Korean J Transplant.
2021 Dec;35(4):238-246. 10.4285/kjt.21.0020.
Recipient efficacy and safety of kidney transplantation from older living donor: consideration for using older kidney as a solution to the shortage of organs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Biomedical Statistics Center, Data Science Research Institute, Research Institute for Future Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Digital Health, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2523673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.21.0020
Abstract
- Background
As a solution to organ shortages, studies on kidney transplantation (KT) from older donors are being conducted. However, many controversies remain about its safety and efficacy.
Methods
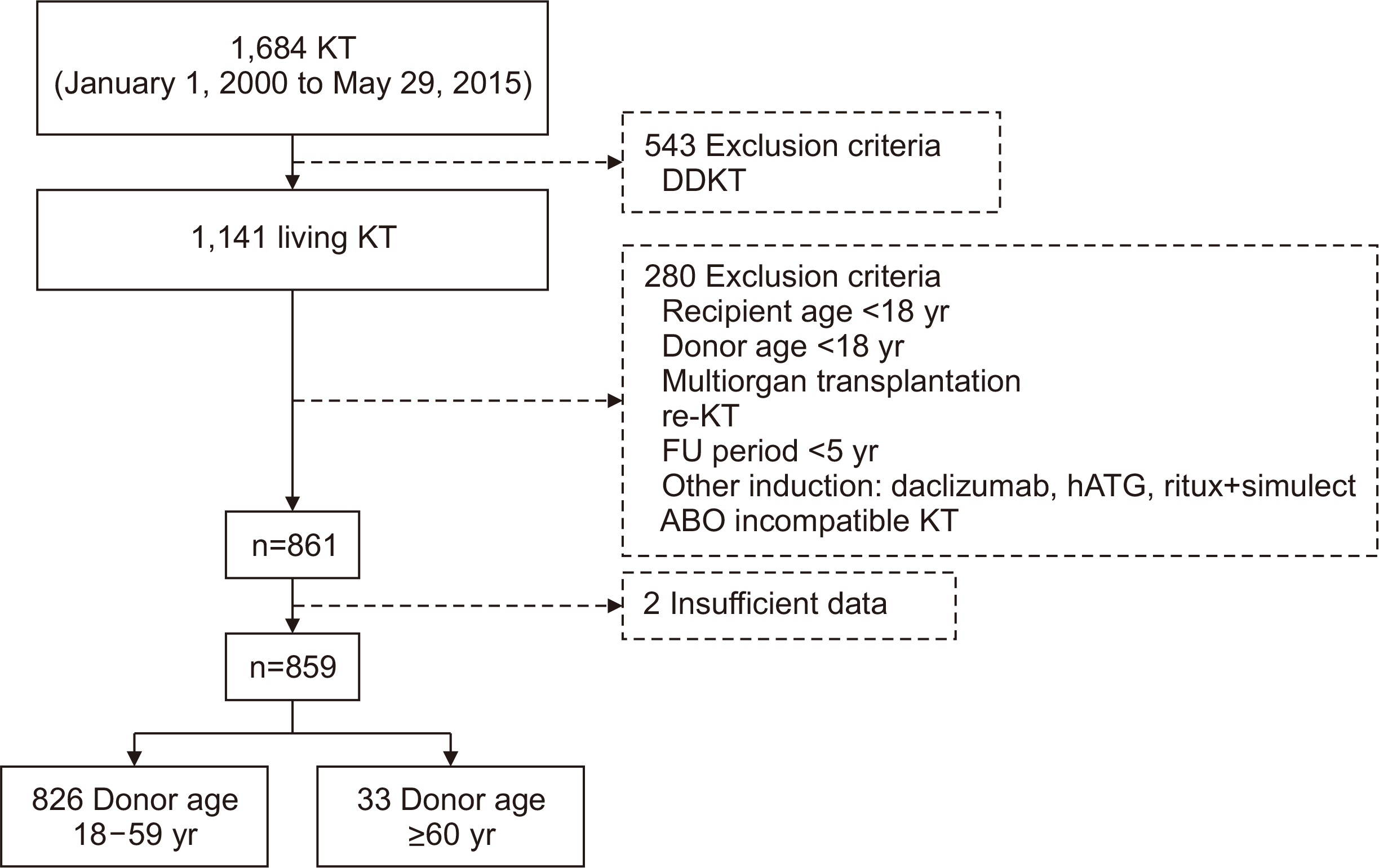
In Samsung Medical Center, from January 2000 to May 2015, 1,141 patients underwent living KT. Cases of retransplantation, recipient and donor aged younger than 18 years, and multiorgan transplantation were excluded, and a total of 859 cases were selected. Analysis was performed by dividing the patents into two groups: a younger do-nor group (donors <60 years old; n=826) and an older donor group (donors ≥60 years old; n=33).
Results
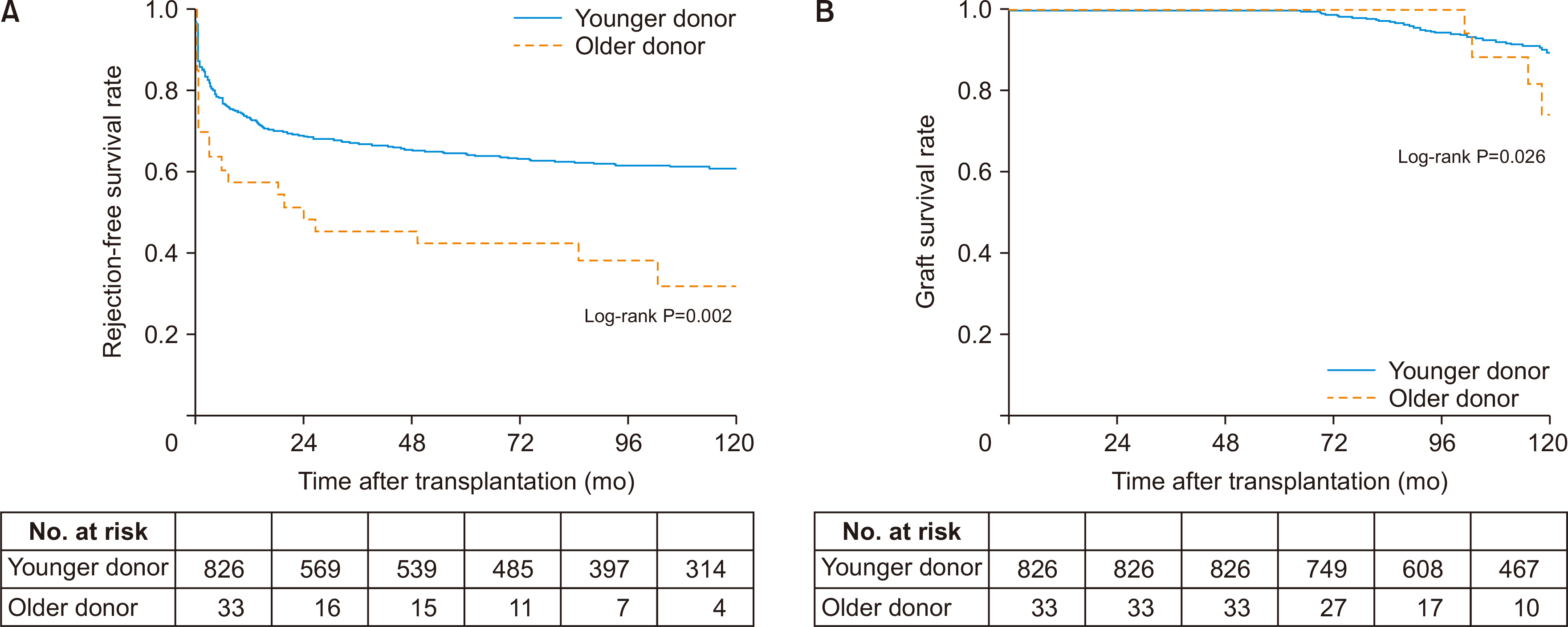
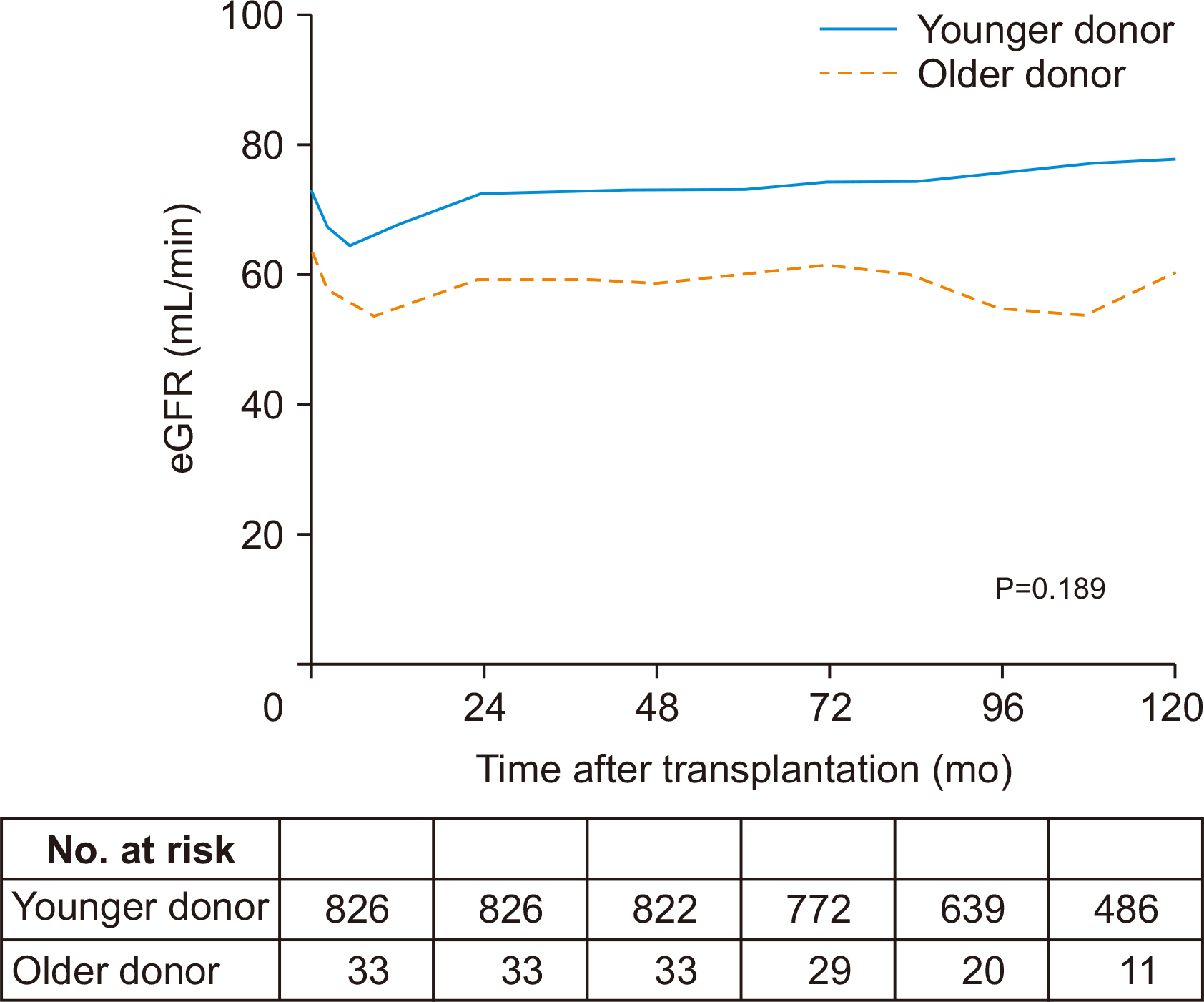
There were no significant differences between the two groups in patient death (log-rank P=0.173) or in postoperative complications. The older donor group had a higher acute rejection (P=0.034; hazard ratio [HR], 1.704) and graft failure rate (P=0.029, HR=2.352). There was no significant difference in the trend of estimated glomerular filtration rate over time (P=0.189).
Conclusions
KT using kidneys from old-aged donors is safe, but there is room for improvement due to problems with higher acute rejection and graft failure rate
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oikawa M, Hatakeyama S, Narita T, Yamamoto H, Hosogoe S, Imai A, et al. 2016; Safety and effectiveness of marginal donor in living kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 48:701–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.09.067. PMID: 27234717.
Article2. Tekin S, Yavuz HA, Yuksel Y, Yucetin L, Ateş I, Tuncer M, et al. 2015; Kidney transplantation from elderly donor. Transplant Proc. 47:1309–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.04.015. PMID: 26093706.
Article3. Gill JS, Gill J, Rose C, Zalunardo N, Landsberg D. 2006; The older living kidney donor: part of the solution to the organ shortage. Transplantation. 82:1662–6. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000250715.32241.8a. PMID: 17198256.
Article4. Toyoda M, Yamanaga S, Kawabata C, Hidaka Y, Inadome A, Arakane F, et al. 2014; Long-term safety of living kidney donors aged 60 and older. Transplant Proc. 46:318–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.11.019. PMID: 24655952.
Article5. Le Meur Y. 2015; What immunosuppression should be used for old-to-old recipients? Transplant Rev (Orlando). 29:231–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.trre.2015.08.004. PMID: 26409505.
Article6. Fijter JW, Mallat MJ, Doxiadis II, Ringers J, Rosendaal FR, Claas FH, et al. 2001; Increased immunogenicity and cause of graft loss of old donor kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:1538–46. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.V1271538. PMID: 11423584.
Article7. Colvin MM, Smith CA, Tullius SG, Goldstein DR. 2017; Aging and the immune response to organ transplantation. J Clin Invest. 127:2523–9. DOI: 10.1172/JCI90601. PMID: 28504651. PMCID: PMC5490761.
Article8. Ulrich F, Niedzwiecki S, Pascher A, Kohler S, Weiss S, Fikatas P, et al. 2011; Long-term outcome of ATG vs. Basiliximab induction. Eur J Clin Invest. 41:971–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02490.x. PMID: 21382021.
Article9. Hardinger KL, Brennan DC, Klein CL. 2013; Selection of induction therapy in kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 26:662–72. DOI: 10.1111/tri.12043. PMID: 23279211.
Article10. Bächler K, Amico P, Hönger G, Bielmann D, Hopfer H, Mihatsch MJ, et al. 2010; Efficacy of induction therapy with ATG and intravenous immunoglobulins in patients with low-level donor-specific HLA-antibodies. Am J Transplant. 10:1254–62. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03093.x. PMID: 20353473.
Article11. Naesens M, Lerut E, de Jonge H, Van Damme B, Vanrenterghem Y, Kuypers DR. 2009; Donor age and renal P-glycoprotein expression associate with chronic histological damage in renal allografts. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:2468–80. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009020192. PMID: 19762492. PMCID: PMC2799173.
Article12. Greenfeld Z, Peleg I, Brezis M, Rosen S, Pisanty S. 1994; Potential interaction between prolonged cyclosporin administration and aging in the rat kidney. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 717:209–12. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb12089.x. PMID: 8030836.
Article13. Legendre C, Brault Y, Morales JM, Oberbauer R, Altieri P, Riad H, et al. 2007; Factors influencing glomerular filtration rate in renal transplantation after cyclosporine withdrawal using sirolimus-based therapy: a multivariate analysis of results at five years. Clin Transplant. 21:330–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2007.00645.x. PMID: 17488381.
Article14. Naesens M, Kuypers DR, Sarwal M. 2009; Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 4:481–508. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.04800908. PMID: 19218475.
Article15. Bhat M, Mara K, Dierkhising R, Watt KD. 2018; Immunosuppression, race, and donor-related risk factors affect de novo cancer incidence across solid organ transplant recipients. Mayo Clin Proc. 93:1236–46. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.025. PMID: 30064826.16. Xia T, Zhu S, Wen Y, Gao S, Li M, Tao X, et al. 2018; Risk factors for calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity after renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 12:417–28. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S149340. PMID: 29535503. PMCID: PMC5836651.
Article17. Filiopoulos V, Boletis JN. 2016; Renal transplantation with expanded criteria donors: which is the optimal immunosuppression? World J Transplant. 6:103–14. DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.103. PMID: 27011908. PMCID: PMC4801786.
Article18. Moers C, Kornmann NS, Leuvenink HG, Ploeg RJ. 2009; The influence of deceased donor age and old-for-old allocation on kidney transplant outcome. Transplantation. 88:542–52. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181b0fa8b. PMID: 19696638.
Article19. Fritsche L, Hörstrup J, Budde K, Reinke P, Giessing M, Tullius S, et al. 2003; Old-for-old kidney allocation allows successful expansion of the donor and recipient pool. Am J Transplant. 3:1434–9. DOI: 10.1046/j.1600-6135.2003.00251.x. PMID: 14525606.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recipient outcomes of kidney transplantation from older living donor
- Evaluation of the Recipient and Donor in Living Kidney Transplantation
- Exchange Living-donor Kidney Transplantation: The Present and Future
- Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation from Spousal Donors: Comparison with Kidney Transplantation from Living-related Donors
- Successful Reuse of a Kidney Allograft from a Brain-Dead Donor into a Second Recipient: A Case Report