J Surg Ultrasound.
2020 Nov;7(2):42-46. 10.46268/jsu.2020.7.2.42.
The Cause of Abnormal Skin Findings after Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Cyanoacrylate Glue in an Animal Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2511904
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2020.7.2.42
Abstract
- Purpose
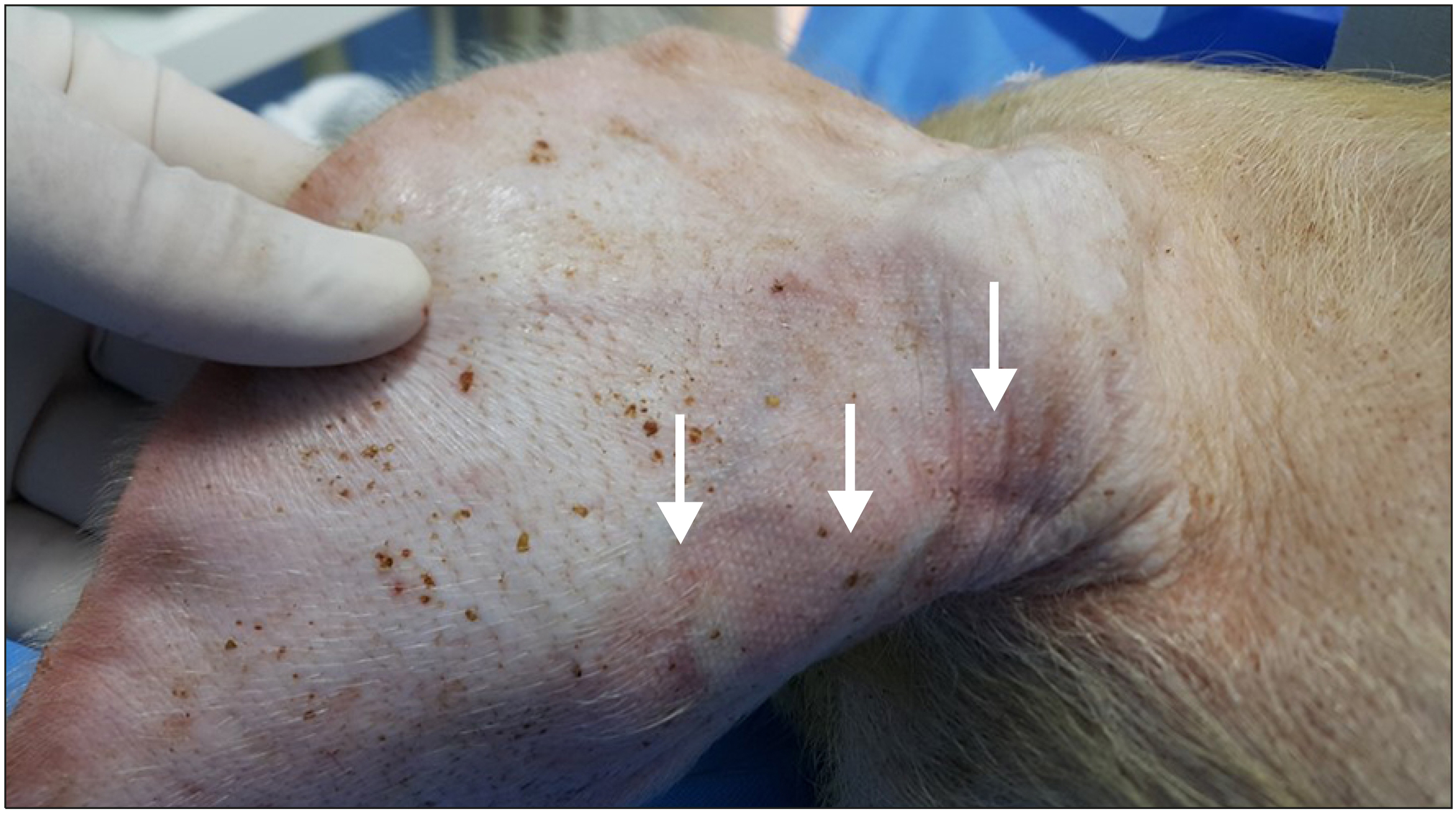
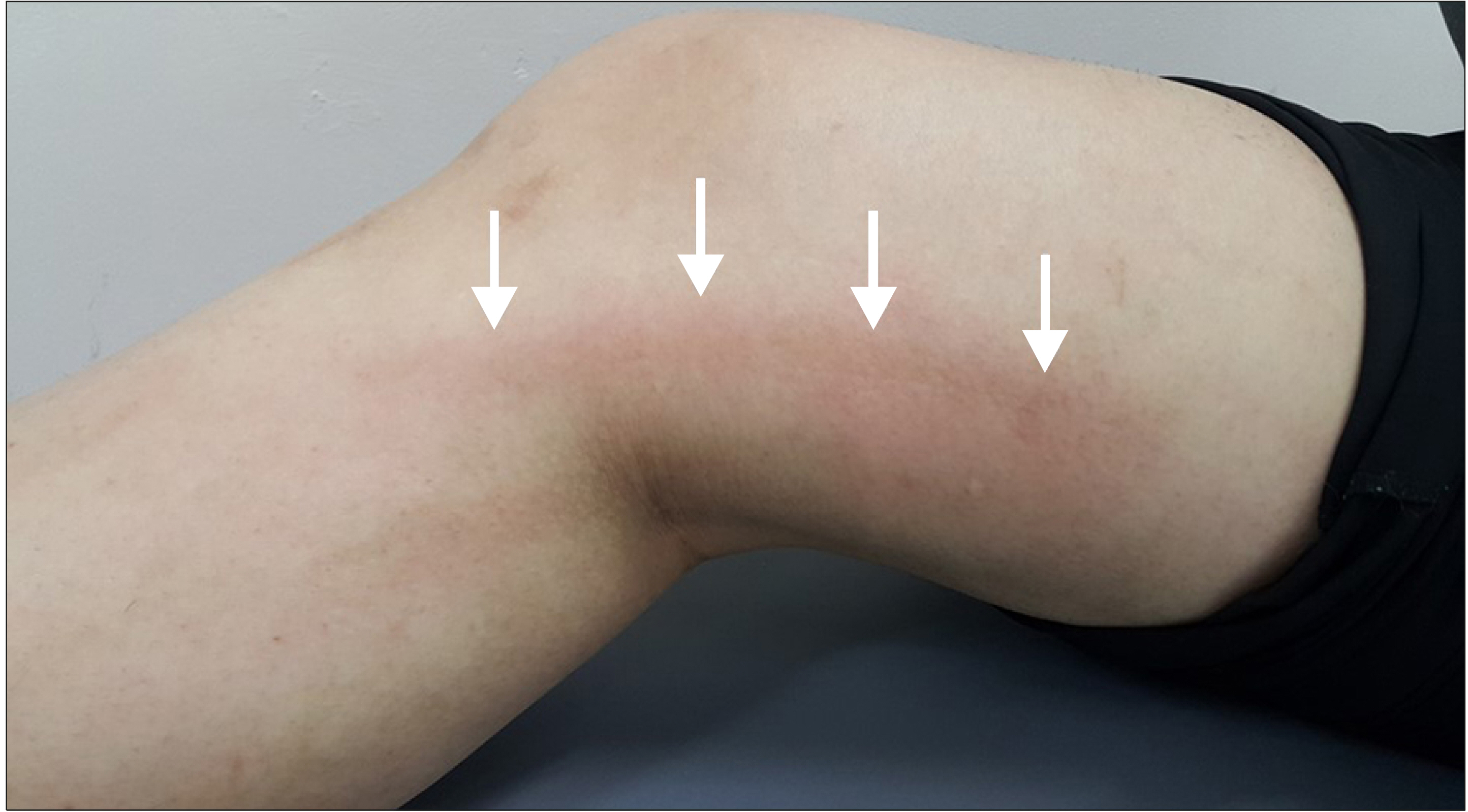
Cyanoacrylate closure has been recently introduced as a non-thermal method for the treatment of varicose veins. An abnormal skin finding can be an extremely worrisome complication after a cyanoacrylate closure. This study aimed at identifying if joint movement could be a possible cause for this reaction using a pig model.
Methods
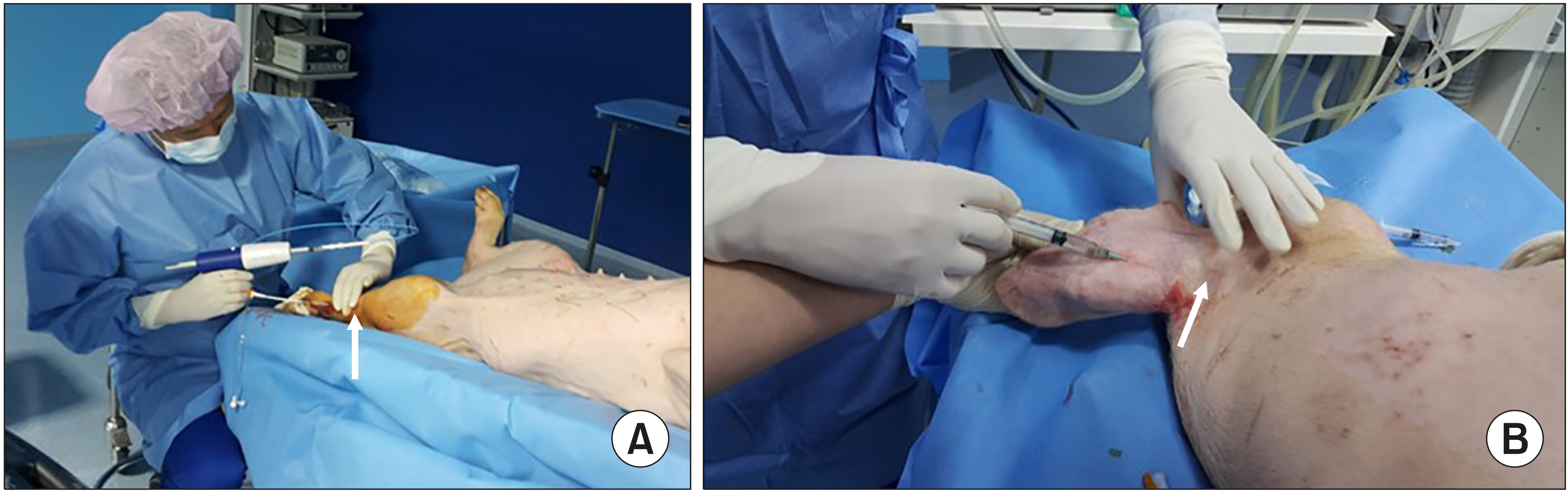
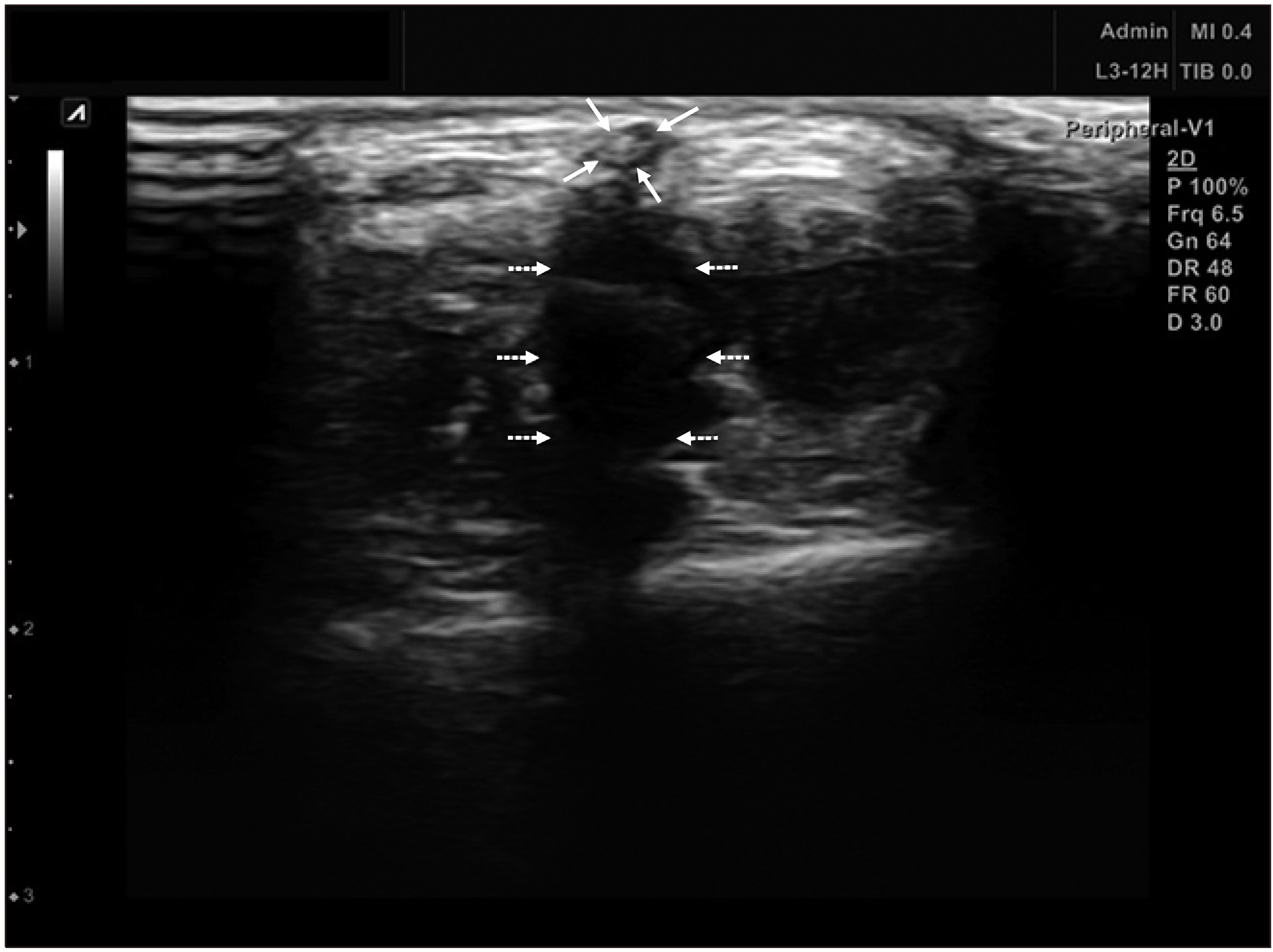
The pigs were administered general anesthesia and monitored by a veterinarian. After aseptic preparation, the cyanoacrylate glue was injected into the leg vein through a delivery catheter, or into the ear vein through a 22G needle. The pigs were divided into 2 groups according to the involvement of the joints, with the injected glue. Ten days after the glue was injected, the veins were harvested, and pathologic findings were analysed.
Results
We obtained 6 vein specimens with the surrounding tissue. Both the groups, involving the joint, and not involving the joint included one leg vein and 2 ear veins. The pathologic finding in the group not involving the joint showed that inflammatory cells (mainly lymphocytes) infiltrated the vein wall. In the group involving the joints, the same inflammatory cells infiltrated both the vein wall and surrounding tissue.
Conclusion
In this animal study, the injected glue triggered an inflammatory reaction. When the glue was injected across a joint, an inflammatory reaction developed in the vein wall as well as the surrounding tissue. It may be assumed that cyanoacrylate glue injected during closure of the vein can result in an abnormal skin finding if there is an active movement of the joint involved.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Almeida JI, Javier JJ, Mackay E, Bautista C, Proebstle TM. 2013; First human use of cyanoacrylate adhesive for treatment of saphenous vein incompetence. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 1:174–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2012.09.010. PMID: 26992340.
Article2. Almeida JI, Javier JJ, Mackay EG, Cher DJ, Proebstle TM. BautistaC. 2017; Thirty-sixth-month follow-up of first-in-human use of cyanoacrylate adhesive for treatment of saphenous vein incompetence. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 5:658–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2017.03.016. PMID: 28818217.
Article3. Proebstle TM, Alm J, Dimitri S, Rasmussen L, Whiteley M, Lawson J, et al. 2015; The European multicenter cohort study on cyanoacrylate embolization of refluxing great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 3:2–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2014.09.001. PMID: 26993674.
Article4. Morrison N, Gibson K, Vasquez M, Weiss R, Cher D, Madsen M, et al. 2017; VeClose trial 12-month outcomes of cyanoacrylate closure versus radiofrequency ablation for incompetent great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 5:321–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.12.005. PMID: 28411697.
Article5. Gibson K, Morrison N, Kolluri R, Vasquez M, Weiss R, Cher D, et al. 2018; Twenty-four month results from a randomized trial of cyanoacrylate closure versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of incompetent great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 6:606–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2018.04.009. PMID: 29914814.
Article6. Min RJ, Almeida JI, McLean DJ, Madsen M, Raabe R. 2012; Novel vein closure procedure using a proprietary cyanoacrylate adhesive: 30-day swine model results. Phlebology. 27:398–403. DOI: 10.1258/phleb.2011.011084. PMID: 22262871.
Article7. Park I, Jeong MH, Park CJ, Park WI, Park DW, Joh JH. 2019; Clinical features and management of "Phlebitis-like abnormal reaction" after cyanoacrylate closure for the treatment of incompetent saphenous veins. Ann Vasc Surg. 55:239–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2018.07.040. PMID: 30217712.
Article8. Jones AD, Boyle EM, Woltjer R, Jundt JP, Williams AN. 2019; Persistent type IV hypersensitivity after cyanoacrylate closure of the great saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 5:372–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2019.05.004. PMID: 31440717. PMCID: PMC6699189.
Article9. Lam YL, De Maeseneer M, Lawson J, De Borst GJ, Boersma D. 2017; Expert review on the VenaSealⓇ system for endovenous cyano-acrylate adhesive ablation of incompetent saphenous trunks in patients with varicose veins. Expert Rev Med Devices. 14:755–62. DOI: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1378093. PMID: 28892412.10. Levrier O, Mekkaoui C, Rolland PH, Murphy K, Cabrol P, Moulin G, et al. 2003; Efficacy and low vascular toxicity ofembolization with radical versus anionic polymerization of n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA). An experimental study in the swine. J Neuroradiol. 30:95–102. PMID: 12717295.11. Pollak JS, White RI Jr. 2001; The use of cyanoacrylate adhesives in peripheral embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 12:907–13. DOI: 10.1016/S1051-0443(07)61568-1. PMID: 11487670.
Article12. Germolec DR, Shipkowski KA, Frawley RP, Evans E. 2018; Markers of inflammation. Methods Mol Biol. 1803:57–79. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8549-4_5. PMID: 29882133.
Article13. Sakai Y, Kobayashi M. 2015; Lymphocyte 'homing' and chronic inflammation. Pathol Int. 65:344–54. DOI: 10.1111/pin.12294. PMID: 25831975.
Article14. Germolec DR, Frawley RP, Evans E. 2010; Markers of inflammation. Methods Mol Biol. 598:53–73. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60761-401-2_5. PMID: 19967506.
Article15. Almeida JI, Javier JJ, Mackay EG, Bautista C, Cher DJ, Proebstle TM. 2015; Two-year follow-up of first human use of cyanoacrylate adhesive for treatment of saphenous vein incompetence. Phlebology. 30:397–404. DOI: 10.1177/0268355514532455. PMID: 24789750.
Article16. Morrison N, Gibson K, McEnroe S, Goldman M, King T, Weiss R, et al. 2015; Randomized trial comparing cyanoacrylate embolization andradiofrequency ablation for incompetent great saphenous veins (VeClose). J Vasc Surg. 61:985–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.11.071. PMID: 25650040.17. Vinters HV, Galil KA, Lundie MJ, Kaufmann JC. 1985; The histotoxicity of cyanoacrylates. A selective review. Neuroradiology. 27:279–91. DOI: 10.1007/BF00339559. PMID: 3900798.18. Spiegel SM, Viñuela F, Goldwasser JM, Fox AJ, Pelz DM. 1986; Adjusting the polymerization time of isobutyl-2 cyanoacrylate. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 7:109–12. PMID: 3082125.19. Novotny K, Campr V. 2019; Histopathological changes to the vascular wall after treatment of great saphenous veins using n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate. Vasa. 48:399–404. DOI: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000797. PMID: 31063085.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2-Octyl Cyanoacrylate Glue Application on Split-Thickness Skin Graft for Lower Extremity Reconstruction
- The Results of Cyanoacrylate Glue Application for Corneal Perforation and Impending Perforation
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided coiling and glue is safe and superior to endoscopic glue injection in gastric varices with severe liver disease: a retrospective case control study
- Successful endoscopic closure of an esophageal leak after endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticoesophagostomy by using n-butyl-2 cyanoacrylate
- Usefulness of Ultrasound for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Proven in Meta-Analysis Studies