Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junghs@snu.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2466257
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.382
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Conflicting results have been reported on the efficacy of insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) compared to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes. We investigated the effects of changing basal insulin to IDegAsp on glycemic control and sought to identify factors related to those effects.
METHODS
In this retrospective study of patients from three referral hospitals, patients with type 2 diabetes using basal insulin with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels less than 11.0% were enrolled. Basal insulin was replaced with IDegAsp, and data were analyzed from 3 months before to 3 months after the replacement.
RESULTS
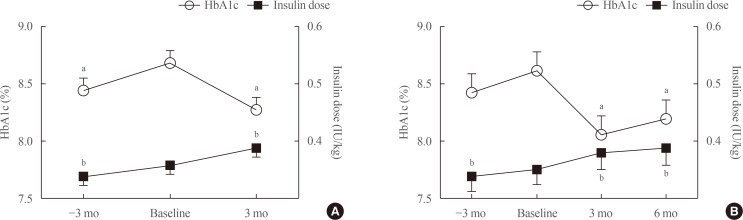
Eighty patients were recruited (52.5% male; mean age, 67.0±9.8 years; mean duration of diabetes, 18.9±8.5 years; mean HbA1c, 8.7%±1.0%). HbA1c levels increased during 3 months of basal insulin use, but significantly decreased after changing to IDegAsp (8.28%±1.10%, P=0.0001). The reduction was significant at 6 months in 35 patients whose longer-term data were available. Patients with a measured fasting plasma glucose (m-FPG) lower than their predicted FPG (p-FPG) by regression from HbA1c showed a significant HbA1c reduction caused by the change to IDegAsp, even without a significantly increased insulin dose. However, patients whose m-FPG was higher than their p-FPG did not experience a significant HbA1c reduction, despite a significantly increased insulin dose. Furthermore, the HbA1c reduction caused by IDegAsp was significant in patients with low fasting C-peptide levels and high insulin doses.
CONCLUSION
We observed a significant glucose-lowering effect by replacing basal insulin with IDegAsp, especially in patients with a lower m-FPG than p-FPG.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Letter: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (
Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
Sang Youl Rhee
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):192-193. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.192.Response: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (
Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
Han Na Jang, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):194-195. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.194.Efficacy and Safety of IDegAsp in a Real-World Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shinae Kang, Yu-Bae Ahn, Tae Keun Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung Wan Chun, Boram Bae, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Sungeun Jung, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(5):929-936. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0297.
Reference
-
1. Ha KH, Park CY, Jeong IK, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim WJ, et al. Clinical characteristics of people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes between 2015 and 2016: difference by age and body mass index. Diabetes Metab J. 2018; 42:137–146. PMID: 29676543.
Article2. Rudenski AS, Hadden DR, Atkinson AB, Kennedy L, Matthews DR, Merrett JD, et al. Natural history of pancreatic islet B-cell function in type 2 diabetes mellitus studied over six years by homeostasis model assessment. Diabet Med. 1988; 5:36–41. PMID: 2964326.
Article3. Lee BW, Kim JH, Ko SH, Hur KY, Kim NH, Rhee SY, et al. Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017. Diabetes Metab J. 2017; 41:367–373. PMID: 29086534.
Article4. Lamos EM, Younk LM, Tate DB, Davis SN. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin glargine-insulin glulisine basal-bolus and twice-daily premixed analog insulin in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients during three standardized meals. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2015; 3:14–20. PMID: 29159123.
Article5. Sarbacker GB, Urteaga EM. Adherence to insulin therapy. Diabetes Spectr. 2016; 29:166–170. PMID: 27574371.6. Anyanwagu U, Mamza J, Gordon J, Donnelly R, Idris I. Premixed vs basal-bolus insulin regimen in type 2 diabetes: comparison of clinical outcomes from randomized controlled trials and real-world data. Diabet Med. 2017; 34:1728–1736. PMID: 28945928.
Article7. Havelund S, Ribel U, Hubalek F, Hoeg-Jensen T, Wahlund PO, Jonassen I. Investigation of the physico-chemical properties that enable co-formulation of basal insulin degludec with fast-acting insulin aspart. Pharm Res. 2015; 32:2250–2258. PMID: 25563978.
Article8. Haahr H, Fita EG, Heise T. A review of insulin degludec/insulin aspart: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and their implications in clinical use. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017; 56:339–354. PMID: 27696221.
Article9. Heise T, Nosek L, Bottcher SG, Hastrup H, Haahr H. Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012; 14:944–950. PMID: 22726241.
Article10. Yang W, Ma J, Hong T, Liu M, Miao H, Peng Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus biphasic insulin aspart 30 in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes: a phase III, open-label, 2:1 randomized, treat-to-target trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019; 21:1652–1660. PMID: 30869183.
Article11. Onishi Y, Yamada K, Zacho J, Ekelund J, Iwamoto Y. Insulin degludec/insulin aspart vs biphasic insulin aspart 30 twice daily in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes Investig. 2017; 8:210–217.
Article12. Kumar S, Jang HC, Demirag NG, Skjoth TV, Endahl L, Bode B. Efficacy and safety of once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart compared with once-daily insulin glargine in participants with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, treat-to-target study. Diabet Med. 2017; 34:180–188. PMID: 27027878.
Article13. Onishi Y, Ono Y, Rabol R, Endahl L, Nakamura S. Superior glycaemic control with once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus insulin glargine in Japanese adults with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with oral drugs: a randomized, controlled phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:826–832. PMID: 23557077.
Article14. Liebl A, Davidson J, Mersebach H, Dykiel P, Tack CJ, Heise T. A novel insulin combination of insulin degludec and insulin aspart achieves a more stable overnight glucose profile than insulin glargine: results from continuous glucose monitoring in a proof-of-concept trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013; 7:1328–1336. PMID: 24124961.
Article15. Kumar A, Franek E, Wise J, Niemeyer M, Mersebach H, Simo R. Efficacy and safety of once-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus insulin glargine (U100) for 52 weeks in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0163350. PMID: 27760129.16. Rohlfing CL, Wiedmeyer HM, Little RR, England JD, Tennill A, Goldstein DE. Defining the relationship between plasma glucose and HbA(1c): analysis of glucose profiles and HbA(1c) in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:275–278. PMID: 11815495.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
- Response: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
- Switching to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart from Basal Insulin Improves Postprandial Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- Intraoperative and Postoperative Glycemic Management in Patients with Diabetes
- Intensive Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes