Endocrinol Metab.
2020 Sep;35(3):647-655. 10.3803/EnM.2020.658.
Irisin Regulates the Functions of Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2508015
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.658
Abstract
- Background
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are known to play a fundamental role in the progression of liver fibrosis. Once HSCs are activated, they are involved in proliferation, migration, and contractility which are characteristics of liver fibrogenesis. Recent studies have shown that irisin, a myokine secreted during physical exercise, has a protective effect in various metabolic diseases, especially in renal fibrosis. However, whether irisin is involved in HSC activation and other processes associated with liver fibrosis has not yet been investigated. In this study, we reveal the role of irisin in HSC activation as well as in proliferation, migration, and contractile properties of HSCs in vitro.
Methods
LX-2 cells, immortalized human HSCs, were treated with transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), a core regulator of HSC fibrosis, with or without irisin, and markers of the aforementioned processes were analyzed. Further, an inflammatory response was stimulated with TGF-β1 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in combination with irisin and the expression of cytokines was measured.
Results
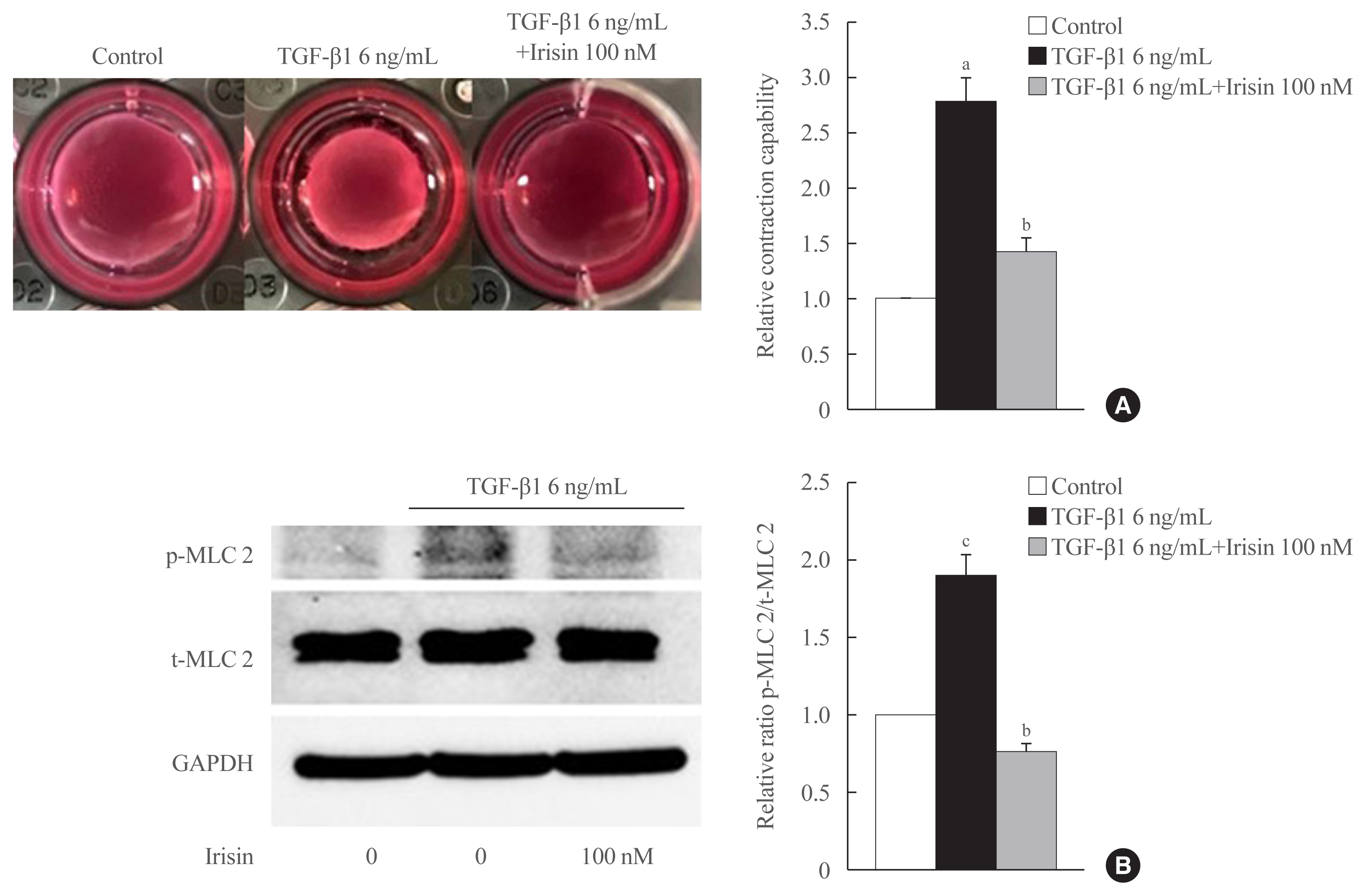
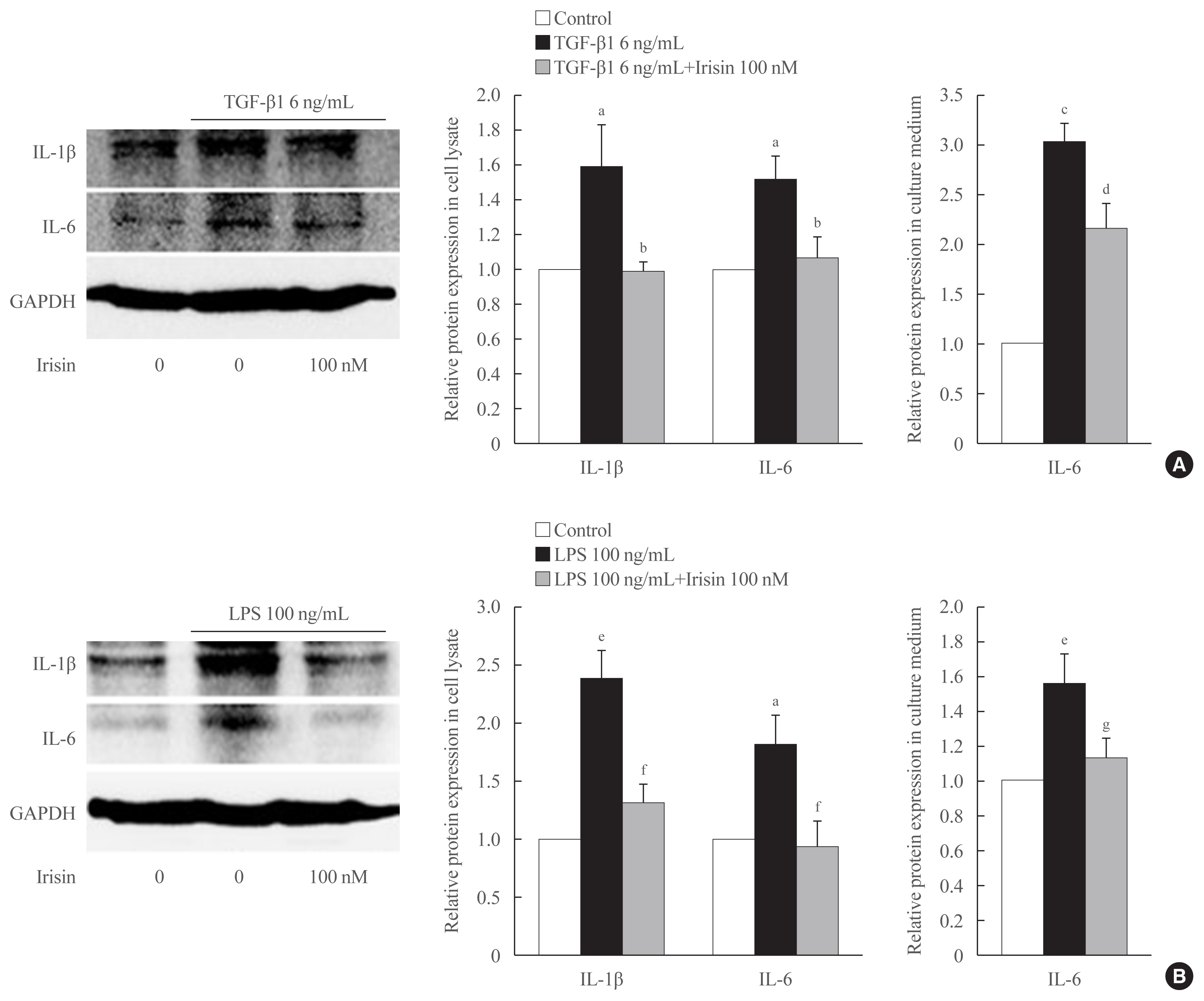
Recombinant irisin significantly suppressed the expression of TGF-β1-stimulated fibrosis markers including alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen type 1 alpha 1 and prevented the TGF-β1-induced proliferation, migration, and contractility of LX-2 cells. Additionally, irisin ameliorated the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-1β induced by TGF-β1 and LPS treatments.
Conclusion
These findings suggested that irisin potently improved the progression of hepatic fibrosis by regulating HSC activation, proliferation, migration, contractility, and HSC-mediated production of inflammatory cytokine.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Effects of Irisin on the Interaction between Hepatic Stellate Cell and Macrophage in Liver Fibrosis
Dinh Vinh Do, So Young Park, Giang Thi Nguyen, Dae Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):620-629. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1412.Irisin Attenuates Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrosis in Bile Duct Ligation Mice Model and Improves Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Thuy Linh Lai, So Young Park, Giang Nguyen, Phuc Thi Minh Pham, Seon Mee Kang, Jeana Hong, Jae-Ho Lee, Seung-Soon Im, Dae-Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(6):908-920. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1984.
Reference
-
1. Li J, Zhao YR, Tian Z. Roles of hepatic stellate cells in acute liver failure: from the perspective of inflammation and fibrosis. World J Hepatol. 2019; 11:412–20.
Article2. Yin C, Evason KJ, Asahina K, Stainier DY. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:1902–10.
Article3. Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev. 2008; 88:125–72.
Article4. Lee UE, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 25:195–206.
Article5. Aydın MM, Akcali KC. Liver fibrosis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018; 29:14–21.
Article6. Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S, Meindl-Beinker AN. TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis: updated 2019. Cells. 2019; 8:1419.
Article7. Dewidar B, Soukupova J, Fabregat I, Dooley S. TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis: updated. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2015; 3:291–305.
Article8. Fabregat I, Caballero-Diaz D. Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell plasticity in liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 2018; 8:357.
Article9. Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V, Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE, et al. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism. 2012; 61:1725–38.
Article10. Roca-Rivada A, Castelao C, Senin LL, Landrove MO, Baltar J, Belen Crujeiras A, et al. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60563.
Article11. Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481:463–8.
Article12. Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J; International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2020; 158:1999–2014.
Article13. Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, Efstathiadou ZA, Makras P, Perakakis N, Kountouras J, et al. Irisin in metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018; 59:260–74.
Article14. Xiong XQ, Chen D, Sun HJ, Ding L, Wang JJ, Chen Q, et al. FNDC5 overexpression and irisin ameliorate glucose/lipid metabolic derangements and enhance lipolysis in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1852:1867–75.
Article15. Perakakis N, Triantafyllou GA, Fernandez-Real JM, Huh JY, Park KH, Seufert J, et al. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017; 13:324–37.
Article16. Peng H, Wang Q, Lou T, Qin J, Jung S, Shetty V, et al. Myokine mediated muscle-kidney crosstalk suppresses metabolic reprogramming and fibrosis in damaged kidneys. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:1493.
Article17. Fabregat I, Moreno-Caceres J, Sanchez A, Dooley S, Dewidar B, Giannelli G, et al. TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. 2016; 283:2219–32.
Article18. Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:209–18.
Article19. Ezhilarasan D, Sokal E, Najimi M. Hepatic fibrosis: it is time to go with hepatic stellate cell-specific therapeutic targets. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018; 17:192–7.
Article20. Tacke F, Weiskirchen R. Update on hepatic stellate cells: pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel isolation techniques. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 6:67–80.
Article21. De Minicis S, Seki E, Uchinami H, Kluwe J, Zhang Y, Brenner DA, et al. Gene expression profiles during hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:1937–46.
Article22. Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007; 13:1324–32.23. Robert S, Gicquel T, Bodin A, Lagente V, Boichot E. Characterization of the MMP/TIMP imbalance and collagen production induced by IL-1β or TNF-α release from human hepatic stellate cells. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0153118.
Article24. Harvey SA, Dangi A, Tandon A, Gandhi CR. The transcriptomic response of rat hepatic stellate cells to endotoxin: implications for hepatic inflammation and immune regulation. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e82159.
Article25. Seki E, Tsutsui H, Nakano H, Tsuji N, Hoshino K, Adachi O, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-18 secretion from murine Kupffer cells independently of myeloid differentiation factor 88 that is critically involved in induction of production of IL-12 and IL-1beta. J Immunol. 2001; 166:2651–7.
Article26. Mazur-Bialy AI, Pochec E, Zarawski M. Anti-inflammatory properties of irisin, mediator of physical activity, are connected with TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18:701.
Article27. Crujeiras AB, Pardo M, Casanueva FF. Irisin: ‘fat’ or artefact. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015; 82:467–74.
Article28. Polyzos SA, Mathew H, Mantzoros CS. Irisin: a true, circulating hormone. Metabolism. 2015; 64:1611–8.
Article29. Polyzos SA, Mantzoros CS. An update on the validity of irisin assays and the link between irisin and hepatic metabolism. Metabolism. 2015; 64:937–42.
Article30. Liu S, Du F, Li X, Wang M, Duan R, Zhang J, et al. Effects and underlying mechanisms of irisin on the proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic β cells. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0175498.
Article31. Park MJ, Kim DI, Choi JH, Heo YR, Park SH. New role of irisin in hepatocytes: the protective effect of hepatic steatosis in vitro. Cell Signal. 2015; 27:1831–9.
Article32. Zhang Y, Li R, Meng Y, Li S, Donelan W, Zhao Y, et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes. 2014; 63:514–25.
Article33. Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M, Guerra E, Pardo G, Tinahones F, et al. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E769–78.
Article34. Tang H, Yu R, Liu S, Huwatibieke B, Li Z, Zhang W. Irisin inhibits hepatic cholesterol synthesis via AMPK-SREBP2 signaling. EBioMedicine. 2016; 6:139–48.
Article35. Zhou B, Ling L, Zhang F, Liu TY, Zhou H, Qi XH, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing 5 attenuates liver fibrosis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 48:227–36.
Article36. Petta S, Valenti L, Svegliati-Baroni G, Ruscica M, Pipitone RM, Dongiovanni P, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 rs3480 A>G polymorphism, irisin, and liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:2660–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Irisin on the Interaction between Hepatic Stellate Cell and Macrophage in Liver Fibrosis
- Irisin Attenuates Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrosis in Bile Duct Ligation Mice Model and Improves Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- Evaluation of the Relationships between Irisin Levels and Cognitive Functions in Individuals with Schizophrenia
- The Role of Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells in Liver Fibrosis, Portal Hypertension and Cancer Angiogenesis
- Role of cytoglobin, a novel radical scavenger, in stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrosis