Restor Dent Endod.
2020 Nov;45(4):e48. 10.5395/rde.2020.45.e48.
Reference values for pulp oxygen saturation as a diagnostic tool in endodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endodontics, Graduate Program in Dentistry, Universidade Luterana do Brasil (ULBRA), Canoas, RS, Brazil
- 2Department of Endodontics, Faculdade Meridional (IMED) School of Dentistry, Passo Fundo, RS, Brazil
- 3Department of Oral Diagnostic, Graduate Program in Dentistry, Universidade Luterana do Brasil (ULBRA), Canoas, RS, Brazil
- 4Department of Operative Dentistry, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) School of Dentistry, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
- 5Department of Endodontics, Graduate Program in Dentistry, Universidade Federal de Goiás (UFG), Goiania, GO, Brazil
- KMID: 2512039
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e48
Abstract
Objectives
This systematic review aimed to identify mean oxygen saturation values (SpO2 ) using pulse oximetry in permanent maxillary anterior teeth.
Materials and Methods
The MEDLINE, Scientific Electronic Library Online, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, and Literatura Latino Americana em Ciências da Saúde electronic databases were searched. Combinations and variations of “oximetry” AND “dental pulp test” were used as search terms. Studies reporting means and standard deviations of SpO2 values were included. Two reviewers independently extracted data following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic, and all analyses were performed using R software. Study quality was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
Results
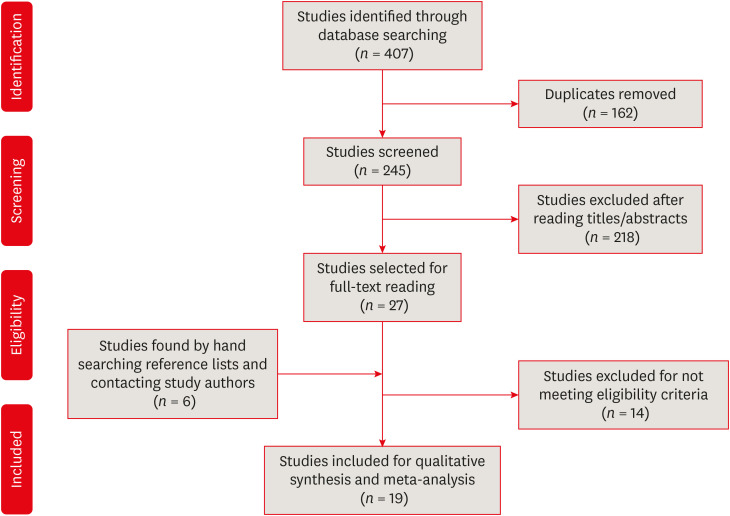
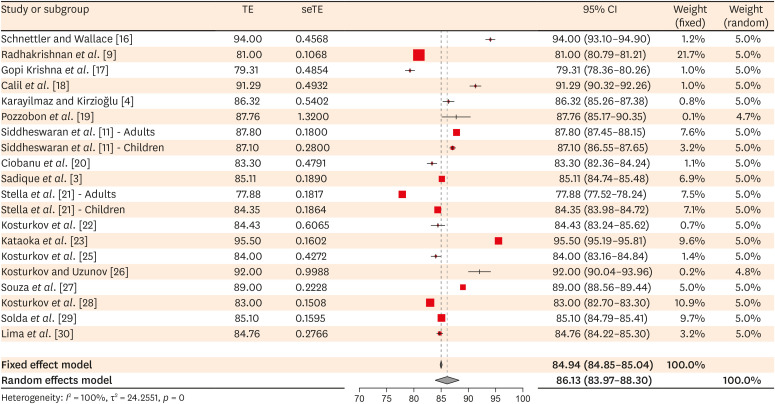
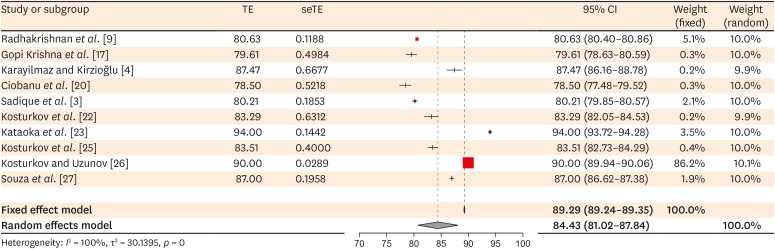
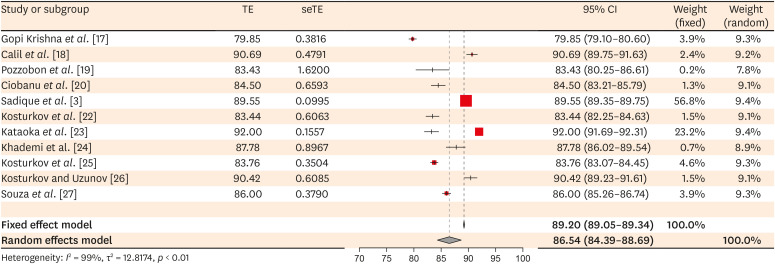
Of the 251 studies identified, 19 met the eligibility criteria and were included (total sample, 4,541 teeth). In the meta-analysis, the mean SpO2 values were 84.94% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84.85%–85.04%) for the central incisors, 89.29% (95% CI, 89.22%– 89.35%) for the lateral incisors, and 89.20% (95% CI, 89.05%–89.34%) for the canines. The studies were predominantly low-quality due to the high risk of bias associated with the index test, unclear risk regarding patient selection, and concerns about outcome assessment.
Conclusions
Although most studies were low-quality, the oxygen saturation levels in normal pulp could be established (minimum saturation, 77.52%). Despite the risk of bias of the included studies, the reference values reported herein are clinically relevant for assessments of changes in pulp status.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kataoka SH, Setzer FC, Gondim-Junior E, Pessoa OF, Gavini G, Caldeira CL. Pulp vitality in patients with intraoral and oropharyngeal malignant tumors undergoing radiation therapy assessed by pulse oximetry. J Endod. 2011; 37:1197–1200. PMID: 21846533.
Article2. Setzer FC, Kataoka SH, Natrielli F, Gondim-Junior E, Caldeira CL. Clinical diagnosis of pulp inflammation based on pulp oxygenation rates measured by pulse oximetry. J Endod. 2012; 38:880–883. PMID: 22703647.
Article3. Sadique M, Ravi SV, Thomas K, Dhanapal P, Simon EP, Shaheen M. Evaluation of efficacy of a pulse oximeter to assess pulp vitality. J Int Oral Health. 2014; 6:70–72. PMID: 25083036.4. Karayilmaz H, Kirzioğlu Z. Comparison of the reliability of laser Doppler flowmetry, pulse oximetry and electric pulp tester in assessing the pulp vitality of human teeth. J Oral Rehabil. 2011; 38:340–347. PMID: 20868433.
Article5. Mejàre IA, Axelsson S, Davidson T, Frisk F, Hakeberg M, Kvist T, Norlund A, Petersson A, Portenier I, Sandberg H, Tranaeus S, Bergenholtz G. Diagnosis of the condition of the dental pulp: a systematic review. Int Endod J. 2012; 45:597–613. PMID: 22329525.
Article6. Giovanella LB, Barletta FB, Felippe WT, Bruno KF, de Alencar AH, Estrela C. Assessment of oxygen saturation in dental pulp of permanent teeth with periodontal disease. J Endod. 2014; 40:1927–1931. PMID: 25282376.
Article7. Gopikrishna V, Tinagupta K, Kandaswamy D. Comparison of electrical, thermal, and pulse oximetry methods for assessing pulp vitality in recently traumatized teeth. J Endod. 2007; 33:531–535. PMID: 17437866.
Article8. Bruno KF, Barletta FB, Felippe WT, Silva JA, Gonçalves de Alencar AH, Estrela C. Oxygen saturation in the dental pulp of permanent teeth: a critical review. J Endod. 2014; 40:1054–1057. PMID: 25069907.
Article9. Radhakrishnan S, Munshi AK, Hegde AM. Pulse oximetry: a diagnostic instrument in pulpal vitality testing. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2002; 26:141–145. PMID: 11874005.
Article10. Estrela C, Oliveira KS, Alencar AH, Barletta FB, Estrela CR, Felippe WT. Oxygen saturation in the dental pulp of maxillary and mandibular molars – Part 2. Braz Dent J. 2017; 28:704–709. PMID: 29211125.
Article11. Siddheswaran V, Adyanthaya R, Shivanna V. Pulse oximetry: a diagnostic instrument in pulpal vitality testing—An in vivo study. World J Dent. 2011; 2:225–230.
Article12. Dastmalchi N, Jafarzadeh H, Moradi S. Comparison of the efficacy of a custom-made pulse oximeter probe with digital electric pulp tester, cold spray, and rubber cup for assessing pulp vitality. J Endod. 2012; 38:1182–1186. PMID: 22892732.
Article13. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097. PMID: 19621072.
Article14. Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA, Bossuyt PM. QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 155:529–536. PMID: 22007046.
Article15. Modesti PA, Reboldi G, Cappuccio FP, Agyemang C, Remuzzi G, Rapi S, et al. Panethnic differences in blood pressure in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0147601. PMID: 26808317.
Article16. Schnettler JM, Wallace JA. Pulse oximetry as a diagnostic tool of pulpal vitality. J Endod. 1991; 17:488–490. PMID: 1812192.
Article17. Gopi Krishna V, Kandaswamy D, Gupta T. Assessment of the efficacy of an indigeniously developed pulse oximeter dental sensor holder for pulp vitality testing. Indian J Dent Res. 2006; 17:111–113. PMID: 17176825.
Article18. Calil E, Caldeira CL, Gavini G, Lemos EM. Determination of pulp vitality in vivo with pulse oximetry. Int Endod J. 2008; 41:741–746. PMID: 18554185.19. Pozzobon MH, de Sousa Vieira R, Alves AM, Reyes-Carmona J, Teixeira CS, de Souza BD, Felippe WT. Assessment of pulp blood flow in primary and permanent teeth using pulse oximetry. Dent Traumatol. 2011; 27:184–188. PMID: 21342436.
Article20. Ciobanu G, Ion I, Ungureanu L. Testing of pulp vitality by pulse oximetry. Odontology. 2012; 16:94–98.21. Stella JP, Barletta FB, Giovanella LB, Grazziotin-Soares R, Tovo MF, Felippe WT, Estrela C. Oxygen saturation in dental pulp of permanent teeth: difference between children/adolescents and adults. J Endod. 2015; 41:1445–1449. PMID: 26093471.
Article22. Kosturkov D, Uzunov TS, Grozdanova R, Ivancheva V. Evaluation of condition of the pulp by pulse oximetry. J Int Med Assoc Bulgaria. 2015; 21:1003–1007.
Article23. Kataoka SH, Setzer FC, Gondim-Junior E, Fregnani ER, Moraes CJ, Pessoa OF, Gavini G, Caldeira CL. Late effects of head and neck radiotherapy on pulp vitality assessed by pulse oximetry. J Endod. 2016; 42:886–889. PMID: 27071975.
Article24. Khademi AA, Shahtouri MM, Attar BM, Rikhtegaran N. Pulp vitality of maxillary canines after alveolar cleft bone grafting: pulse oximetry versus electric pulp test versus cold test. J Craniofac Surg. 2017; 7. 13. [Epub ahead of print].
Article25. Kosturkov D, Uzunov TS, Uzunova P. Pulse oximetry as a diagnostic tool in dental medicine. In : 19th International Conference and School on Quantum Electronics: Laser Physics and Applications; 2016 Sep 26–30; Sozopol, Bulgaria. Bellingham, WA: SPIE - International Society for Optics and Photonics;2017.26. Kosturkov D, Uzunov TS. Pulse oximetry and electric pulp test in intact teeth and teeth with hyperaemia pulpae. Acta Med Bulg. 2017; 44:10–13.
Article27. Souza SF, Thomaz EB, Costa CP. Healthy dental pulp oxygen saturation rates in subjects with homozygous sickle cell anemia: a cross-sectional study nested in a cohort. J Endod. 2017; 43:1997–2000. PMID: 29032814.
Article28. Kosturkov D, Uzunov T, Uzunova P. Influence of the gingival tissues on the measured saturation level of the dental pulp blood flow. Bulgarian J Chem Educ. 2018; 27:454–459.29. Solda C, Barletta FB, Vanni JR, Lambert P, Só MV, Estrela C. Effect of at-home bleaching on oxygen saturation levels in the dental pulp of maxillary central incisors. Braz Dent J. 2018; 29:541–546. PMID: 30517476.
Article30. Lima LF, de Alencar AH, Decurcio DA, Silva JA, Favarão IN, Loureiro MA, Barletta FB, Estrela C. Effect of dental bleaching on pulp oxygen saturation in maxillary central incisors - a randomized clinical trial. J Appl Oral Sci. 2019; 27:e20180442. PMID: 30994776.
Article31. Mainkar A, Kim SG. Diagnostic accuracy of 5 dental pulp tests: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endod. 2018; 44:694–702. PMID: 29571914.
Article32. Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M. Systematic reviews of observational studies. In : Egger M, Davey-Smith G, Altman D, editors. Systematic reviews in healthcare: meta-analysis in context. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons;2007. p. 211–227.33. Gopikrishna V, Tinagupta K, Kandaswamy D. Evaluation of efficacy of a new custom-made pulse oximeter dental probe in comparison with the electrical and thermal tests for assessing pulp vitality. J Endod. 2007; 33:411–414. PMID: 17368329.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part I. General Guidance and Tips
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part II. Statistical Methods of Meta-Analysis
- Dental age estimation using cone-beam computed tomography: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Usefulness of P(50,std) for the Diagnostic Work-up of Patients with Erythrocytosis
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis