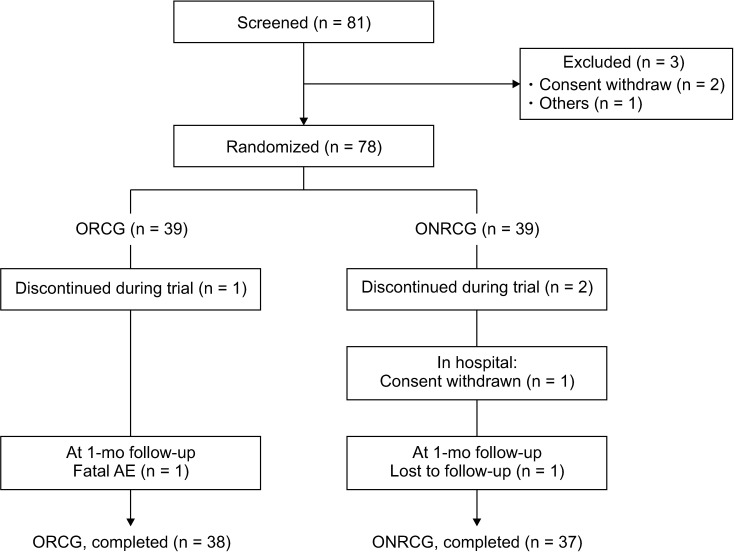
Ann Surg Treat Res.
2021 Apr;100(4):193-199. 10.4174/astr.2021.100.4.193.
A randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy of regenerated and non-regenerated oxidized cellulose gauze for the secondary treatment of local bleeding in patients undergoing hepatic resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- KMID: 2514716
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2021.100.4.193
Abstract
- Purpose
Oxidized cellulose is available in many forms, but manufactured using either a regenerated or non-regenerated process. In this study, we evaluated the effects of 2 different hemostatic agents for the treatment of local bleeding in patients undergoing hepatic resection.
Methods
This was a monocentric, parallel-group, randomized, and controlled clinical trial to compare oxidized regenerated cellulose gauze (ORCG) with oxidized non-regenerated cellulose gauze (ONRCG) in patients undergoing hepatectomy. The primary endpoint was the time to hemostasis at the target bleeding site. The secondary endpoints were the postoperative drainage volume on the first 2 days after surgery and the hospital stay.
Results
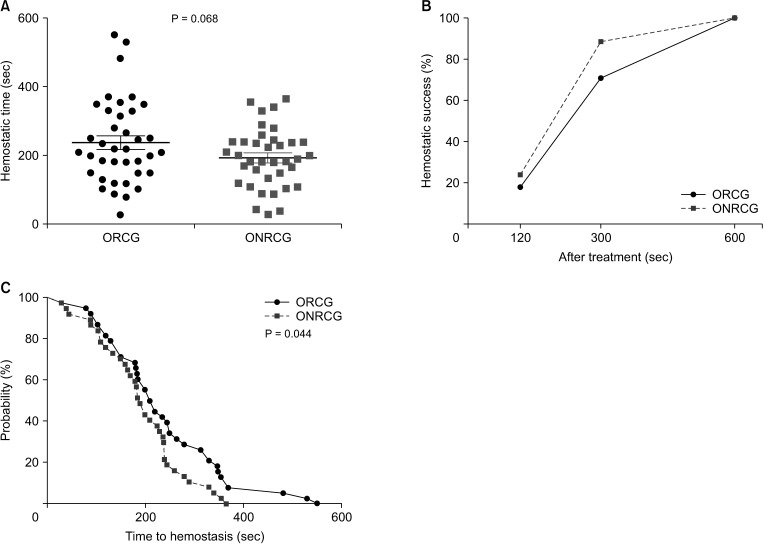
There was no significant difference between the ORCG and ONRCG groups in time to hemostasis from column analysis (238.8 ± 121.6 seconds vs. 193.7 ± 85.3 seconds, P = 0.068), and there were no differences in the rates of hemostatic success between the 2 groups at 120 seconds (18.4% vs. 24.3%; odds ratio [OR], 0.703; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.231–2.136) and 300 seconds (71.1% vs. 89.2%; OR, 0.298; 95% CI, 0.085–1.041). However, the ONRCG group was superior to the ORCG group in hemostasis according to the survival analysis (log-rank test, P = 0.044). Moreover, there were also no significant differences between the 2 groups in postoperative drainage volume on the first 2 days (P = 0.436, P = 0.381) and hospital stay (P = 0.537, P = 0.200).
Conclusion
ONRCG was not inferior to ORCG as a hemostatic agent in patients undergoing liver resection.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial of marine mussel-inspired adhesive hemostatic materials, InnoSEAL Plus
Gyu-Seong Choi, Seoung Hoon Kim, Hyung Il Seo, Je Ho Ryu, Sung Pil Yun, Mi-Young Koh, Moon Sue Lee, Haeshin Lee, Jae Hun Kim
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2021;101(5):299-305. doi: 10.4174/astr.2021.101.5.299.
Reference
-
1. Kubo S, Takemura S, Yamamoto S, Hai S, Ichikawa T, Kodai S, et al. Risk factors for massive blood loss during liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:830–833. PMID: 17591073.2. Lei Z, Chang L, Fan-Di M, Qi-Fei W, Feng T, Ming-Hui T, et al. Exploration on surgical-related factors influencing HCC patients prognosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012; 59:1541–1543. PMID: 22172375.
Article3. Harada N, Shirabe K, Maeda T, Kayashima H, Ishida T, Maehara Y. Blood transfusion is associated with recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy in Child-Pugh class A patients. World J Surg. 2015; 39:1044–1051. PMID: 25446481.
Article4. Li Z, Sun YM, Wu FX, Yang LQ, Lu ZJ, Yu WF. Controlled low central venous pressure reduces blood loss and transfusion requirements in hepatectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:303–309. PMID: 24415886.
Article5. Lau WY, Lai EC, Lau SH. Methods of vascular control technique during liver resection: a comprehensive review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2010; 9:473–481. PMID: 20943455.6. Lee N, Cho CW, Kim JM, Choi GS, Kwon CH, Joh JW. Application of temporary inf low control of the Gl issonean pedicle method provides a safe and easy technique for totally laparoscopic hemihepatectomy by Gl issonean approach. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2017; 92:383–386. PMID: 28480187.7. Doklestic K, Karamarkovic A, Stefanovic B, Stefanovic B, Milic N, Gregoric P, et al. The efficacy of three transection techniques of the liver resection: a randomized clinical trial. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012; 59:1501–1506. PMID: 22115802.8. Wolf RF, Xie H, Petty J, Teach JS, Prahl SA. Argon ion beam hemostasis with albumin after liver resection. Am J Surg. 2002; 183:584–587. PMID: 12034399.
Article9. Rau HG, Wichmann MW, Schinkel S, Buttler E, Pickelmann S, Schauer R, et al. Surgical techniques in hepatic resections: Ultrasonic aspirator versus Jet-Cutter. A prospective randomized clinical trial. Zentralbl Chir. 2001; 126:586–590. PMID: 11518996.10. Arita J, Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Sano K, Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M. Randomized clinical trial of the effect of a saline-linked radiofrequency coagulator on blood loss during hepatic resection. Br J Surg. 2005; 92:954–959. PMID: 16034832.
Article11. Spotnitz WD, Burks S. State-of-the-art review: hemostats, sealants, and adhesives II. Update as well as how and when to use the components of the surgical toolbox. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2010; 16:497–514. PMID: 20699255.
Article12. Frantz VK, Lattes R. Oxidized celluloseabsorbable gauze (cellulosic acid). JAMA. 1945; 129:798–801.13. Lewis KM, Spazierer D, Urban MD, Lin L, Redl H, Goppelt A. Comparison of regenerated and non-regenerated oxidized cellulose hemostatic agents. Eur Surg. 2013; 45:213–220. PMID: 23950762.
Article14. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6,336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:205–213. PMID: 15273542.15. Genyk Y, Kato T, Pomposelli JJ, Wright JK Jr, Sher LS, Tetens V, et al. Fibrin sealant patch (TachoSil) vs oxidized regenerated cellulose patch (Surgicel Original) for the secondary treatment of local bleeding in patients undergoing hepatic resection: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222:261–268. PMID: 26776356.16. Cescon M, Vetrone G, Grazi GL, Ramacciato G, Ercolani G, Ravaioli M, et al. Trends in perioperative outcome after hepatic resection: analysis of 1,500 consecutive unselected cases over 20 years. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:995–1002. PMID: 19474679.17. Wang Z, Liao BY, Qiu SJ, Sun HC, Yang XR, Zhou J, et al. Oxidized regenerated cel lulose reduces the amount of fluid drainage after liver resection: a randomized prospective clinical trial. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015; 62:951–954. PMID: 26902035.18. Lewis PB, Wilson ST, Kentala DR, Barry J, Lewis KM. Computed tomographic characterization of Traumastem: a new oxidized cellulose hemostatic agent. Tomography. 2016; 2:175–178. PMID: 30042962.19. Badenes D, Pijuan L, Curull V, Sánchez-Font A. A foreign body reaction to Surgicel® in a lymph node diagnosed by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Ann Thorac Med. 2017; 12:55–56. PMID: 28197224.
Article20. Habal P, Simek J, Stětina M. [Improving of treatment safety in emergency thoracic surgery]. Rozhl Chir. 2010; 89:261–264. Czech. PMID: 20586166.21. Sefr R, Silák J, Ondrák M, Fiala L. [Use of local hemostyptic drugs in liver resections]. Rozhl Chir. 2009; 88:337–341. Czech. PMID: 19642329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Intraparenchymal Biocompatibility of Oxidized Regenerated Cellulose and Porcine Small Intestine Submucosa in Rat Kidney
- Antiadhesive effect and safety of oxidized regenerated cellulose after thyroidectomy: a prospective, randomized controlled study
- Efficacy of Oxidized Regenerated Cellulose, SurgiGuard®, in Porcine Surgery
- Wound healing effect of regenerated oxidized cellulose versus fibrin sealant patch: An in vivo study
- Efficacy evaluation of SurgiGuard® in partially hepatectomized pigs