Restor Dent Endod.
2020 Nov;45(4):e54. 10.5395/rde.2020.45.e54.
Effects of zinc oxide and calcium–doped zinc oxide nanocrystals on cytotoxicity and reactive oxygen species production in different cell culture models
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Uberlândia, Uberlândia, MG, Brazil
- 2Functional and New Nanostructured Materials Laboratory, Physics Institute, Federal University of Alagoas, Maceió, AL, Brazil
- 3Institute of Chemistry, Federal University of Uberlândia, Uberlândia, MG, Brazil
- 4Department of Pediatric Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Uberlândia, Uberlândia, MG, Brazil
- KMID: 2512045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e54
Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to synthesize nanocrystals (NCs) of zinc oxide (ZnO) and calcium ion (Ca2+ )-doped ZnO with different percentages of calcium oxide (CaO), to evaluate cytotoxicity and to assess the effects of the most promising NCs on cytotoxicity depending on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation.
Materials and Methods
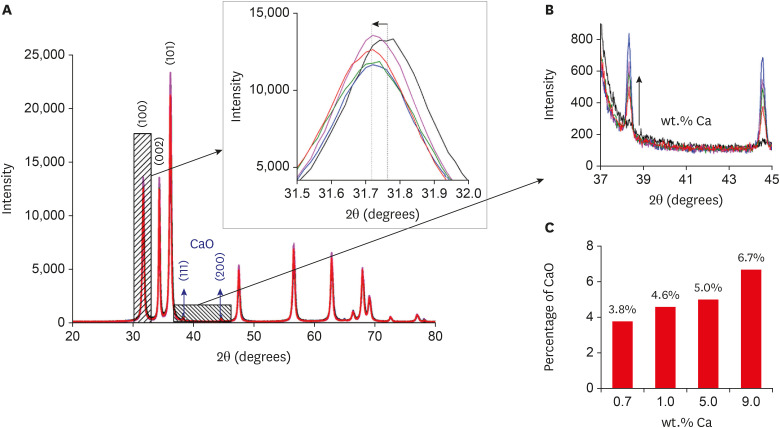
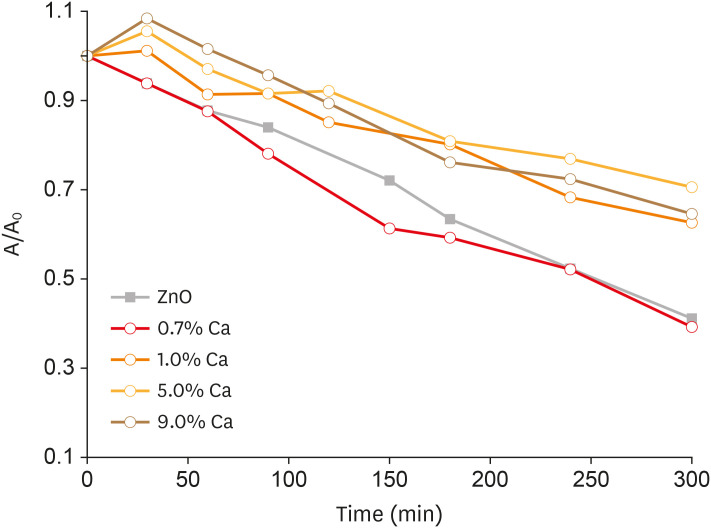
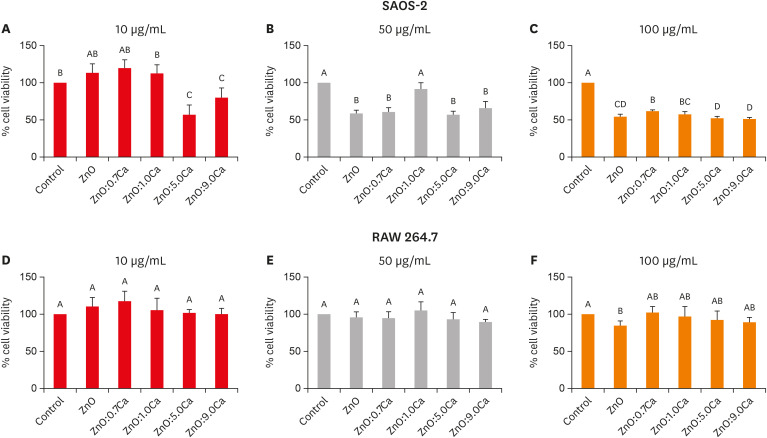
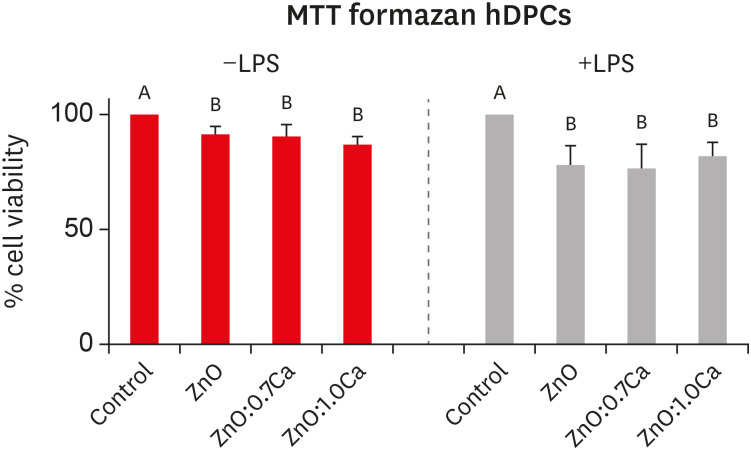
Nanomaterials were synthesized (ZnO and ZnO:xCa, x = 0.7; 1.0; 5.0; 9.0) and characterized using X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and methylene blue degradation. SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7 were treated with NCs, and evaluated for viability using the MTT assay. NCs with lower cytotoxicity were maintained in contact with LPS-stimulated (+LPS) and nonstimulated (−LPS) human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). Cell viability, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were evaluated.Cells kept in culture medium or LPS served as negative and positive controls, respectively. One-way analysis of variance and the Dunnett test (α = 0.05) were used for statistical testing.
Results
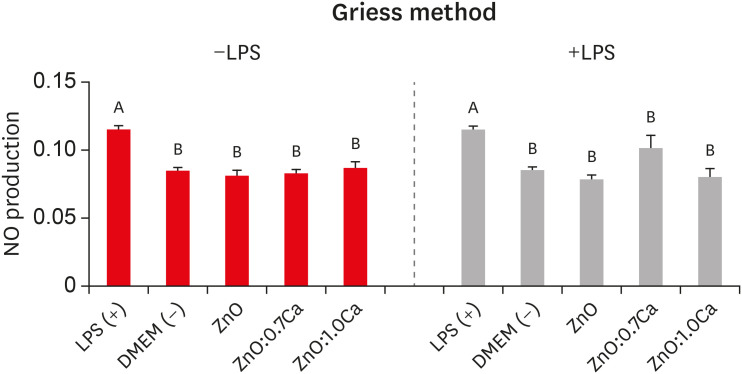
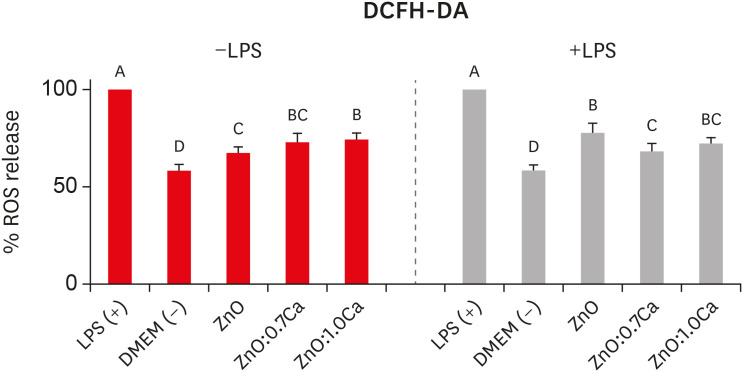
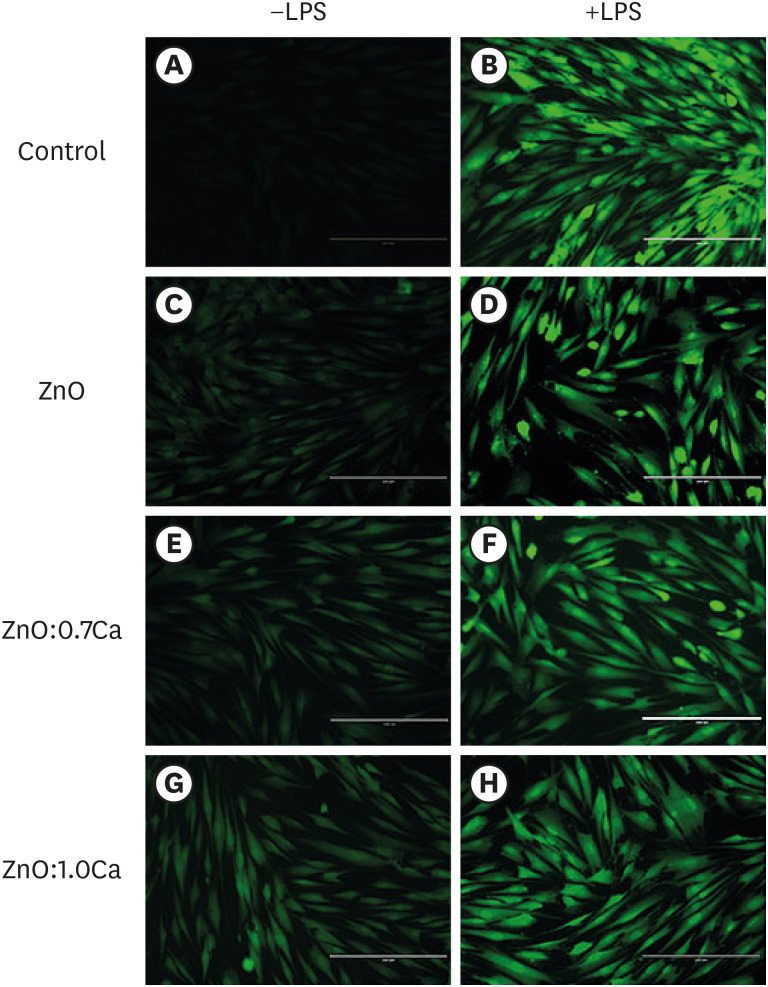
ZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca at 10 µg/mL were not cytotoxic to SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7. +LPS and −LPS hDPCs treated with ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca, and ZnO:1.0Ca presented similar NO production to negative control (p > 0.05) and lower production compared to positive control (p < 0.05). All NCs showed reduced ROS production compared with the positive control group both in +LPS and −LPS cells (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
NCs were successfully synthesized. ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca presented the highest percentages of cell viability, decreased ROS and NO production in +LPS cells, and maintenance of NO production at basal levels.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restor Dent Endod. 2022;47(4):e38. doi: 10.5395/rde.2022.47.e38.
Reference
-
1. Cohenca N, Paranjpe A, Berg J. Vital pulp therapy. Dent Clin North Am. 2013; 57:59–73. PMID: 23174610.
Article2. Landsiedel R, Fabian E, Ma-Hock L, van Ravenzwaay B, Wohlleben W, Wiench K, Oesch F. Toxico-/biokinetics of nanomaterials. Arch Toxicol. 2012; 86:1021–1060. PMID: 22576463.
Article3. Silva AC, Dantas NO, Silva MJ, Spanó MA, Goulart LR. Functional nanocrystals: towards biocompatibility, nontoxicity and biospecificity. In : Shrestha R, editor. Advances in biochemistry & applications in medicine. Las Vegas, NV: Open Access eBooks;2017. p. 1–27.4. Costa e Silva LL, Cosme-Silva L, Sakai VT, Lopes CS, da Silveira AP, Moretti Neto RT, Gomes-Filho JE, Oliveira TM, da Silveira Moretti AB. Comparison between calcium hydroxide mixtures and mineral trioxide aggregate in primary teeth pulpotomy: a randomized controlled trial. J Appl Oral Sci. 2019; 27:e20180030. PMID: 31116277.
Article5. de Melo Reis É, de Rezende AA, Santos DV, de Oliveria PF, Nicolella HD, Tavares DC, Silva AC, Dantas NO, Spanó MA. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of two zinc oxide sources (amorphous and nanoparticles) using the in vitro micronucleus test and the in vivo wing somatic mutation and recombination test. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015; 84:55–63. PMID: 26190540.6. Das M, Saxena N, Dwivedi PD. Emerging trends of nanoparticles application in food technology: safety paradigms. Nanotoxicology. 2009; 3:10–18.
Article7. Silva AC, Silva MJ, da Luz FA, Silva DP, de Deus SL, Dantas NO. Controlling the cytotoxicity of CdSe magic-sized quantum dots as a function of surface defect density. Nano Lett. 2014; 14:5452–5457. PMID: 25162369.
Article8. Valdiglesias V, Kiliç G, Costa C, Fernández-Bertólez N, Pásaro E, Teixeira JP, Laffon B. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles: cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, developmental toxicity, and neurotoxicity. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2015; 56:125–148. PMID: 25209650.
Article9. Pilownic KJ, Gomes AP, Wang ZJ, Almeida LH, Romano AR, Shen Y, Felix AO, Haapasalo M, Pappen FG. Physicochemical and biological evaluation of endodontic filling materials for primary teeth. Braz Dent J. 2017; 28:578–586. PMID: 29215682.
Article10. Gonzalez-Lara A, Ruiz-Rodriguez MS, Pierdant-Perez M, Garrocho-Rangel JA, Pozos-Guillen AJ. Zinc oxide–eugenol pulpotomy in primary teeth: a 24-month follow-up. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016; 40:107–112. PMID: 26950810.
Article11. Söderberg TA, Sunzel B, Holm S, Elmros T, Hallmans G, Sjöberg S. Antibacterial effect of zinc oxide in vitro . Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 1990; 24:193–197. PMID: 2281305.12. Lipovsky A, Nitzan Y, Gedanken A, Lubart R. Antifungal activity of ZnO nanoparticles--the role of ROS mediated cell injury. Nanotechnology. 2011; 22:105101. PMID: 21289395.
Article13. Xia T, Zhao Y, Sager T, George S, Pokhrel S, Li N, Schoenfeld D, Meng H, Lin S, Wang X, Wang M, Ji Z, Zink JI, Mädler L, Castranova V, Lin S, Nel AE. Decreased dissolution of ZnO by iron doping yields nanoparticles with reduced toxicity in the rodent lung and zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano. 2011; 5:1223–1235. PMID: 21250651.
Article14. Silva AC, Zóia MA, Correia LI, Azevedo FV, Paula AT, Maia LP, Carvalho LS, Carvalho LN, Costa MP, Giaretta LC, Rodrigues RS, Ávila VM, Goulart LR, Dantas NO. Biocompatibility of doped semiconductors nanocrystals and nanocomposites. In : Askin Celik T, editor. Cytotoxicity. London: IntechOpen;2018. p. 149–161.15. Adeleye AS, Pokhrel S, Mädler L, Keller AA. Influence of nanoparticle doping on the colloidal stability and toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in synthetic and natural waters. Water Res. 2018; 132:12–22. PMID: 29304444.
Article16. Karthikeyan B, Pandiyarajan T, Mangaiyarkarasi K. Optical properties of sol-gel synthesized calcium doped ZnO nanostructures. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2011; 82:97–101. PMID: 21852189.
Article17. Haja Hameed AS, Karthikeyan C, Sasikumar S, Senthil Kumar V, Kumaresan S, Ravi G. Impact of alkaline metal ions Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ on the structural, optical, thermal and antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J Mater Chem B. 2013; 1:5950–5962. PMID: 32261062.
Article18. Montoro LA, Turrioni AP, Basso FG, de Souza Costa CA, Hebling J. Infrared LED irradiation photobiomodulation of oxidative stress in human dental pulp cells. Int Endod J. 2014; 47:747–755. PMID: 24215116.
Article19. Babele PK, Thakre PK, Kumawat R, Tomar RS. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity by affecting cell wall integrity pathway, mitochondrial function and lipid homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chemosphere. 2018; 213:65–75. PMID: 30212720.
Article20. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983; 65:55–63. PMID: 6606682.
Article21. Honegger P. Overview of cell and tissue culture techniques. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2001; Chapter 12:Unit12.1.
Article22. Wei S, Zhang G, Xu X. Activating BaTaO 2 N by Ca modifications and cobalt oxide for visible light photocatalytic water oxidation reactions. Appl Catal B. 2018; 237:373–381.
Article23. Das BK, Verma SK, Das T, Panda PK, Parashar K, Suar M, Parashar SK. Altered electrical properties with controlled copper doping in ZnO nanoparticles infers their cytotoxicity in macrophages by ROS induction and apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2019; 297:141–154. PMID: 30419219.
Article24. Wójcik-Piotrowicz K, Kaszuba-Zwoińska J, Rokita E, Thor P. Cell viability modulation through changes of Ca2+-dependent signalling pathways. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016; 121:45–53. PMID: 26777586.
Article25. Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 4:517–529. PMID: 12838335.
Article26. Meng F, Liu Y, Wang J, Tan X, Sun H, Liu S, Wang S. Temperature dependent photocatalysis of g-C3N4, TiO2 and ZnO: differences in photoactive mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018; 532:321–330. PMID: 30096526.
Article27. Yang S, Xu CY, Zhang BY, Yang L, Hu SP, Zhen L. Ca(II) doped β-In2 S3 hierarchical structures for photocatalytic hydrogen generation and organic dye degradation under visible light irradiation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017; 491:230–237. PMID: 28038395.
Article28. Li C, Hu R, Zhou T, Wu H, Song K, Liu X, Wang R. Special morphologies of Mg, Ca, and Y-doped ZnO/La2O3 composite for photocatalysis. Mater Lett. 2014; 124:81–84.
Article29. Rodríguez-Lozano FJ, Bueno C, Insausti CL, Meseguer L, Ramírez MC, Blanquer M, Marín N, Martínez S, Moraleda JM. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues. Int Endod J. 2011; 44:800–806. PMID: 21477154.
Article30. Wang X, Sha XJ, Li GH, Yang FS, Ji K, Wen LY, Liu SY, Chen L, Ding Y, Xuan K. Comparative characterization of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2012; 57:1231–1240. PMID: 22455989.
Article31. Lai WY, Kao CT, Hung CJ, Huang TH, Shie MY. An evaluation of the inflammatory response of lipopolysaccharide-treated primary dental pulp cells with regard to calcium silicate-based cements. Int J Oral Sci. 2014; 6:94–98. PMID: 24556955.
Article32. Kim DH, Jang JH, Lee BN, Chang HS, Hwang IN, Oh WM, Kim SH, Min KS, Koh JT, Hwang YC. Anti-inflammatory and mineralization effects of ProRoot MTA and Endocem MTA in studies of human and rat dental pulps in vitro and in vivo . J Endod. 2018; 44:1534–1541. PMID: 30174104.
Article33. Kim JC, Lee YH, Yu MK, Lee NH, Park JD, Bhattarai G, Yi HK. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of PPARγ on LPS-induced pulp cells: role of the ROS removal activity. Arch Oral Biol. 2012; 57:392–400. PMID: 21996491.
Article34. Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H, Moilanen E. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005; 4:471–479. PMID: 16101524.
Article35. Min KS, Hwang YH, Ju HJ, Chang HS, Kang KH, Pi SH, Lee SK, Lee SK, Kim EC. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates cytoprotection against nitric oxide-induced cytotoxicity via the cGMP pathway in human pulp cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 102:803–808. PMID: 17138185.
Article36. El-Hussein A, Hamblin MR. ROS generation and DNA damage with photo-inactivation mediated by silver nanoparticles in lung cancer cell line. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017; 11:173–178. PMID: 28477000.
Article37. Zhang J, Song W, Guo J, Zhang J, Sun Z, Ding F, Gao M. Toxic effect of different ZnO particles on mouse alveolar macrophages. J Hazard Mater. 2012; 219-220:148–155. PMID: 22521135.
Article38. Zhang R, Liu X, Xiong Z, Huang Q, Yang X, Yan H, Ma J, Feng Q, Shen Z. The immunomodulatory effects of Zn-incorporated micro/nanostructured coating in inducing osteogenesis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 46:1123–1130. PMID: 29517404.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
- Oxidative Stress; Reactive Oxygen Species and Nitric Oxide
- Antibacterial properties of composite resins incorporating silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus
- Effect of High Glucose on the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species in Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Regulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells