Switching to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart from Basal Insulin Improves Postprandial Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Faculty of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan.
- 2Clinical Research and Medical Innovation Center, Hokkaido University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan.
- 3Manda Memorial Hospital, Sapporo, Japan.
- 4Kurihara Clinic, Sapporo, Japan.
- 5Aoki Clinic, Sapporo, Japan.
- 6Division of Diabetes and Obesity, Faculty of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan.
- KMID: 2513013
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0093
Abstract
Background To explore the efficacy and safety of switching from once-daily basal insulin therapy to once-daily pre-meal injection insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) with respect to the glycemic control of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
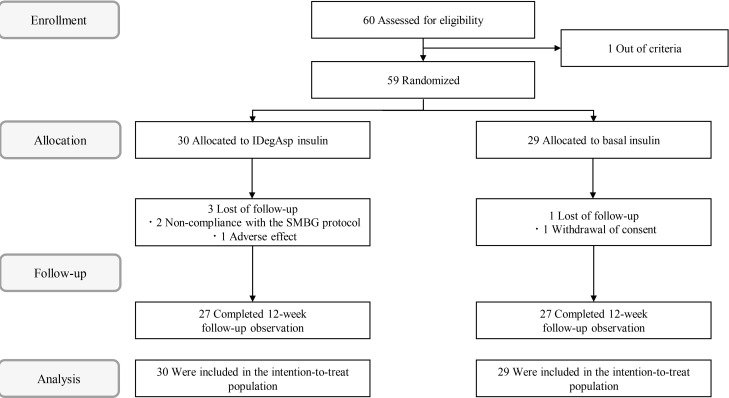
Methods In this multicenter, open-label, prospective, randomized, parallel-group comparison trial, participants on basal insulin therapy were switched to IDegAsp (IDegAsp group;
n =30) or continued basal insulin (Basal group;n =29). The primary endpoint was the superiority of IDegAsp in causing changes in the daily blood glucose profile, especially post-prandial blood glucose concentration after 12 weeks.Results Blood glucose concentrations after dinner and before bedtime were lower in the IDegAsp group, and the improvement in blood glucose before bedtime was significantly greater in the IDegAsp group than in the Basal group at 12 weeks (−1.7±3.0 mmol/L vs. 0.3±2.1 mmol/L,
P <0.05). Intriguingly, glycemic control after breakfast was not improved by IDegAsp injection before breakfast, in contrast to the favorable effect of injection before dinner on blood glucose after dinner. Glycosylated hemoglobin significantly decreased only in the IDegAsp group (58 to 55 mmol/mol,P <0.05). Changes in daily insulin dose, body mass, and recorded adverse effects, including hypoglycemia, were comparable between groups.Conclusion IDegAsp was more effective than basal insulin at reducing blood glucose after dinner and before bedtime, but did not increase the incidence of hypoglycemia. Switching from basal insulin to IDegAsp does not increase the burden on the patient and positively impacts glycemic control in patients with T2DM.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Butler PC, Meier JJ, Butler AE, Bhushan A. The replication of beta cells in normal physiology, in disease and for therapy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 3:758–768. PMID: 17955017.2. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:140–149. PMID: 25538310.
Article3. Ishii H, Iwamoto Y, Tajima N. An exploration of barriers to insulin initiation for physicians in Japan: findings from the Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes And Needs (DAWN) JAPAN study. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e36361. PMID: 22719830.
Article4. Holman RR, Thorne KI, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, Keenan JF, Paul S, Levy JC. 4-T Study Group. Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:1716–1730.
Article5. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. American Diabetes Association. European Association for Study of Diabetes. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:193–203. PMID: 18945920.
Article6. Pontiroli AE, Miele L, Morabito A. Metabolic control and risk of hypoglycaemia during the first year of intensive insulin treatment in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:433–446. PMID: 22142056.
Article7. Jehle PM, Micheler C, Jehle DR, Breitig D, Boehm BO. Inadequate suspension of neutral protamine Hagendorn (NPH) insulin in pens. Lancet. 1999; 354:1604–1607. PMID: 10560676.
Article8. Haahr H, Fita EG, Heise T. A review of insulin degludec/insulin aspart: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and their implications in clinical use. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017; 56:339–354. PMID: 27696221.
Article9. Niskanen L, Leiter LA, Franek E, Weng J, Damci T, Munoz-Torres M, Donnet JP, Endahl L, Skjoth TV, Vaag A. Comparison of a soluble co-formulation of insulin degludec/insulin aspart vs biphasic insulin aspart 30 in type 2 diabetes: a randomised trial. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012; 167:287–294. PMID: 22660026.
Article10. Wysham C, Bhargava A, Chaykin L, de la Rosa R, Handelsman Y, Troelsen LN, Kvist K, Norwood P. Effect of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine U100 on hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the SWITCH 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017; 318:45–56. PMID: 28672317.11. Heise T, Norskov M, Nosek L, Kaplan K, Famulla S, Haahr HL. Insulin degludec: lower day-to-day and within-day variability in pharmacodynamic response compared with insulin glargine 300 U/mL in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017; 19:1032–1039. PMID: 28295934.12. Fulcher GR, Christiansen JS, Bantwal G, Polaszewska-Muszynska M, Mersebach H, Andersen TH, Niskanen LK. BOOST: Intensify Premix I Investigators. Intensify Premix I Investigators. Comparison of insulin degludec/insulin aspart and biphasic insulin aspart 30 in uncontrolled, insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a phase 3a, randomized, treat-to-target trial. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:2084–2090. PMID: 24812432.13. Onishi Y, Ono Y, Rabol R, Endahl L, Nakamura S. Superior glycaemic control with once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus insulin glargine in Japanese adults with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with oral drugs: a randomized, controlled phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:826–832. PMID: 23557077.
Article14. Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:881–885. PMID: 12610053.
Article15. Kumar A, Franek E, Wise J, Niemeyer M, Mersebach H, Simo R. Efficacy and safety of once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus insulin glargine (U100) for 52 weeks in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0163350. PMID: 27760129.16. Liebl A, Davidson J, Mersebach H, Dykiel P, Tack CJ, Heise T. A novel insulin combination of insulin degludec and insulin aspart achieves a more stable overnight glucose profile than insulin glargine: results from continuous glucose monitoring in a proof-of-concept trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013; 7:1328–1336. PMID: 24124961.
Article17. Nagai Y, Nishine A, Hashimoto E, Nakayama T, Sasaki Y, Murakami M, Ishii S, Kato H, Tanaka Y. Efficacy and safety of switching from basal insulin to once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a 4-week, randomized, open-label, treat-to-target study. J Diabetes Investig. 2017; 9:567–572.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
- Response: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
- Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- Clinical Use of New Insulins and New Insulin Delivery Systems
- Exenatide versus Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in a Subgroup of Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus