Surveillance of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Testing in Clinical Laboratories in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2512670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2021.41.2.225
Abstract
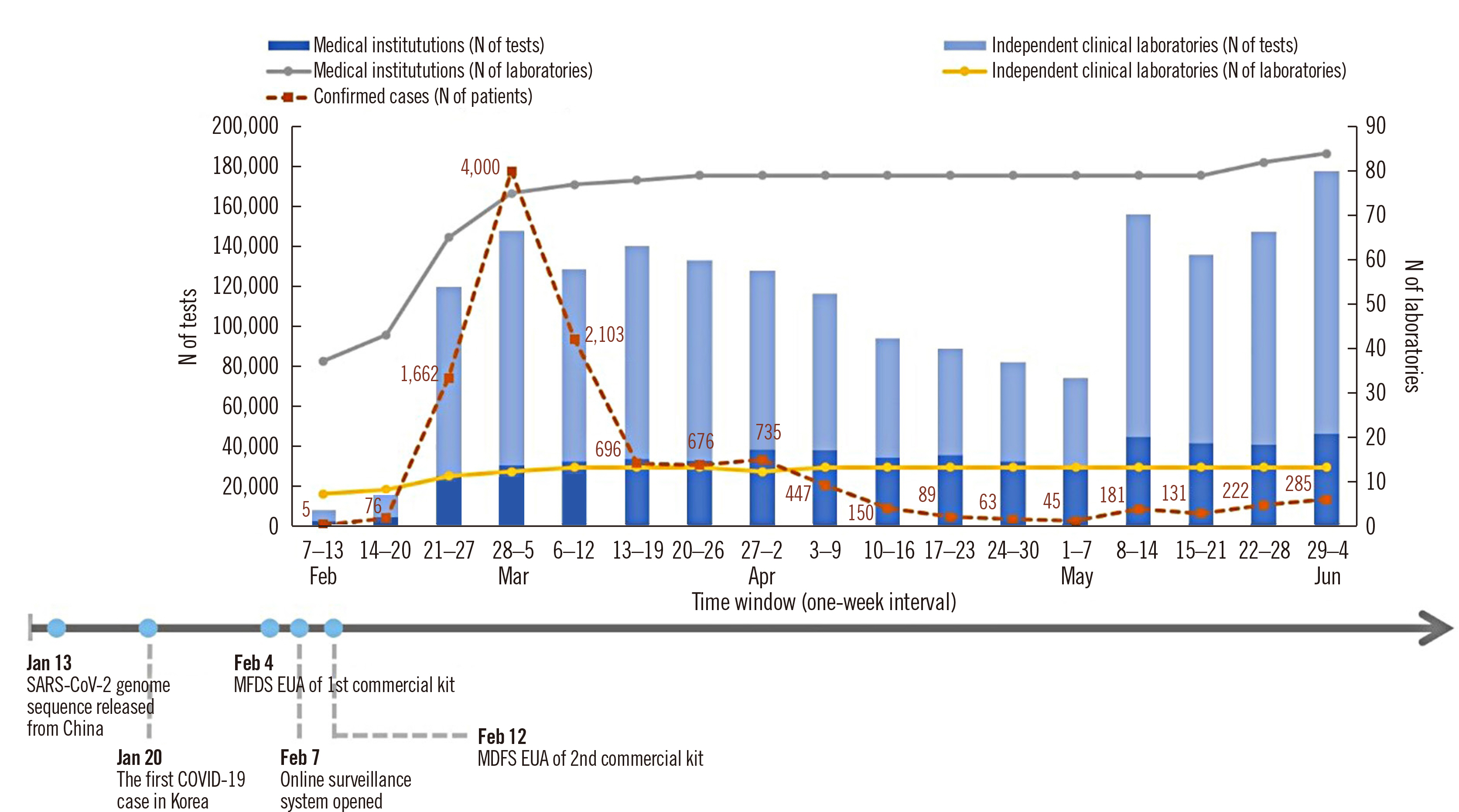
- In response to the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, an online laboratory surveillance system was established to monitor severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) real-time reverse transcription-PCR (rRT-PCR) testing capacities and results. SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR testing data were collected from 97 clinical laboratories, including 84 medical institutions and 13 independent clinical laboratories in Korea. We assessed the testing capacities to utilize SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR based on surveillance data obtained from February 7th to June 4th, 2020 and evaluated positive result characteristics according to the reagents used and sample types. A total of 1,890,319 SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR testing were performed, 2.3% of which were positive. Strong correlations were observed between the envelope (E ) gene and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp )/nucleocapsid (N ) genes threshold cycle (Ct) values for each reagent. No statistically significant differences in gene Ct values were observed between the paired upper and lower respiratory tract samples, except in the N gene for nasopharyngeal swab and sputum samples. Our study showed that clinical laboratories in Korea have rapidly expanded their testing capacities in response to the COVID-19 outbreak, with a peak daily capacity of 34,193 tests. Rapid expansion in testing capacity is a critical component of the national response to the ongoing pandemic.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Clinical and Virologic Effectiveness of Remdesivir Treatment for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a Nationwide Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Eun-Jeong Joo, Jae-Hoon Ko, Seong Eun Kim, Seung-Ji Kang, Ji Hyeon Baek, Eun Young Heo, Hye Jin Shi, Joong Sik Eom, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Seongman Bae, Sang Hyun Ra, Da Young Kim, Baek-Nam Kim, Yu Min Kang, Ji Yeon Kim, Jin-Won Chung, Hyun-Ha Chang, Sohyun Bae, Shinhyea Cheon, Yoonseon Park, Heun Choi, Eunjung Lee, Bo young Lee, Jung Wan Park, Yujin Sohn, Jung Yeon Heo, Sung-Han Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(11):e83. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83.Response of Clinical Laboratories to the Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic
Young Jin Kim, Heungsup Sung, Chang-Seok Ki, Mina Hur
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(6):519-520. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.6.519.Clinical Performance of the Standard Q COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test and Simulation of its Real-World Application in Korea
Jaehyeon Lee, So Yeon Kim, Hee Jae Huh, Namsu Kim, Heungsup Sung, Hyukmin Lee, Kyoung Ho Roh, Taek Soo Kim, Ki Ho Hong
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(6):588-592. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.6.588.Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses and Seroconversion in COVID-19 Patients Using Twelve Commercial Immunoassays
Sojeong Yun, Ji Hyeong Ryu, Joo Hee Jang, Hyunjoo Bae, Seung-Hyo Yoo, Ae-Ran Choi, Sung Jin Jo, Jihyang Lim, Jehoon Lee, Hyejin Ryu, Sung-Yeon Cho, Dong-Gun Lee, Jongmin Lee, Seok Chan Kim, Yeon-Joon Park, Hyeyoung Lee, Eun-Jee Oh
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(6):577-587. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.6.577.Clinical Evaluation of the Rapid STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test for the Screening of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Hyung Woo Kim, Mikyoung Park, Jong Ho Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(1):100-104. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.1.100.Performance Evaluation of the PowerChek SARS-CoV-2, Influenza A & B Multiplex Real-Time PCR Kit in Comparison with the BioFire Respiratory Panel
Tae Yeul Kim, Ji-Youn Kim, Hyang Jin Shim, Sun Ae Yun, Ja-Hyun Jang, Hee Jae Huh, Jong-Won Kim, Nam Yong Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2022;42(4):473-477. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.473.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Updated on 18 Jul 2020.2. Cheng MP, Papenburg J, Desjardins M, Kanjilal S, Quach C, Libman M, et al. 2020; Diagnostic testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2: a narrative review. Ann Intern Med. 172:726–34. DOI: 10.7326/M20-1301. PMID: 32282894. PMCID: PMC7170415.3. Rothe C, Schunk M, Sothmann P, Bretzel G, Froeschl G, Wallrauch C, et al. 2020; Transmission of 2019-nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. N Engl J Med. 382:970–1. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2001468. PMID: 32003551. PMCID: PMC7120970.
Article4. Tang YW, Schmitz JE, Persing DH, Stratton CW. 2020; Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19: current issues and challenges. J Clin Microbiol. 58:e00512–20. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00512-20. PMID: 32245835. PMCID: PMC7269383.
Article5. Kim YJ, Sung H, Ki CS, Hur M. 2020; COVID-19 testing in South Korea: current status and the need for faster diagnostics. Ann Lab Med. 40:349–50. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.5.349. PMID: 32237287. PMCID: PMC7169622.
Article6. Sung H, Yoo CK, Han MG, Lee SW, Lee H, Chun S, et al. 2020; Preparedness and rapid implementation of external quality assessment helped quickly increase COVID-19 testing capacity in the Republic of Korea. Clin Chem. 66:979–81. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa097. PMID: 32321159. PMCID: PMC7188181.
Article7. Hong KH, Lee SW, Kim TS, Huh HJ, Lee J, Kim SY, et al. 2020; Guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 40:351–60. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.5.351. PMID: 32237288. PMCID: PMC7169629.
Article8. Lee YJ, Lim Y, Hur KW, Sung H, Kim MN. 2020; Quality of ribonucleic acid extraction for real-time reverse transcription-PCR (rRT-PCR) of SARS-CoV-2: importance of internal control monitoring. Ann Lab Med. 40:490–2. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.6.490. PMID: 32539306.
Article9. Sung H, Roh KH, Hong KH, Seong MW, Ryoo N, Kim HS, et al. 2020; COVID-19 molecular testing in Korea: practical essentials and answers from experts based on experiences of emergency use authorization assays. Ann Lab Med. 40:439–47. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.6.439. PMID: 32539299.
Article10. Lee MK, Kim S, Kim MN, Kweon OJ, Lim YK, Ki CS, et al. 2016; Survey of clinical laboratory practices for 2015 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus outbreak in the Republic of Korea. Ann Lab Med. 36:154–61. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.154. PMID: 26709263. PMCID: PMC4713849.
Article11. Zhao H, Green H, Lackenby A, Donati M, Ellis J, Thompson C, et al. 2014; A new laboratory-based surveillance system (Respiratory DataMart System) for influenza and other respiratory viruses in England: results and experience from 2009 to 2012. Euro Surveill. 19:20680. DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES2014.19.3.20680. PMID: 24480060.
Article12. Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, Lu R, Han K, Wu G, et al. 2020; Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA. 323:1843–4. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.3786. PMID: 32159775. PMCID: PMC7066521.
Article13. Pan Y, Zhang D, Yang P, Poon LLM, Wang Q. 2020; Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect Dis. 20:411–2. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30113-4.
Article14. Lin C, Xiang J, Yan M, Li H, Huang S, Shen C. 2020; Comparison of throat swabs and sputum specimens for viral nucleic acid detection in 52 cases of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)-infected pneumonia (COVID-19). Clin Chem Lab Med. 58:1089–94. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2020-0187. PMID: 32301745.
Article15. Mohammadi A, Esmaeilzadeh E, Li Y, Bosch RJ, Li JZ. 2020; SARS-CoV-2 detection in different respiratory sites: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EBioMedicine. 59:102903. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102903. PMID: 32718896. PMCID: PMC7380223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical implications of coronavirus disease 2019 in neonates
- Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Early Stage of Outbreak
- Response Guidelines for Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Newborn Infants: A 2021 Update
- Comparison Study of Molecular Diagnostic Reagents for COVID-19 Pooling Test
- Response Guidelines for Newborn Infants Born to Mothers with Suspected or Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019