Hypoxia Increases β-Cell Death by Activating Pancreatic Stellate Cells within the Islet
- Affiliations
-
- 0Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2513055
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0181
Abstract
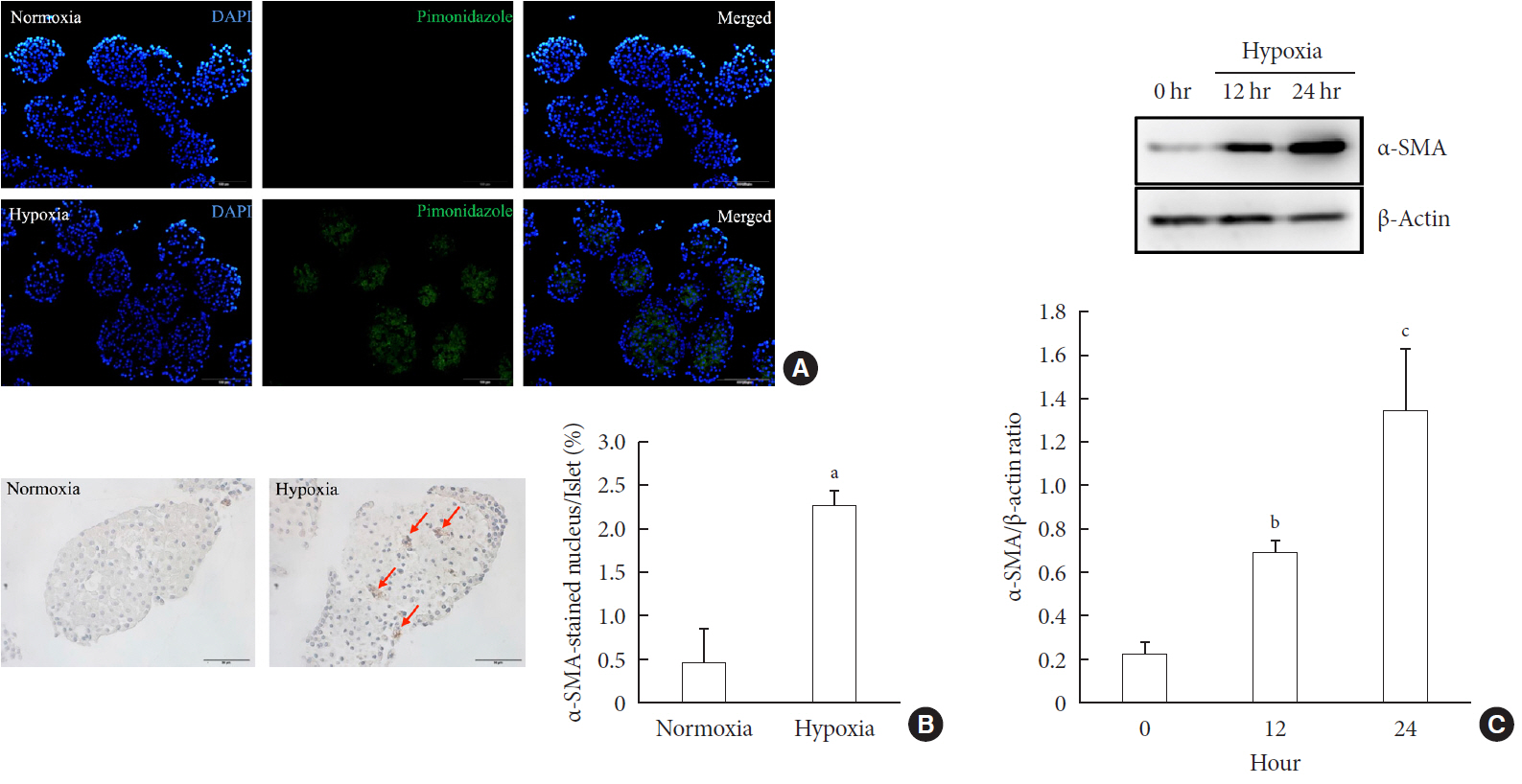
Background Hypoxia can occur in pancreatic islets in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) are activated during hypoxia. Here we aimed to investigate whether PSCs within the islet are also activated in hypoxia, causing β-cell injury.
