Clin Endosc.
2021 Mar;54(2):222-228. 10.5946/ce.2020.090.
Histological Architecture of Gastric Epithelial Neoplasias That Showed Absent Microsurface Patterns, Visualized by Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow-Band Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endoscopy, Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan
- 2Department of Pathology, Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Fukuoka University Chikushi Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan
- KMID: 2514176
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.090
Abstract
- Background/Aims
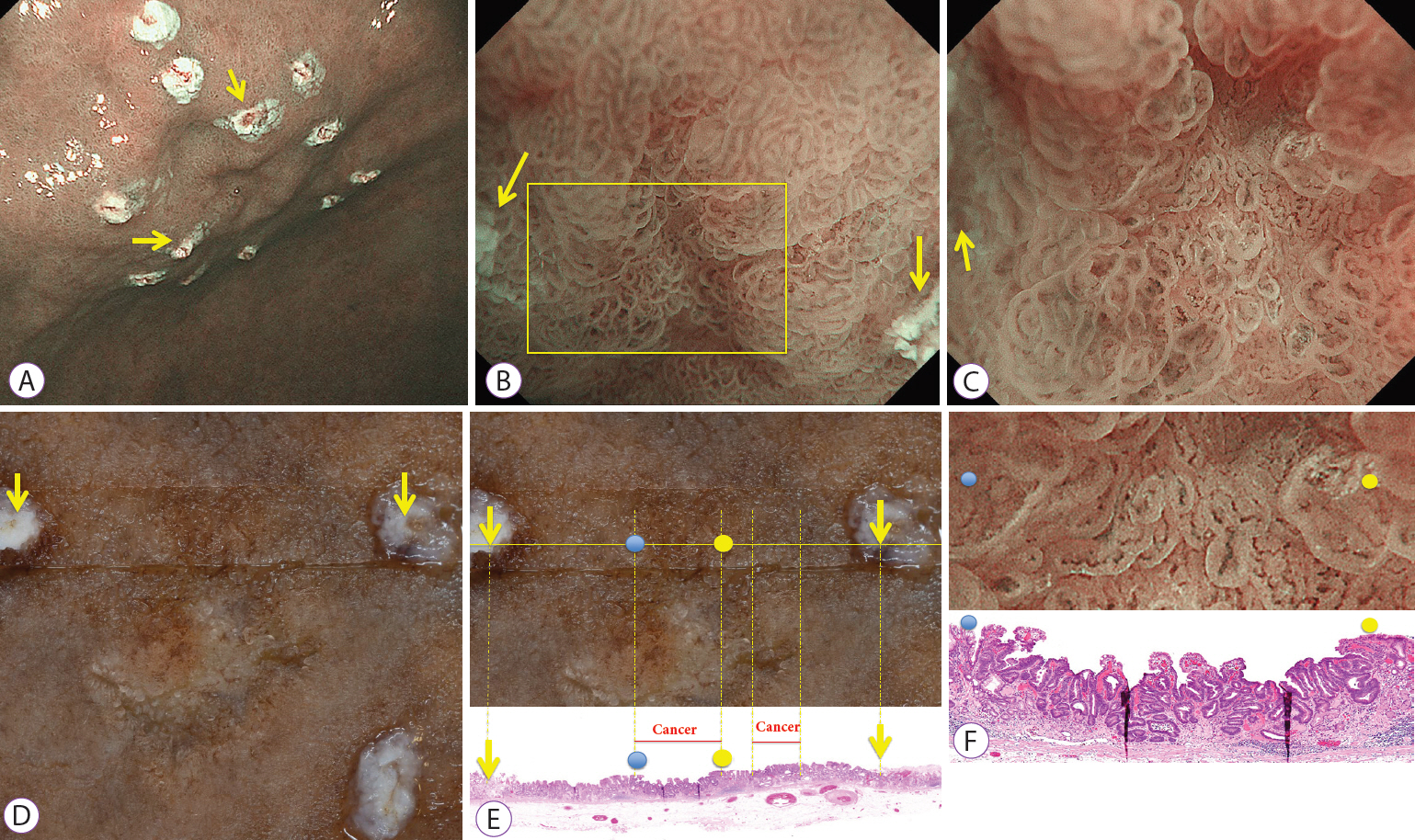
The objective of this study was to elucidate the histological structure of the absent microsurface patterns (MSPs) that were visualized by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI).
Methods
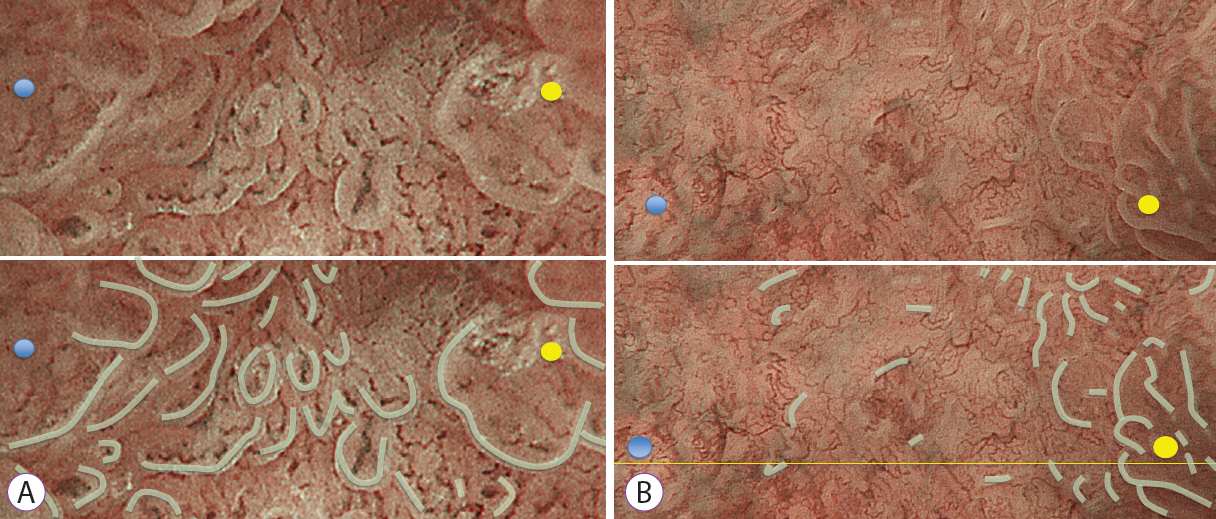
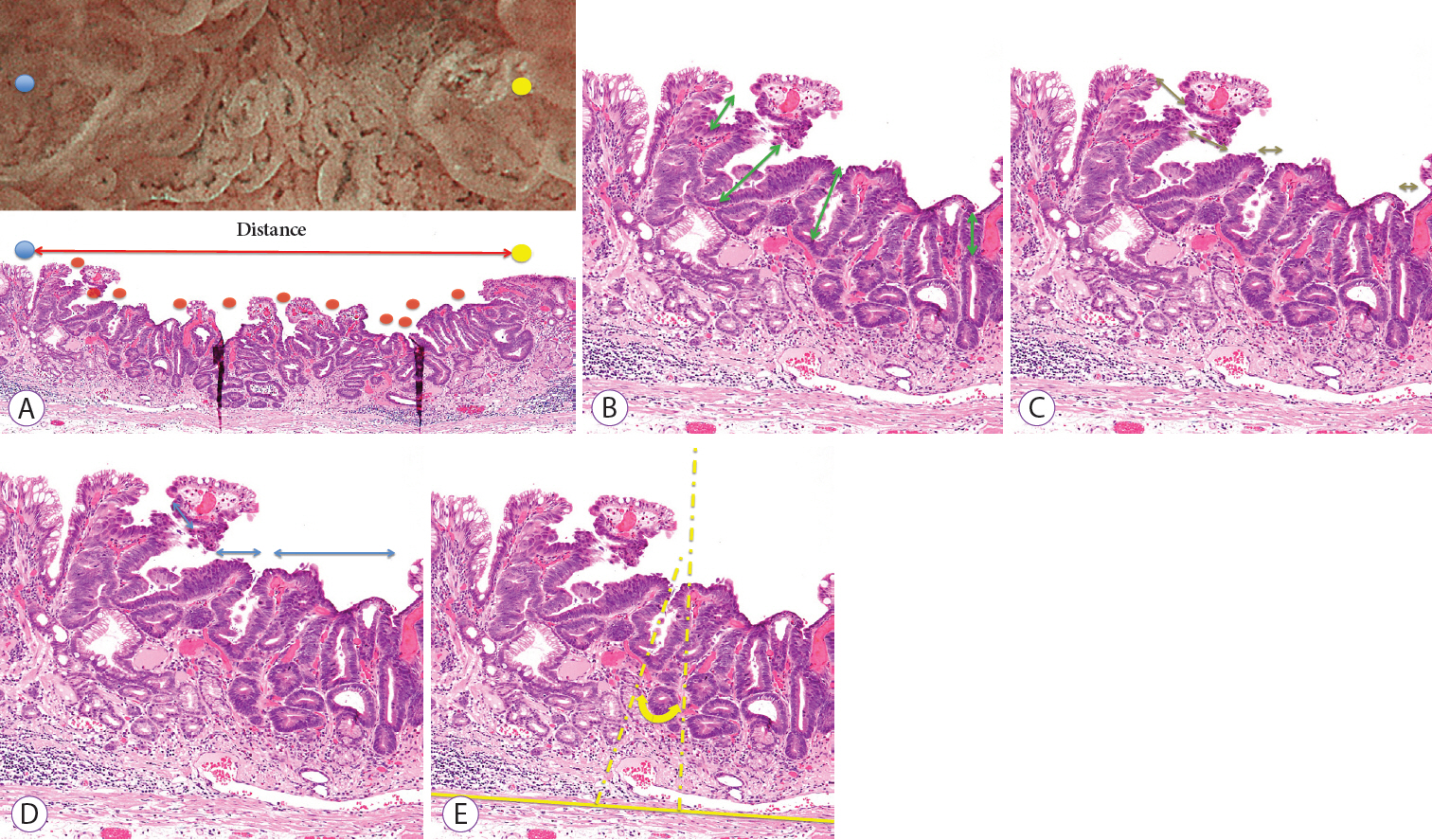
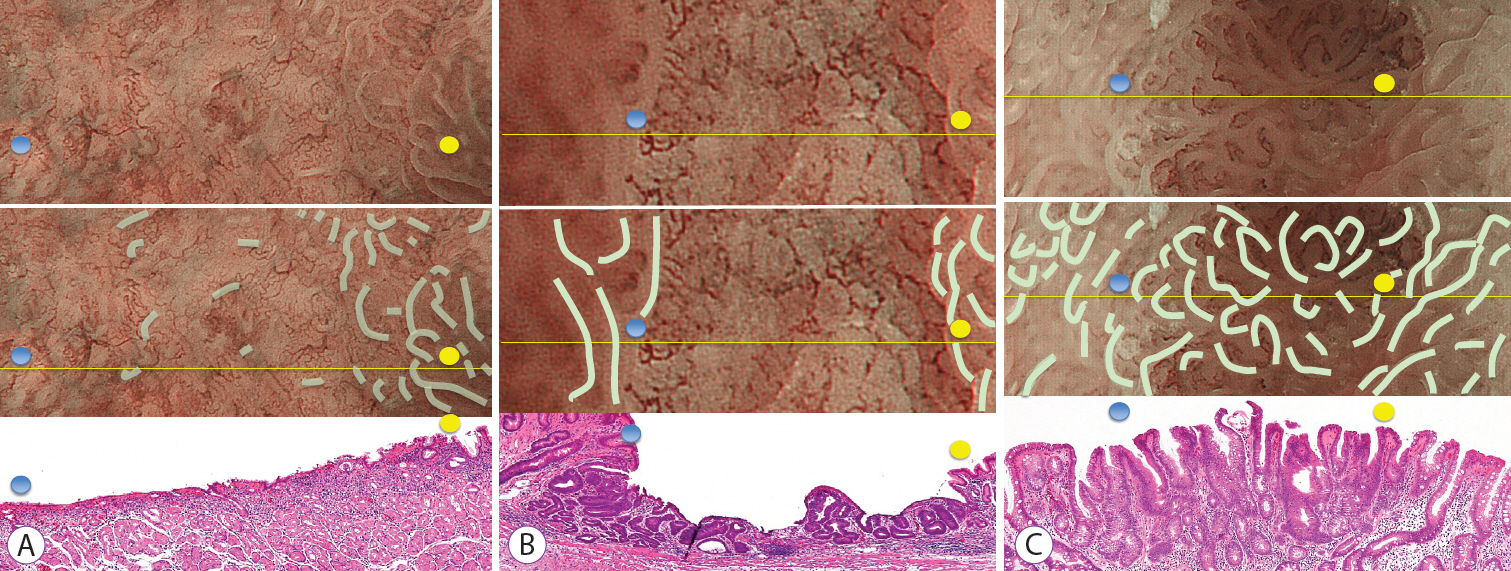
The study included consecutive gastric epithelial neoplasias for which M-NBI findings and histological findings could be compared on a one-to-one basis. The lesions were classified as absent MSPs and present MSPs based on the findings obtained using M-NBI. Of the histopathological findings for each lesion that corresponded to M-NBI findings, crypt opening densities, crypt lengths, crypt opening diameters, intercrypt distances, and crypt angles were measured and compared.
Results
Thirty-six lesions were included in the analysis; of these, 17 lesions exhibited absent MSP and 19 lesions exhibited present MSP. Comparing the histological measurements for absent MSPs vs. present MSPs, median crypt opening density was 0.9 crypt openings/mm vs. 4.8 crypt openings/mm (p<0.001), respectively. The median crypt length, median crypt opening diameter, median intercrypt distance, and median crypt angle were 80.0 μm vs. 160 μm (p<0.001), 40.0 μm vs. 44.2 μm (p=0.09), 572.5 μm vs. 166.7 μm (p<0.001), and 21.6 degrees vs. 15.5 degrees (p<0.001), respectively.
Conclusions
Histological findings showed that lesions exhibiting absent MSPs had lower crypt opening density, shorter crypt length, greater intercrypt distance, and larger crypt angle.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ezoe Y, Muto M, Uedo N, et al. Magnifying narrowband imaging is more accurate than conventional white-light imaging in diagnosis of gastric mucosal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:2017–2025.e3.
Article2. Uedo N, Ishihara R, Iishi H, et al. A new method of diagnosing gastric intestinal metaplasia: narrow-band imaging with magnifying endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:819–824.
Article3. Kanemitsu T, Yao K, Nagahama T, et al. The vessels within epithelial circle (VEC) pattern as visualized by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (ME-NBI) is a useful marker for the diagnosis of papillary adenocarcinoma: a case-controlled study. Gastric Cancer. 2014; 17:469–477.
Article4. Kanesaka T, Sekikawa A, Tsumura T, et al. Absent microsurface pattern is characteristic of early gastric cancer of undifferentiated type: magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1194–1198.e1.
Article5. Kanesaka T, Sekikawa A, Tsumura T, et al. Dense-type crypt opening seen on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging is a feature of gastric adenoma. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26:57–62.
Article6. Nakayoshi T, Tajiri H, Matsuda K, Kaise M, Ikegami M, Sasaki H. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video). Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1080–1084.
Article7. Doyama H, Yoshida N, Tsuyama S, et al. The “white globe appearance” (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI). Endosc Int Open. 2015; 3:E120–E124.
Article8. Yagi K, Nozawa Y, Endou S, Nakamura A. Diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with NBI from viewpoint of histological imaging: mucosal patterning in terms of white zone visibility and its relationship to histology. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012; 2012:954809.
Article9. Kobayashi M, Takeuchi M, Ajioka Y, et al. Mucin phenotype and narrow-band imaging with magnifying endoscopy for differentiated-type mucosal gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:1064–1070.
Article10. Uchita K, Yao K, Uedo N, et al. Highest power magnification with narrow-band imaging is useful for improving diagnostic performance for endoscopic delineation of early gastric cancers. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015; 15:155.
Article11. Yao K, Imamura K, Yamaoka R, et al. [How to construct for gastrointrestinal imaging]. Stomach and Intestine. 2016; 51:1131–1148.12. Doyama H, Nakanishi H, Yoshida N, Takeda Y, Tsuyama S, Kurumaya H. [Techniques for comparing endoscopic and histopathological results in early gastric cancer]. Stomach and Intestine. 2016; 51:1203–1210.13. Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Ragunath K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:462–467.
Article14. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 2011; 14:101–112.15. Yao K. Zoom gastroscopy: magnifying endoscopy in the stomach. Tokyo: Springer Japan;2014.16. Yagi K, Saka A, Nozawa Y, Nakamura A, Umezu H. [The characteristic finding of histological mixed type of gastric adenocarcinoma in magnifying endoscopy]. Stomach and Intestine. 2013; 48:1609–1618.17. Phalanusitthepha C, Grimes KL, Ikeda H, et al. Endoscopic features of early-stage signet-ring-cell carcinoma of the stomach. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:741–746.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Role of Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow-band Imaging in the Diagnosis of Early Gastric Cancer
- Usefulness of Narrow-Band Imaging in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of the Stomach
- Application of artificial intelligence for diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
- Image-Enhanced Endoscopy and Its Corresponding Histopathology in the Stomach
- What Have We Accomplished in Endoscopic Image Analysis for Atrophic Gastritis?