Exenatide versus Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in a Subgroup of Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yoonk@catholic.ac.kr
- 2AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, MD, USA.
- 3Pharmapace, San Diego, CA, USA.
- KMID: 2368531
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.69
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity is increasing in Korea. Clinical studies in patients with T2DM have shown that combining the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exenatide twice daily with basal insulin is an effective glucose-lowering strategy. However, these studies were predominantly conducted in non-Asian populations.
METHODS
We conducted a subgroup analysis of data from a multinational, 30-week, randomized, open-label trial to compare the effects of exenatide twice daily (n=10) or three times daily mealtime insulin lispro (n=13) among Korean patients with T2DM inadequately controlled (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] >7.0%) on metformin plus optimized insulin glargine.
RESULTS
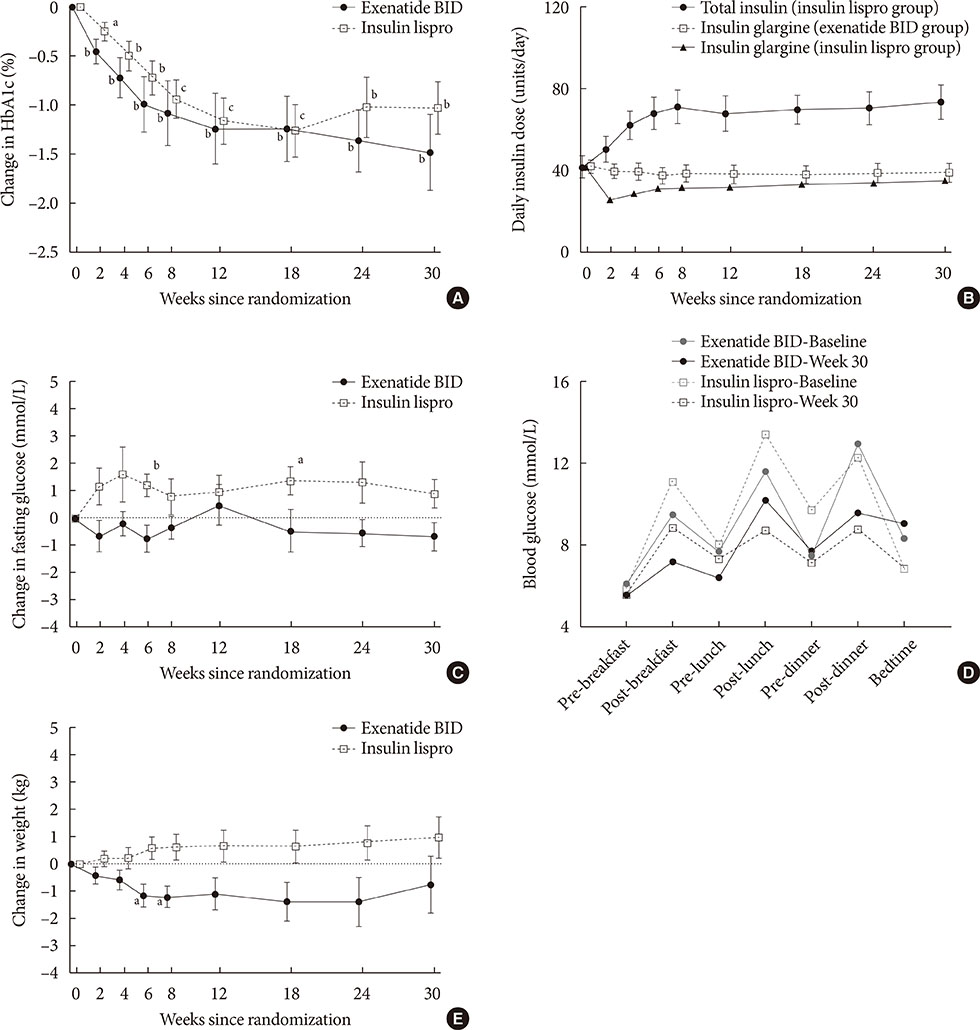
Exenatide twice daily and insulin lispro both reduced HbA1c (mean −1.5% and −1.0%, respectively; P<0.01 vs. baseline). Fasting glucose and weight numerically decreased with exenatide twice daily (−0.7 mmol/L and −0.7 kg, respectively) and numerically increased with insulin lispro (0.9 mmol/L and 1.0 kg, respectively). Minor hypoglycemia occurred in four patients receiving exenatide twice daily and three patients receiving insulin lispro. Gastrointestinal adverse events were the most common with exenatide twice daily treatment.
CONCLUSION
This analysis found treatment with exenatide twice daily improved glycemic control without weight gain in Korean patients with T2DM unable to achieve glycemic control on metformin plus basal insulin.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Hyun Jin Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(1):35-40. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.1.35.Injectable Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus: Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist
Inkuk Lee, Eun Seok Kang
J Korean Diabetes. 2019;20(3):149-156. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2019.20.3.149.Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Hyun Jin Kim, Seok O Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Kyung Mook Choi,
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):423-429. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.423.
Reference
-
1. Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009; 301:2129–2140.2. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.3. WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004; 363:157–163.4. Kim CS, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Lim S, Choi SH, Song KH, Won JC, Kim DJ, Cha BY; Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Prevalence, awareness, and management of obesity in Korea: data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1998-2011). Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:35–43.5. Son JW, Park CY, Kim S, Lee HK, Lee YS; Insulin Resistance as Primary Pathogenesis in Newly Diagnosed, Drug Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Korea (SURPRISE) Study Group. Changing clinical characteristics according to insulin resistance and insulin secretion in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2015; 39:387–394.6. Shimizu H, Uehara Y, Okada S, Mori M. Contribution of fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia to hemoglobin A1c in insulin-treated Japanese diabetic patients. Endocr J. 2008; 55:753–756.7. Venn BS, Williams SM, Mann JI. Comparison of postprandial glycaemia in Asians and Caucasians. Diabet Med. 2010; 27:1205–1208.8. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:140–149.9. Nielsen LL, Young AA, Parkes DG. Pharmacology of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4): a potential therapeutic for improved glycemic control of type 2 diabetes. Regul Pept. 2004; 117:77–88.10. Meier JJ. GLP-1 receptor agonists for individualized treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012; 8:728–742.11. Buse JB, Bergenstal RM, Glass LC, Heilmann CR, Lewis MS, Kwan AY, Hoogwerf BJ, Rosenstock J. Use of twice-daily exenatide in basal insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 154:103–112.12. Diamant M, Nauck MA, Shaginian R, Malone JK, Cleall S, Reaney M, de Vries D, Hoogwerf BJ, MacConell L, Wolffenbuttel BH. 4B Study Group. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist or bolus insulin with optimized basal insulin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:2763–2773.13. Balena R, Hensley IE, Miller S, Barnett AH. Combination therapy with GLP-1 receptor agonists and basal insulin: a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:485–502.14. Shin J, Chang JS, Kim HS, Ko SH, Cha BY, Son HY, Yoon KH, Cho JH. Effects of a 6-month exenatide therapy on HbA1c and weight in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:364–370.15. Song SO, Kim KJ, Lee BW, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lee HC. Tolerability, effectiveness and predictive parameters for the therapeutic usefulness of exenatide in obese, Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2014; 5:554–562.16. Lu CH, Wu TJ, Shih KC, Ni E, Reed V, Yu M, Sheu WH, Chuang LM. Safety and efficacy of twice-daily exenatide in Taiwanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Formos Med Assoc. 2013; 112:144–150.17. Kadowaki T, Namba M, Imaoka T, Yamamura A, Goto W, Boardman MK, Sowa H. Improved glycemic control and reduced bodyweight with exenatide: a double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study in Japanese patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes over 24 weeks. J Diabetes Investig. 2011; 2:210–217.18. Inagaki N, Ueki K, Yamamura A, Saito H, Imaoka T. Long-term safety and efficacy of exenatide twice daily in Japanese patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2011; 2:448–456.19. Sheu WH, Brunell SC, Blase E. Efficacy and tolerability of exenatide twice daily and exenatide once weekly in Asian versus White patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016; 114:160–172.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases Reports of Prevention of Hypoglycemia with Administration of Insulin lispro on Diabetes in Pregnancy
- Effect of Insulin Glargine in Adolescents with Uncontrolled type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Determining the Factors that Influence the Insulin Requirements in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Intraoperative and Postoperative Glycemic Management in Patients with Diabetes
- Two Cases of hypoglycemia in IDDM patients with insulin antibody