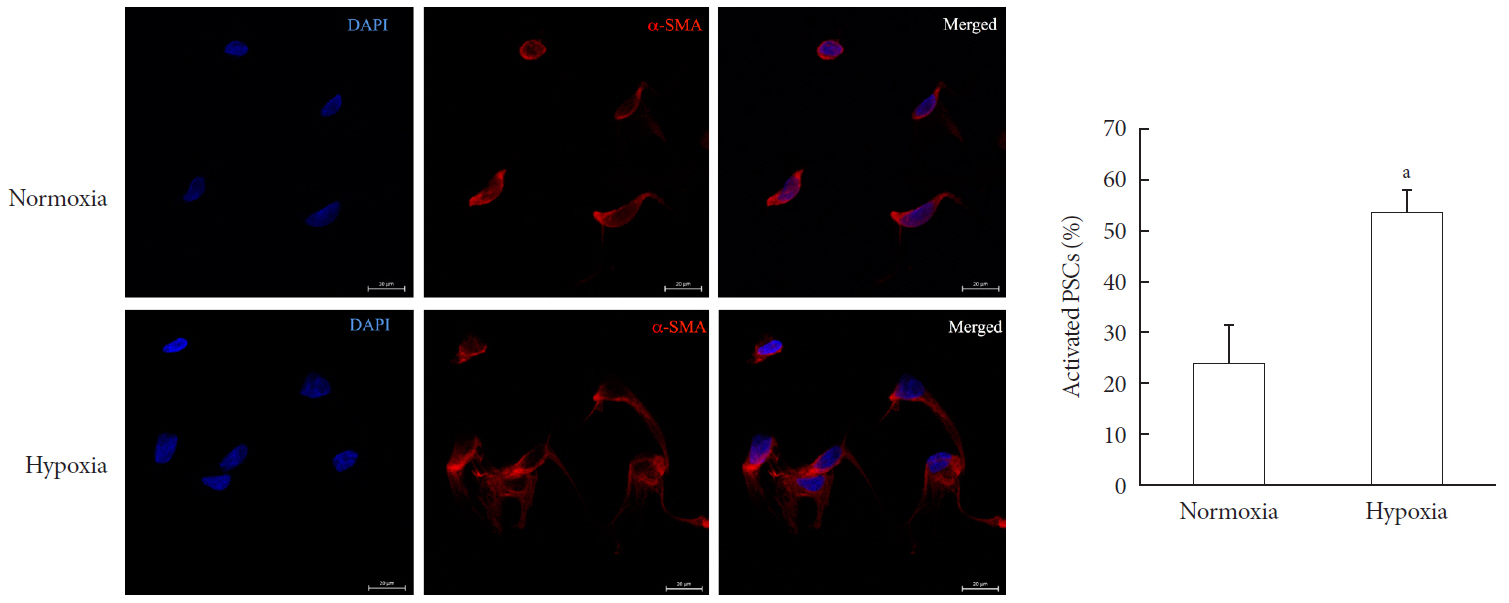
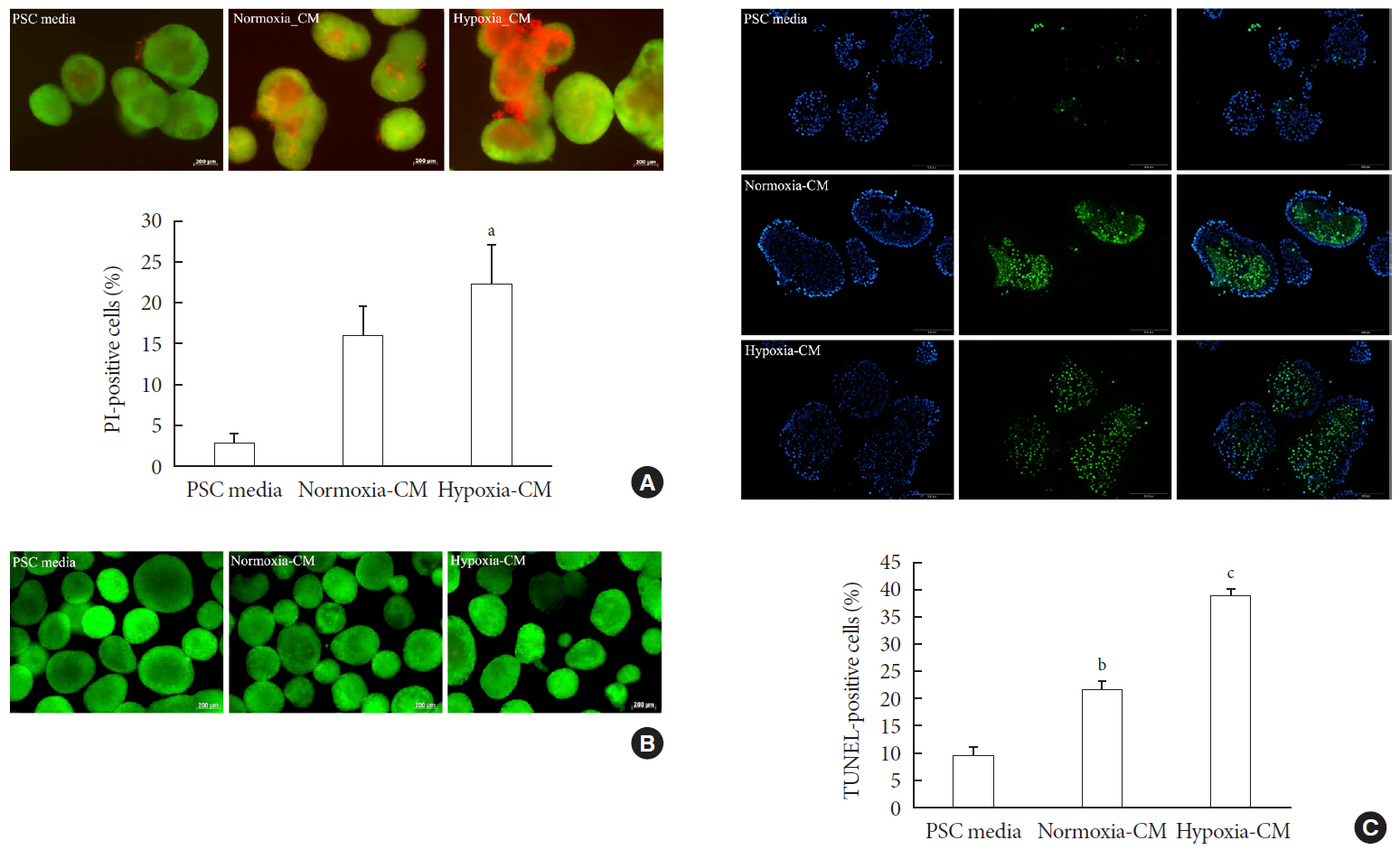
Methods Islet and primary PSCs were isolated from Sprague Dawley rats, and cultured in normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2). The expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), as measured by immunostaining and Western blotting, was used as a marker of PSC activation. Conditioned media (hypoxia-CM) were obtained from PSCs cultured in hypoxia.
