J Korean Soc Matern Child Health.
2021 Jul;25(3):162-168. 10.21896/jksmch.2021.25.3.162.
Response Guidelines for Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Newborn Infants: A 2021 Update
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2518919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21896/jksmch.2021.25.3.162
Abstract
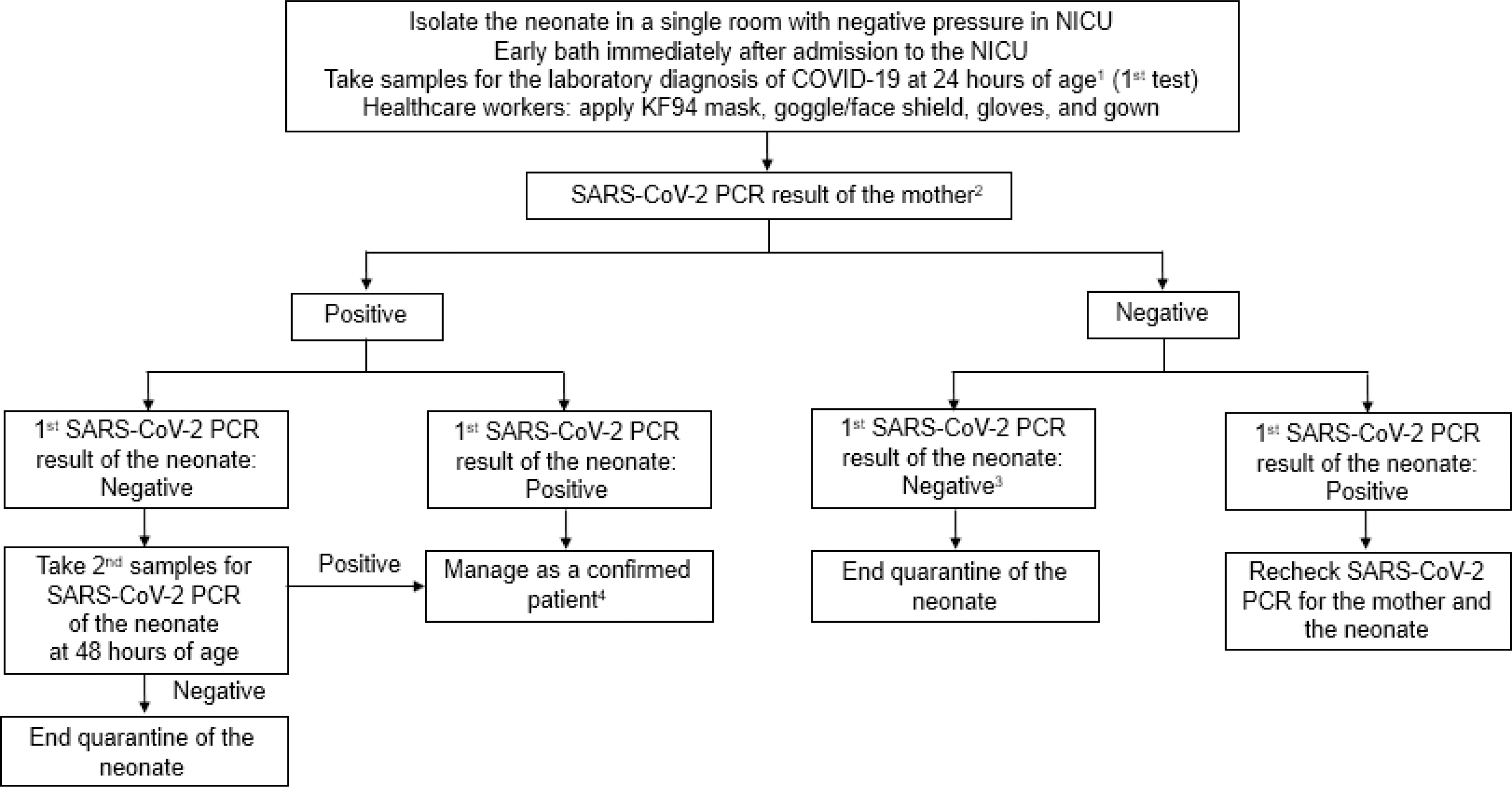
- Since the first report of neonatal case on March 29, 2020, a small number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases in newborn infants have been reported in Korea. The COVID-19 pandemic in Korea has urged the development of response guidelines for newborn infants born to mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19. These guidelines have been revised following further updates on COVID-19. The Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and the Korean Society of Neonatology issued updated guidelines for COVID-19 in newborn infants on December 31, 2020. The present review introduces the management of newborn infants born to mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, based on current updated guidelines for COVID-19. The management includes infection precautions for healthcare workers, neonatal resuscitation, neonatal isolation and medical care, breastfeeding, testing for COVID-19, and mother/baby contact.
Figure
Reference
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Breastfeeding and caring for newborns [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): CDC;2021. [cited 2021 Jun 8]. Available from:. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-pre-cautions/pregnancy-breastfeeding.html.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Evaluation and management considerations for neonates at risk for COVID–19 [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): CDC;2020. [cited 2021 Jun 7]. Available from:. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/caring-for-newborns.html.Cha HH., Seong WJ. Coronavirus disease 2019 and pregnancy. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2021. 25:10–20.
ArticleChandrasekharan P., Vento M., Trevisanuto D., Partridge E., Underwood MA., Wiedeman J, et al. Neonatal resuscitation and postresuscitation care of infants born to mothers with suspected or confirmed SARS–CoV–2 infection. Am J Perinatol. 2020. 37:813–24.
ArticleCook J., Harman K., Zoica B., Verma A., D'Silva P., Gupta A. Horizontal transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 to a premature infant: multiple organ injury and association with markers of inflammation. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020. 4:548–51.
ArticleHan MS., Seong MW., Heo EY., Park JH., Kim N., Shin S, et al. Sequential analysis of viral load in a neonate and her mother infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. 71:2236–9.
ArticleHopwood AJ., Jordan–Villegas A., Gutierrez LD., Cowart MC., Vega–Montalvo W., Cheung WL, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus–2 pneumonia in a newborn treated with remdesivir and coronavirus disease 2019 convalescent plasma. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021. 10:691–4.
ArticleKim DH. Response guidelines for newborn infants born to mothers with suspected or confirmed coronavirus disease 2019. Neonatal Med. 2020. 27:45–50.
ArticleKim KH., Cho EY., Kim DH., Kim HW., Park JY., Eun BW, et al. Guidelines for coronavirus disease 2019 response in children and adolescents. Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2020. 27:24–34.
ArticleKorea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease (COVID–19) response guidelines 9–4th edition [Internet]. Sejong (Korea): Ministry of Health and Welfare;2020. [cited 2021 Jun 7]. Available from:. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/.Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Coronavirus Disease–19 in Republic of Korea, as of 15 July, 2021. Cheongju (Korea): Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency;2021. [cited 2021 Jul 15]. Available from:. http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/.Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. COVID–19 response guidelines (newborn, infant, child and adolescent) [Internet]. Seoul (Korea): Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases;2020. [cited 2021 Jun 7]. Available from:. http://www.kspid.or.kr/.Salvatore CM., Han JY., Acker KP., Tiwari P., Jin J., Brandler M, et al. Neonatal management and outcomes during the COVID–19 pandemic: an observation cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020. 4:721–7.
ArticleSankaran D., Nakra N., Cheema R., Blumberg D., Lakshminrusimha S. Perinatal SARS–CoV–2 infection and neonatal COVID–19: a 2021 update. Neoreviews. 2021. 22:e284–95.
ArticleShalish W., Lakshminrusimha S., Manzoni P., Keszler M., Sant'-Anna GM. COVID–19 and neonatal respiratory care: current evidence and practical approach. Am J Perinatol. 2020. 37:780–91.
ArticleSwann OV., Holden KA., Turtle L., Pollock L., Fairfield CJ., Drake TM, et al. Clinical characteristics of children and young people admitted to hospital with covid–19 in United Kingdom: prospective multicentre observational cohort study. BMJ. 2020. 370:m3249.
ArticleWalker KF., O'Donoghue K., Grace N., Dorling J., Comeau JL., Li W, et al. Maternal transmission of SARS–COV–2 to the neonate, and possible routes for such transmission: a systematic review and critical analysis. BJOG. 2020. 127:1324–36.
ArticleWardell H., Campbell JI., VanderPluym C., Dixit A. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in febrile neonates. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2020. 9:630–5.
ArticleWorld Health Organization. Breastfeeding and COVID–19 [Internet]. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization;2020. [cited 2021 Jun 8]. Available from:. https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/breastfeeding-and-covid-19.World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID–19) dashboard [Internet]. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization;2021. [cited 2021 Jul 15]. Available from:. https://covid19.who.int/.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Response Guidelines for Newborn Infants Born to Mothers with Suspected or Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Coronavirus Disease 2019-Liver InjuryLiterature Review and Guidelines Based on the Recommendations of Hepatological Societies
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Pregnancy
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-Associated Urogenital Disease: A Current Update
- Current laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019