infarction via parallel activation of α-crystallin B and Nrf2. J Cell Physiol. 229:1272–1282. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24565. PMID: 24464634.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Protective Effect of Sauchinone Against Regional Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Inhibition of p38 MAPK and JNK Death Signaling Pathways
- D-Limonene mitigate myocardial injury in rats through MAPK/ ERK/NF-κB pathway inhibition
- Fibroblast-derived interleukin-6 exacerbates adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction
- Ras Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling and Kinase Suppressor of Ras as Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Naloxone Postconditioning Alleviates Rat Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting JNK Activity