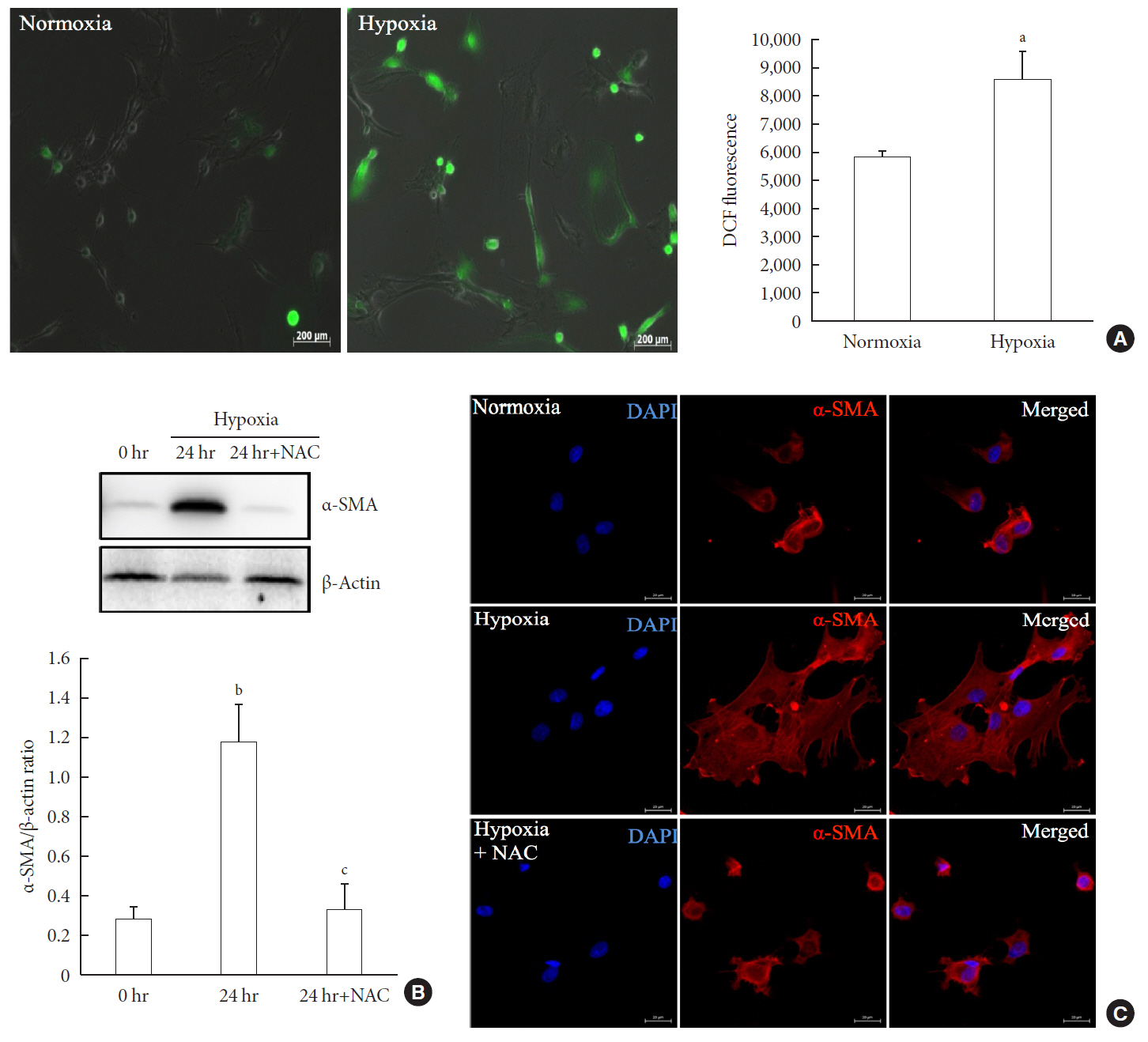
Results Islets and PSCs cultured in hypoxia exhibited higher expressions of α-SMA than did those cultured in normoxia. Hypoxia increased the production of reactive oxygen species. The addition of N-acetyl-L-cysteine, an antioxidant, attenuated the hypoxia-induced PSC activation in islets and PSCs. Islets cultured in hypoxia-CM showed a decrease in cell viability and an increase in apoptosis.
Conclusion PSCs within the islet are activated in hypoxia through oxidative stress and promote islet cell death, suggesting that hypoxia-induced PSC activation may contribute to β-cell loss in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Halban PA, Polonsky KS, Bowden DW, Hawkins MA, Ling C, Mather KJ, Powers AC, Rhodes CJ, Sussel L, Weir GC. β-Cell failure in type 2 diabetes: postulated mechanisms and prospects for prevention and treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:1983–1992.
Article2. Olsson R, Olerud J, Pettersson U, Carlsson PO. Increased numbers of low-oxygenated pancreatic islets after intraportal islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2350–2353.
Article3. Sato Y, Endo H, Okuyama H, Takeda T, Iwahashi H, Imagawa A, Yamagata K, Shimomura I, Inoue M. Cellular hypoxia of pancreatic beta-cells due to high levels of oxygen consumption for insulin secretion in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286:12524–12532.4. Bensellam M, Duvillie B, Rybachuk G, Laybutt DR, Magnan C, Guiot Y, Pouyssegur J, Jonas JC. Glucose-induced O2 consumption activates hypoxia inducible factors 1 and 2 in rat insulin-secreting pancreatic beta-cells. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e29807.5. Bensellam M, Maxwell EL, Chan JY, Luzuriaga J, West PK, Jonas JC, Gunton JE, Laybutt DR. Hypoxia reduces ER-to-Golgi protein trafficking and increases cell death by inhibiting the adaptive unfolded protein response in mouse beta cells. Diabetologia. 2016; 59:1492–1502.
Article6. Cantley J, Grey ST, Maxwell PH, Withers DJ. The hypoxia response pathway and β-cell function. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010; 12 Suppl 2:159–167.
Article7. Zhao HL, Lai FM, Tong PC, Zhong DR, Yang D, Tomlinson B, Chan JC. Prevalence and clinicopathological characteristics of islet amyloid in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003; 52:2759–2766.
Article8. Hogan MF, Hull RL. The islet endothelial cell: a novel contributor to beta cell secretory dysfunction in diabetes. Diabetologia. 2017; 60:952–959.
Article9. Kaelin WG Jr. ROS: really involved in oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 2005; 1:357–358.
Article10. Masamune A, Kikuta K, Watanabe T, Satoh K, Hirota M, Shimosegawa T. Hypoxia stimulates pancreatic stellate cells to induce fibrosis and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008; 295:G709–G717.
Article11. Lei J, Huo X, Duan W, Xu Q, Li R, Ma J, Li X, Han L, Li W, Sun H, Wu E, Ma Q. α-Mangostin inhibits hypoxia-driven ROS-induced PSC activation and pancreatic cancer cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2014; 347:129–138.
Article12. Omary MB, Lugea A, Lowe AW, Pandol SJ. The pancreatic stellate cell: a star on the rise in pancreatic diseases. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:50–59.
Article13. Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H, Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Grunert A, Adler G. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology. 1998; 115:421–432.
Article14. Apte MV, Haber PS, Darby SJ, Rodgers SC, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Wilson JS. Pancreatic stellate cells are activated by proinflammatory cytokines: implications for pancreatic fibrogenesis. Gut. 1999; 44:534–541.
Article15. Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim SR, Moon SD, Ahn YB, Song KH, Son HS, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Park CG, Lee IK, Yoon KH. Ramipril treatment suppresses islet fibrosis in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 316:114–122.
Article16. Ko SH, Hong OK, Kim JW, Ahn YB, Song KH, Cha BY, Son HY, Kim MJ, Jeong IK, Yoon KH. High glucose increases extracellular matrix production in pancreatic stellate cells by activating the renin-angiotensin system. J Cell Biochem. 2006; 98:343–355.
Article17. Nomiyama Y, Tashiro M, Yamaguchi T, Watanabe S, Taguchi M, Asaumi H, Nakamura H, Otsuki M. High glucose activates rat pancreatic stellate cells through protein kinase C and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Pancreas. 2007; 34:364–372.
Article18. Lee E, Ryu GR, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Yoon KH, Ha H, Song KH. Antioxidant treatment may protect pancreatic beta cells through the attenuation of islet fibrosis in an animal model of type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 414:397–402.
Article19. Saito R, Yamada S, Yamamoto Y, Kodera T, Hara A, Tanaka Y, Kimura F, Takei I, Umezawa K, Kojima I. Conophylline suppresses pancreatic stellate cells and improves islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrinology. 2012; 153:621–630.
Article20. Ryu GR, Lee E, Chun HJ, Yoon KH, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Song KH. Oxidative stress plays a role in high glucose-induced activation of pancreatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 439:258–263.
Article21. Lee E, Ryu GR, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Song KH. A role of pancreatic stellate cells in islet fibrosis and β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017; 485:328–334.
Article22. Zha M, Li F, Xu W, Chen B, Sun Z. Isolation and characterization of islet stellate cells in rat. Islets. 2014; 6:e28701.
Article23. Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S. Five stages of evolving beta-cell dysfunction during progression to diabetes. Diabetes. 2004; 53 Suppl 3:S16–S21.
Article24. Hayden MR. Islet amyloid and fibrosis in the cardiometabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2007; 2:70–75.
Article25. Kim JW, Ko SH, Cho JH, Sun C, Hong OK, Lee SH, Kim JH, Lee KW, Kwon HS, Lee JM, Song KH, Son HY, Yoon KH. Loss of beta-cells with fibrotic islet destruction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Biosci. 2008; 13:6022–6033.
Article26. Kikuta K, Masamune A, Hamada S, Takikawa T, Nakano E, Shimosegawa T. Pancreatic stellate cells reduce insulin expression and induce apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 433:292–297.
Article27. Zha M, Xu W, Zhai Q, Li F, Chen B, Sun Z. High glucose aggravates the detrimental effects of pancreatic stellate cells on beta-cell function. Int J Endocrinol. 2014; 2014:165612.
Article28. Zang G, Sandberg M, Carlsson PO, Welsh N, Jansson L, Barbu A. Activated pancreatic stellate cells can impair pancreatic islet function in mice. Ups J Med Sci. 2015; 120:169–180.
Article29. Ko SH, Ryu GR, Kim S, Ahn YB, Yoon KH, Kaneto H, Ha H, Kim YS, Song KH. Inducible nitric oxide synthase-nitric oxide plays an important role in acute and severe hypoxic injury to pancreatic beta cells. Transplantation. 2008; 85:323–330.
Article30. Gross MW, Karbach U, Groebe K, Franko AJ, Mueller-Klieser W. Calibration of misonidazole labeling by simultaneous measurement of oxygen tension and labeling density in multicellular spheroids. Int J Cancer. 1995; 61:567–573.
Article31. Masamune A, Shimosegawa T. Signal transduction in pancreatic stellate cells. J Gastroenterol. 2009; 44:249–260.
Article32. Yan B, Cheng L, Jiang Z, Chen K, Zhou C, Sun L, Cao J, Qian W, Li J, Shan T, Lei J, Ma Q, Ma J. Resveratrol inhibits ROS-promoted activation and glycolysis of pancreatic stellate cells via suppression of miR-21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018; 2018:1346958.
Article33. Guzy RD, Schumacker PT. Oxygen sensing by mitochondria at complex III: the paradox of increased reactive oxygen species during hypoxia. Exp Physiol. 2006; 91:807–819.
Article34. Chandel NS, Budinger GR. The cellular basis for diverse responses to oxygen. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007; 42:165–174.
Article35. Li FF, Chen BJ, Li W, Li L, Zha M, Zhou S, Bachem MG, Sun ZL. Islet stellate cells isolated from fibrotic islet of Goto-Kakizaki rats affect biological behavior of beta-cell. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:6924593.
Article36. Kim KA, Lee MS. Recent progress in research on beta-cell apoptosis by cytokines. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009; 14:657–664.
Article37. Xue R, Jia K, Wang J, Yang L, Wang Y, Gao L, Hao J. A rising star in pancreatic diseases: pancreatic stellate cells. Front Physiol. 2018; 9:754.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pancreatic islet-cell adenoma
- Pheochromocytoma with pancreatic islet cell tumor: a case report
- Cell Replacement and Regeneration Therapy for Diabetes
- Immunohistochemical Study on the Distribution of Carbonic Anhydrase Isozymes in Pancreatic Islet of Rat
- Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Protects Pancreatic Islet Dysfunction by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in vitro