Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University Medical Center, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine and Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 6Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, Busan St. Mary's Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2520850
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0107
Abstract
Background Only few studies have shown the efficacy and safety of glucose-control strategies using the quadruple drug combination. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the usefulness of the quadruple combination therapy with oral hypoglycemic agents (OHAs) in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods From March 2014 to December 2018, data of patients with T2DM, who were treated with quadruple hypoglycemic medications for over 12 months in 11 hospitals in South Korea, were reviewed retrospectively. We compared glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels before and 12 months after quadruple treatment with OHAs. The safety, maintenance rate, and therapeutic patterns after failure of the quadruple therapy were also evaluated.
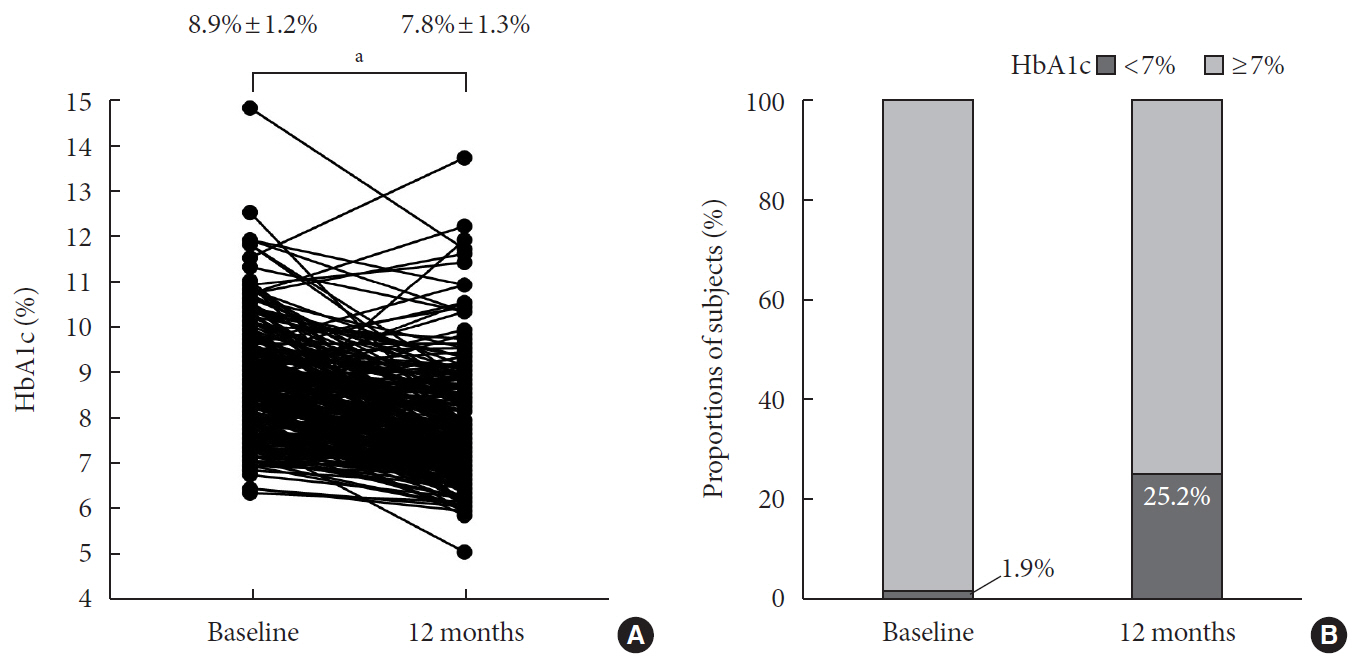
Results In total, 357 patients were enrolled for quadruple OHA therapy, and the baseline HbA1c level was 9.0%±1.3% (74.9±14.1 mmol/mol). After 12 months, 270 patients (75.6%) adhered to the quadruple therapy and HbA1c was significantly reduced from 8.9%±1.2% to 7.8%±1.3% (mean change, −1.1%±1.2%;
P <0.001). The number of patients with HbA1c <7% increased significantly from 5 to 68 (P <0.005). In addition, lipid profiles and liver enzyme levels were also improved whereas no changes in body weight. There was no significant safety issue in patients treated with quadruple OHA therapy.Conclusion This study shows the therapeutic efficacy of the quadruple OHA regimen T2DM and demonstrates that it can be an option for the management of T2DM patients who cannot use insulin or reject injectable therapy.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment Patterns of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed Using a Common Data Model Based on Electronic Health Records of 2000–2019
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Yong-Jin Im, Eun-Young Kim, Tae Sun Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(36):e230. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e230.
