Intest Res.
2021 Jul;19(3):341-348. 10.5217/ir.2020.00057.
Effect of gut microbiome on minor complications after a colonoscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2518690
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2020.00057
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Minor complications that might occur after colonoscopy, including abdominal discomfort, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation, could a barrier for patients to undergo a screening colonoscopy. In this study, we aimed to identify the effect of gut microbial diversity and composition on minor complications after colonoscopy.
Methods
A total of 24 healthy subjects provided their stools before bowel preparation and on the 7th and 28th day after colonoscopy. On the 7th day after colonoscopy, the presence of minor complications was investigated using a questionnaire. We divided patients into 2 groups, the no complication group and complications group. The fecal microbial diversity, distribution, and composition were then compared between the groups.
Results
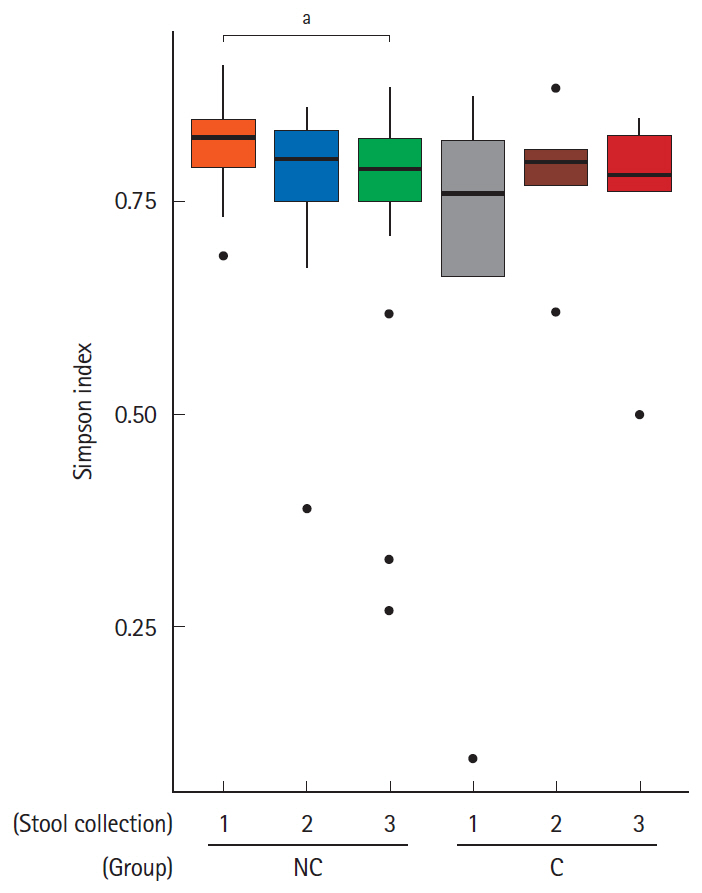
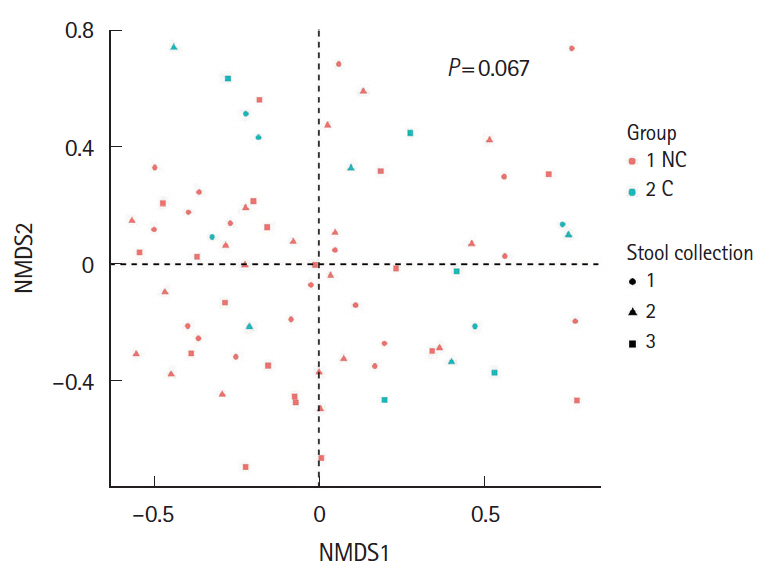
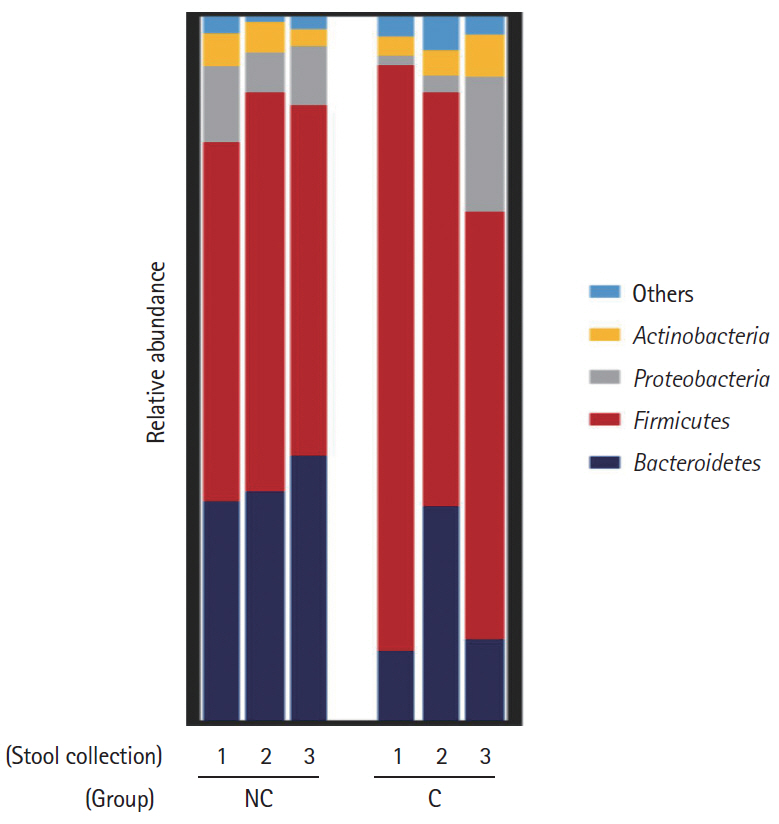
Five of the 24 subjects reported that they had undergone minor complications after colonoscopy. Most of the symptoms were mild and self-limited, but 1 patient needed medication. Interestingly, the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the initial stool samples before bowel preparation in the complication group was significantly higher than that in no complication group. After bowel preparation, the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the complication group decreased, but not in the no complication group. The microbial diversity of the no complication group decreased after bowel preparation, but not in the complication group.
Conclusions
The gut microbial composition and diversity before and after bowel preparation could be considered as one of the causes of minor complications after colonoscopy. Further studies are needed to delineate the role of gut microbiota in the occurrence of minor complications after colonoscopy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. US Preventive Services Task Force, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016; 315:2564–2575.2. Inadomi JM, Vijan S, Janz NK, et al. Adherence to colorectal cancer screening: a randomized clinical trial of competing strategies. Arch Intern Med. 2012; 172:575–582.3. Denberg TD, Melhado TV, Coombes JM, et al. Predictors of nonadherence to screening colonoscopy. J Gen Intern Med. 2005; 20:989–995.
Article4. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Fisher DA, Maple JT, et al. Complications of colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:745–752.
Article5. Ko CW, Riffle S, Shapiro JA, et al. Incidence of minor complications and time lost from normal activities after screening or surveillance colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:648–656.
Article6. Cho HS, Han DS, Park HS, et al. The incidence of minor complications and patients’ time requirements for colonoscopy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 39:205–211.7. Round JL, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:313–323.
Article8. Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kitamoto S, Kuffa P, Kamada N. Pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Intest Res. 2016; 14:127–138.
Article9. Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012; 10:735–742.
Article10. Yu LC, Wei SC, Ni YH. Impact of microbiota in colorectal carcinogenesis: lessons from experimental models. Intest Res. 2018; 16:346–357.
Article11. Wong SH, Kwong TNY, Wu CY, Yu J. Clinical applications of gut microbiota in cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019; 55:28–36.
Article12. Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006; 444:1027–1031.
Article13. Drago L, Toscano M, De Grandi R, Casini V, Pace F. Persisting changes of intestinal microbiota after bowel lavage and colonoscopy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 28:532–537.
Article14. O’Brien CL, Allison GE, Grimpen F, Pavli P. Impact of colonoscopy bowel preparation on intestinal microbiota. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e62815.
Article15. Harrell L, Wang Y, Antonopoulos D, et al. Standard colonic lavage alters the natural state of mucosal-associated microbiota in the human colon. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e32545.
Article16. Nagata N, Tohya M, Fukuda S, et al. Effects of bowel preparation on the human gut microbiome and metabolome. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:4042.
Article17. Jalanka J, Salonen A, Salojärvi J, et al. Effects of bowel cleansing on the intestinal microbiota. Gut. 2015; 64:1562–1568.
Article18. Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009; 75:7537–7541.
Article19. Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, et al. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and webbased tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41:D590–D596.
Article20. Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics. 2011; 27:2194–2200.
Article21. Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:D141–D145.
Article22. Johansson ME, Gustafsson JK, Holmén-Larsson J, et al. Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and patients with ulcerative colitis. Version 2. Gut. 2014; 63:281–291.
Article23. Bini EJ, Firoozi B, Choung RJ, Ali EM, Osman M, Weinshel EH. Systematic evaluation of complications related to endoscopy in a training setting: a prospective 30-day outcomes study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:8–16.
Article24. Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Version 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:11070–11075.25. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006; 444:1022–1023.26. Million M, Lagier JC, Yahav D, Paul M. Gut bacterial microbiota and obesity. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19:305–313.
Article27. Jeffery IB, O’Toole PW, Öhman L, et al. An irritable bowel syndrome subtype defined by species-specific alterations in faecal microbiota. Gut. 2012; 61:997–1006.
Article28. Tap J, Derrien M, Törnblom H, et al. Identification of an intestinal microbiota signature associated with severity of irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:111–123.
Article29. Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, et al. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 2009; 9:123.
Article