J Surg Ultrasound.
2021 May;8(1):19-24. 10.46268/jsu.2021.8.1.19.
Risk Factors for Complex Hypersensitivity and Irritation Reactions after an Ultrasound-Guided Cyanoacrylate Closure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2525876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2021.8.1.19
Abstract
- Purpose
Cyanoacrylate closure (CAC) has been introduced for the treatment of the incompetent saphenous vein. Although there have been no severe procedure- or device-related adverse events, the post-treatment complex hypersensitivity and irritation reactions (CHAIR) might be a troublesome complication.
Methods
A retrospective review was performed from prospectively collected data of CAC patients. The CAC was performed in patients with symptomatic great saphenous veins (GSV), small saphenous veins (SSV), and/or accessory saphenous veins (ASV) in a single session. We assessed the possible risk factors for the development of a hypersensitivity reaction including the amount of injected adhesive, access site, treated segment, compression stocking application, and other clinical factors. For the statistical analyses, data were analyzed using the IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 22.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
During the study period, 190 saphenous veins were treated in 100 patients. Sixty-four (64%) patients were female. The mean age was 55.5 ± 12.8 years (19-84). Complete occlusion was achieved in all patients. After CAC, the mean visual analogue scale (VAS) was 2.59 and 0.32 on postoperative 0 and 7 days, respectively (P < 0.001). Post-treatment CHAIR occurred in 5 (5%) patients. The significant risk factors for the development of CHAIR were younger age, GSV treatment, and below-the-knee access site for the introduction of a catheter.
Conclusion
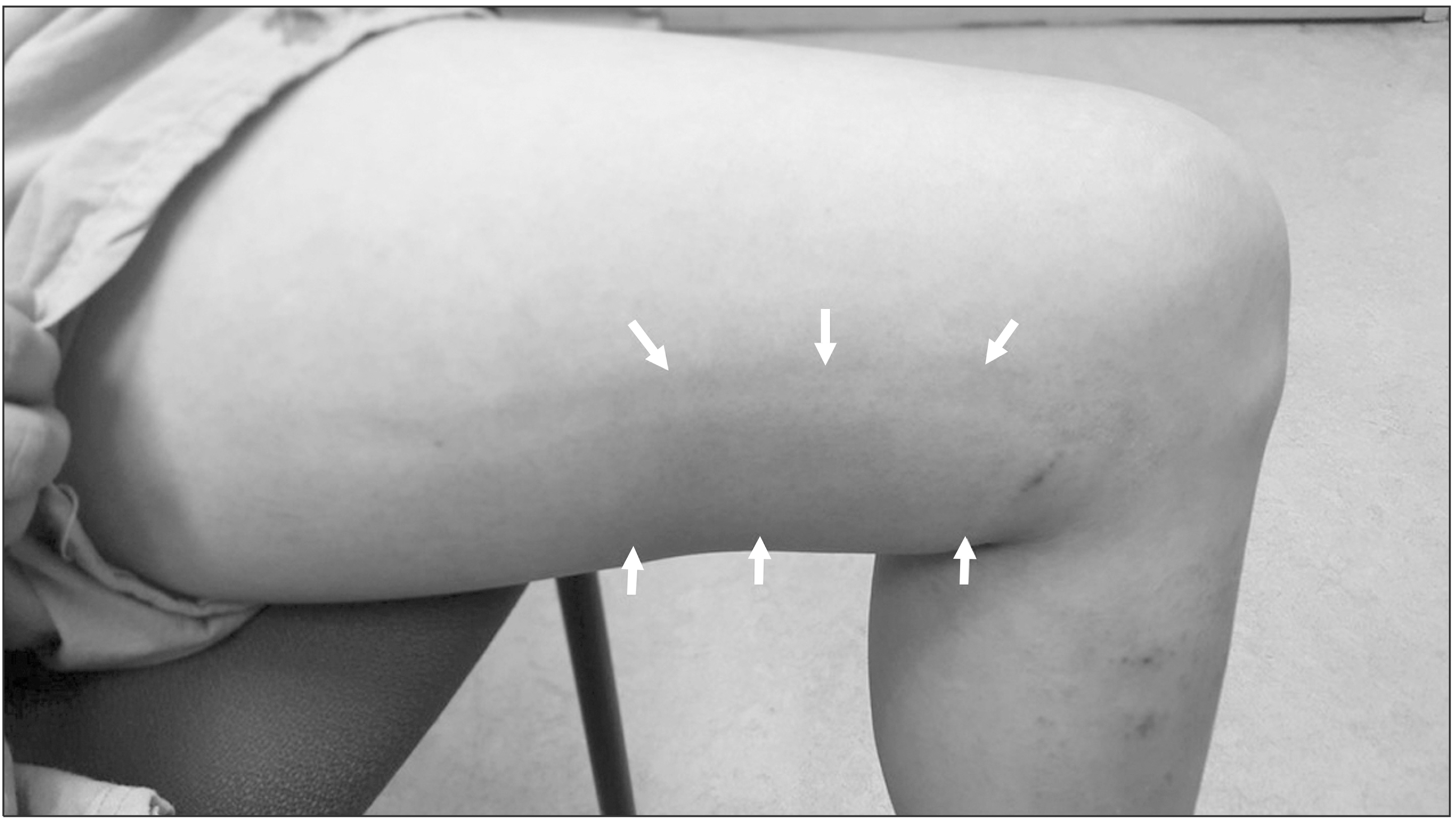
CHAIR occurred when the adhesive was injected at the below-the-knee GSV segment. The mechanical irritation due to knee joint movement might be a possible mechanism for the development of the hypersensitivity reaction.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Almeida JI, Javier JJ, Mackay EG, Bautista C, Cher DJ, Proebstle TM. 2017; Thirty-sixth-month follow-up of first-in-human use of cyanoacrylate adhesive for treatment of saphenous vein incompetence. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 5:658–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2017.03.016. PMID: 28818217.
Article2. Navarro-Triviño FJ, Cuenca-Manteca J, Ruiz-Villaverde R. 2020; Allergic contact dermatitis with systemic symptoms caused by VenaSeal. Contact Dermatitis. 82:185–7. DOI: 10.1111/cod.13431. PMID: 31674037.
Article3. Lurie F, Creton D, Eklof B, Kabnick LS, Kistner RL, Pichot O, et al. 2005; Prospective randomised study of endovenous radiofrequency obliteration (closure) versus ligation and vein stripping (EVOLVeS): two-year follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 29:67–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2004.09.019. PMID: 15570274.
Article4. Darwood RJ, Theivacumar N, Dellagrammaticas D, Mavor AI, Gough MJ. 2008; Randomized clinical trial comparing endovenous laser ablation with surgery for the treatment of primary great saphenous varicose veins. Br J Surg. 95:294–301. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.6101. PMID: 18278775.
Article5. Almeida JI, Javier JJ, Mackay E, Bautista C, Proebstle TM. 2013; First human use of cyanoacrylate adhesive for treatment of saphenous vein incompetence. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 1:174–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2012.09.010. PMID: 26992340.
Article6. Morrison N, Gibson K, Vasquez M, Weiss R, Jones A. 2020; Five-year extension study of patients from a randomized clinical trial (VeClose) comparing cyanoacrylate closure versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of incompetent great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 8:978–89. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2019.12.080. PMID: 32205125.
Article7. Jones AD, Boyle EM, Woltjer R, Jundt JP, Williams AN. 2019; Persistent type IV hypersensitivity after cyanoacrylate closure of the great saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 5:372–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2019.05.004. PMID: 31440717. PMCID: PMC6699189.
Article8. Dimech AP, Cassar K. 2020; Efficacy of cyanoacrylate glue ablation of primary truncal varicose veins compared to existingendovenous techniques: a systematic review of the literature. Surg J (N Y). 6:e77–86. DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1708866. PMID: 32577526. PMCID: PMC7305022.9. Cho S, Gibson K, Lee SH, Kim SY, Joh JH. 2020; Incidence, classification, and risk factors of endovenousglue-induced thrombosis after cyanoacrylate closure of the incompetent saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 8:991–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.01.009. PMID: 32179036.10. Proebstle TM, Alm J, Dimitri S, Rasmussen L, Whiteley M, Lawson J, et al. 2015; The European multicenter cohort study on cyanoacrylate embolization of refluxing great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 3:2–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2014.09.001. PMID: 26993674.
Article11. Morrison N, Gibson K, McEnroe S, Goldman M, King T, Weiss R, et al. 2015; Randomized trial comparing cyanoacrylate embolization and radiofrequency ablation for incompetent great saphenous veins (VeClose). J Vasc Surg. 61:985–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.11.071. PMID: 25650040.
Article12. Tang TY, Tiwari A. 2018; The VenaSealTM abnormal red skin reaction: looks like but is not phlebitis! Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 55:841. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.02.003. PMID: 29503084.
Article13. Korkmaz Ö, Göksel S, Gül M, Başçil H, Yildir Y, Berkan Ö. 2018; Does the use of N-butyl-2 cyanoacrylate in the treatment of lower extremity superficial varicose veins cause acute systemic inflammation and allergic reactions? Cardiovasc J Afr. 29:213–7. DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2018-012. PMID: 30204219.
Article14. Anderson JM, Rodriguez A, Chang DT. 2008; Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 20:86–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.11.004. PMID: 18162407. PMCID: PMC2327202.
Article15. Park I, Jeong MH, Park CJ, Park WI, Park DW, Joh JH. 2019; Clinical features and management of “phlebitis-like abnormal reaction” after cyanoacrylate closure for the treatment of incompetent saphenous veins. Ann Vasc Surg. 55:239–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2018.07.040. PMID: 30217712.
Article16. Gibson K, Minjarez R, Rinehardt E, Ferris B. 2020; Frequency and severity of hypersensitivity reactions in patients after VenaSealTM cyanoacrylate treatment of superficial venous insufficiency. Phlebology. 35:337–44. DOI: 10.1177/0268355519878618. PMID: 31554473.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent Systemic Urticaria Following Cyanoacrylate Closure for the Treatment of Incompetent Saphenous Veins
- Complex Hypersensitivity and Irritation Reaction (CHAIR) Phenomenon after Cyanoacrylate Closure of Varicose Vein
- Successful endoscopic closure of an esophageal leak after endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticoesophagostomy by using n-butyl-2 cyanoacrylate
- The Cause of Abnormal Skin Findings after Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Cyanoacrylate Glue in an Animal Model
- Hypersensitivity Reactions to Antineoplastic Agents: Characteristics and Premedication Strategies