Reference
-
1. Defronzo RA. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2009; 58:773–795.2. Schwartz SS, Epstein S, Corkey BE, Grant SF, Gavin JR 3rd, Aguilar RB. The time is right for a new classification system for diabetes: rationale and implications of the β-cell-centric classification schema. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:179–186.
Article3. American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:Suppl 1. S98–S110.4. Sorli C, Heile MK. Identifying and meeting the challenges of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2014; 7:267–282.
Article5. Spann SJ, Nutting PA, Galliher JM, Peterson KA, Pavlik VN, Dickinson LM, et al. Management of type 2 diabetes in the primary care setting: a practice-based research network study. Ann Fam Med. 2006; 4:23–31.
Article6. Karter AJ, Subramanian U, Saha C, Crosson JC, Parker MM, Swain BE, et al. Barriers to insulin initiation: the translating research into action for diabetes insulin starts project. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:733–735.
Article7. Davies MJ, D'Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:2669–2701.
Article8. Kim BY, Won JC, Lee JH, Kim HS, Park JH, Ha KH, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2018: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:487–494.
Article9. Ko SH, Han K, Lee YH, Noh J, Park CY, Kim DJ, et al. Past and current status of adult type 2 diabetes mellitus management in Korea: a National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis. Diabetes Metab J. 2018; 42:93–100.
Article10. Kim SG, Kim NH, Ku BJ, Shon HS, Kim DM, Park TS, et al. Delay of insulin initiation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with oral hypoglycemic agents (analysis of patient- and physician-related factors): a prospective observational DIPP-FACTOR study in Korea. J Diabetes Investig. 2017; 8:346–353.
Article11. Tahrani AA, Barnett AH, Bailey CJ. Pharmacology and therapeutic implications of current drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016; 12:566–592.
Article12. Jeon HJ, Ku EJ, Oh TK. Dapagliflozin improves blood glucose in diabetes on triple oral hypoglycemic agents having inadequate glucose control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 142:188–194.
Article13. Ku EJ, Lee DH, Jeon HJ, Oh TK. Effectiveness and safety of empagliflozin-based quadruple therapy compared with insulin glargine-based therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: an observational study in clinical practice. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019; 21:173–177.
Article14. Ku EJ, Lee DH, Jeon HJ, Oh TK. Empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin, glimepiride and dipeptidyl peptide 4 inhibitors: a 52-week prospective observational study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 151:65–73.
Article15. Ryder RE. Pioglitazone has a dubious bladder cancer risk but an undoubted cardiovascular benefit. Diabet Med. 2015; 32:305–313.
Article16. Choe EY, Cho Y, Choi Y, Yun Y, Wang HJ, Kwon O, et al. The effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:211–219.
Article17. Fan M, Li Y, Zhang S. Effects of sitagliptin on lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e2386.18. Cha SA, Park YM, Yun JS, Lim TS, Song KH, Yoo KD, et al. A comparison of effects of DPP-4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor on lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2017; 16:58.
Article19. Basu D, Huggins LA, Scerbo D, Obunike J, Mullick AE, Rothenberg PL, et al. Mechanism of increased LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and decreased triglycerides with SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibition. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018; 38:2207–2216.
Article20. Home P. Cardiovascular outcome trials of glucose-lowering medications: an update. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:357–369.
Article21. Capoccia K, Odegard PS, Letassy N. Medication adherence with diabetes medication: a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Educ. 2016; 42:34–71.22. Benford M, Milligan G, Pike J, Anderson P, Piercy J, Fermer S. Fixed-dose combination antidiabetic therapy: real-world factors associated with prescribing choices and relationship with patient satisfaction and compliance. Adv Ther. 2012; 29:26–40.
Article23. Oh TJ, Yu JM, Min KW, Son HS, Lee MK, Yoon KH, et al. Efficacy and safety of voglibose plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Metab J. 2019; 43:276–286.24. Kim SS, Kim IJ, Lee KJ, Park JH, Kim YI, Lee YS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin/metformin fixed-dose combination compared with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicenter randomized double-blind study. J Diabetes. 2017; 9:412–422.
Article25. Moon MK, Hur KY, Ko SH, Park SO, Lee BW, Kim JH, et al. Combination therapy of oral hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Intern Med. 2017; 32:974–983.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:675-83)
- Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:675-83)
- Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
- A Pregnant Woman with Type 2 Diabetes Unintentionally Exposed to Metformin and Voglibose until the Second Trimester of Pregnancy: A Case Report
- Clinical Practice Guideline 2015: Oral Hypoglycemic Agents for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes