Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Oct;52(4):1162-1177. 10.4143/crt.2020.138.
FGFR4 Gly388Arg Polymorphism Affects the Progression of Gastric Cancer by Activating STAT3 Pathway to Induce Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery and Institute of Clinical Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Tongchuan People's Hospital, Shanxi, China
- 3Department of Thyroid, and Breast Surgery, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang, China
- 4Department of Infectious Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 5Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- KMID: 2507942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2020.138
Abstract
- Purpose
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) plays a critical role in cancer progression involving in tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. This study clarified the role of FGFR4-Arg388 variant in gastric cancer (GC), and more importantly highlighted the possibility of this single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) as potential therapeutic targets.
Materials and Methods
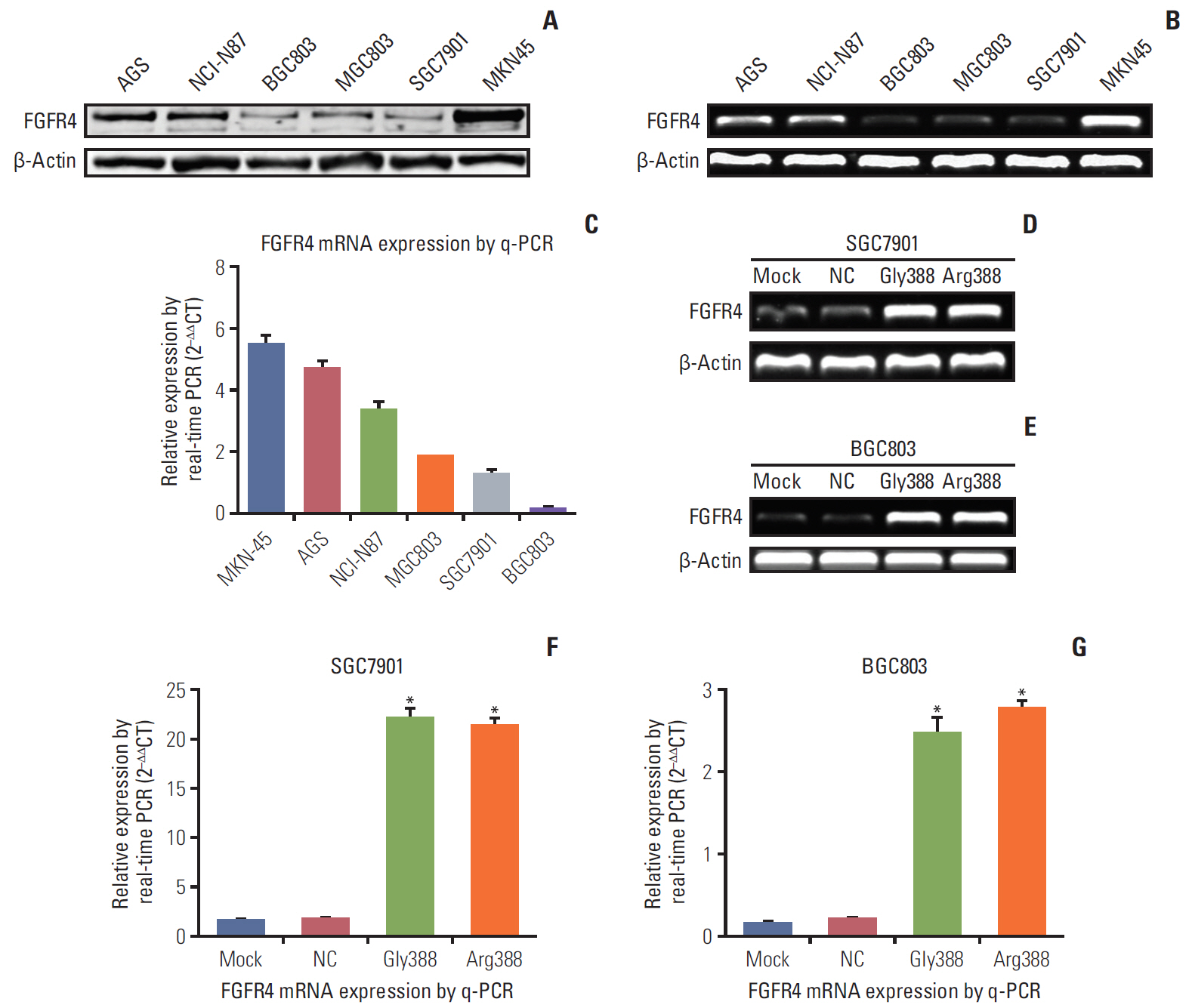
FGFR4 polymorphism was characterized in advanced GC patients to perform statistical analysis. FGFR4-dependent signal pathways involving cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and resistance to oxaliplatin (OXA) in accordance with the SNP were also assessed in transfected GC cell lines.
Results
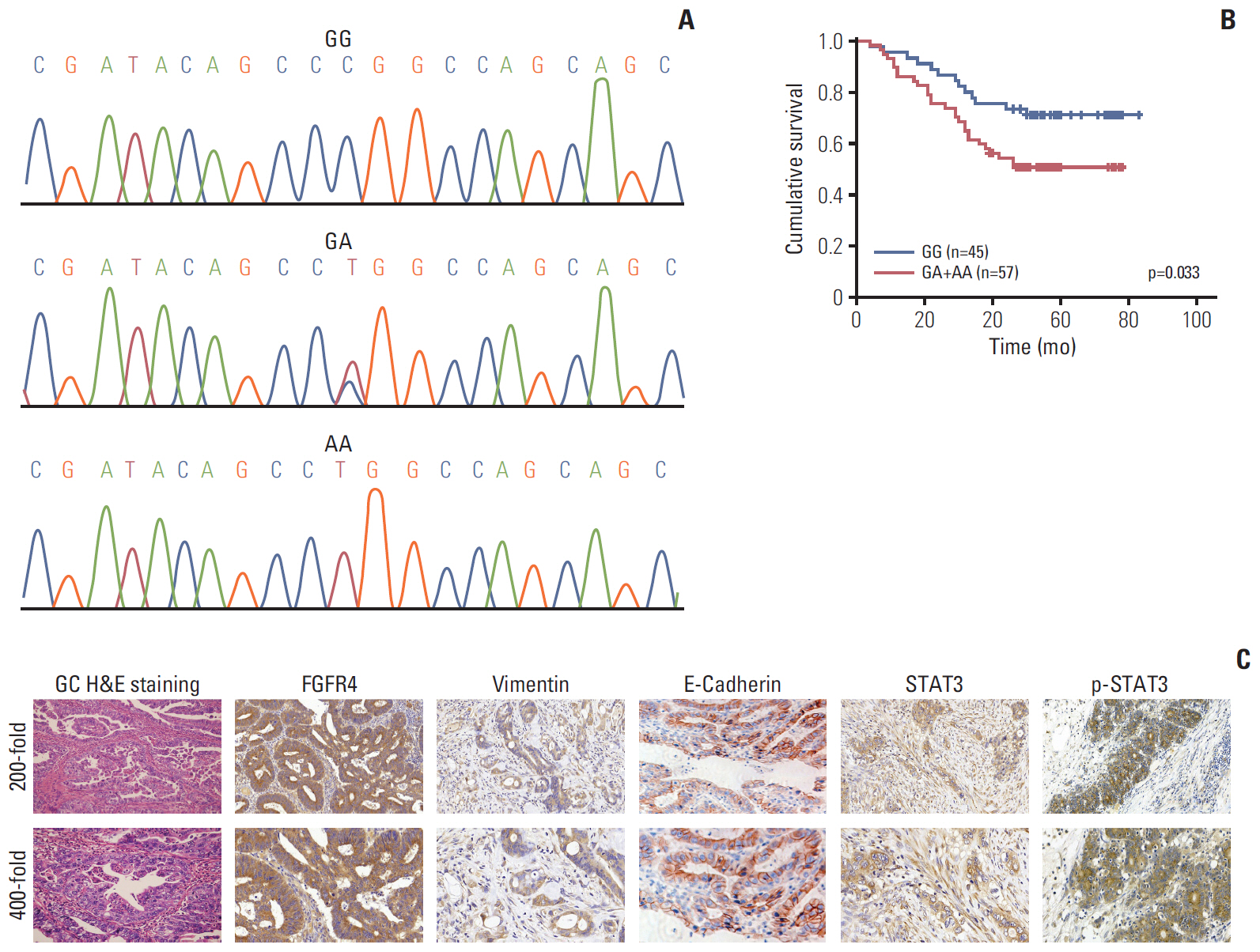
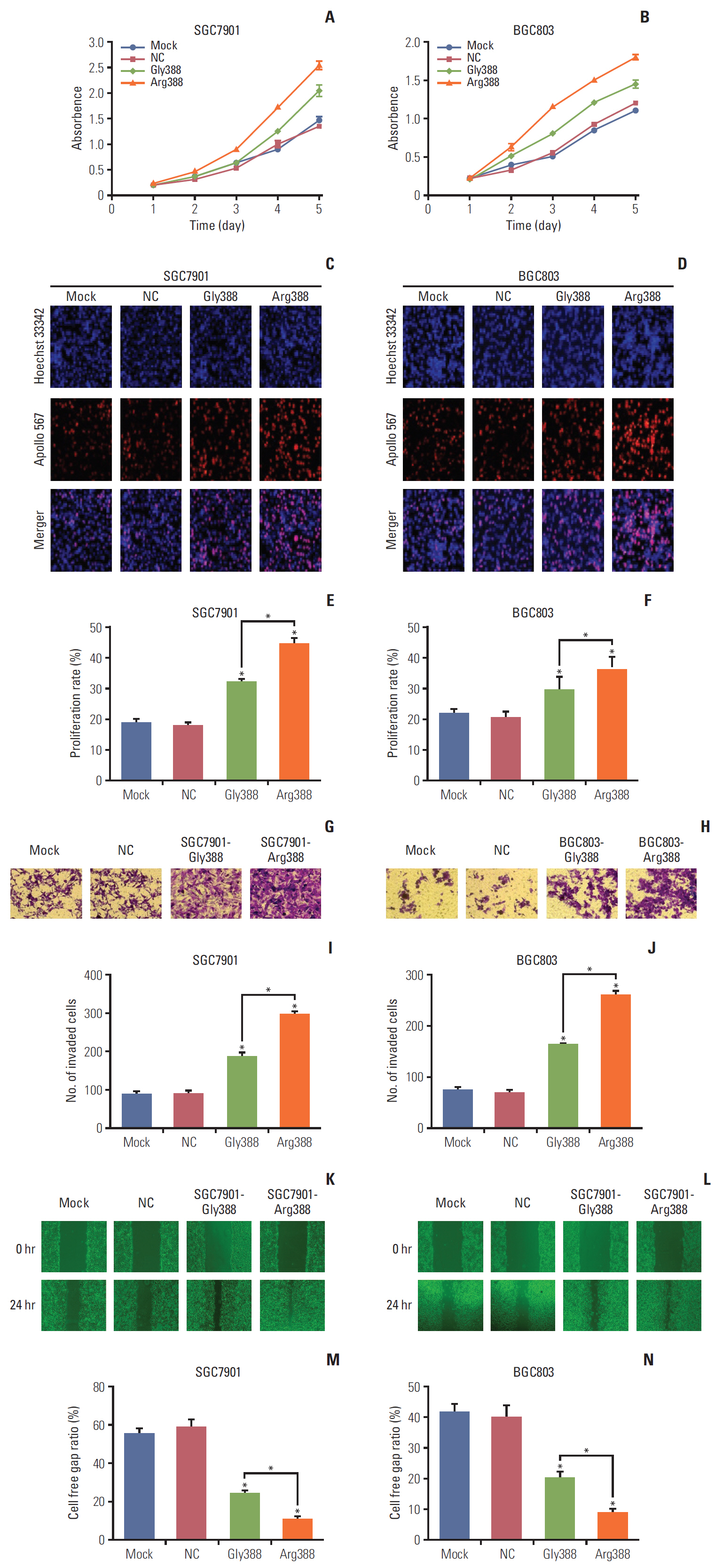
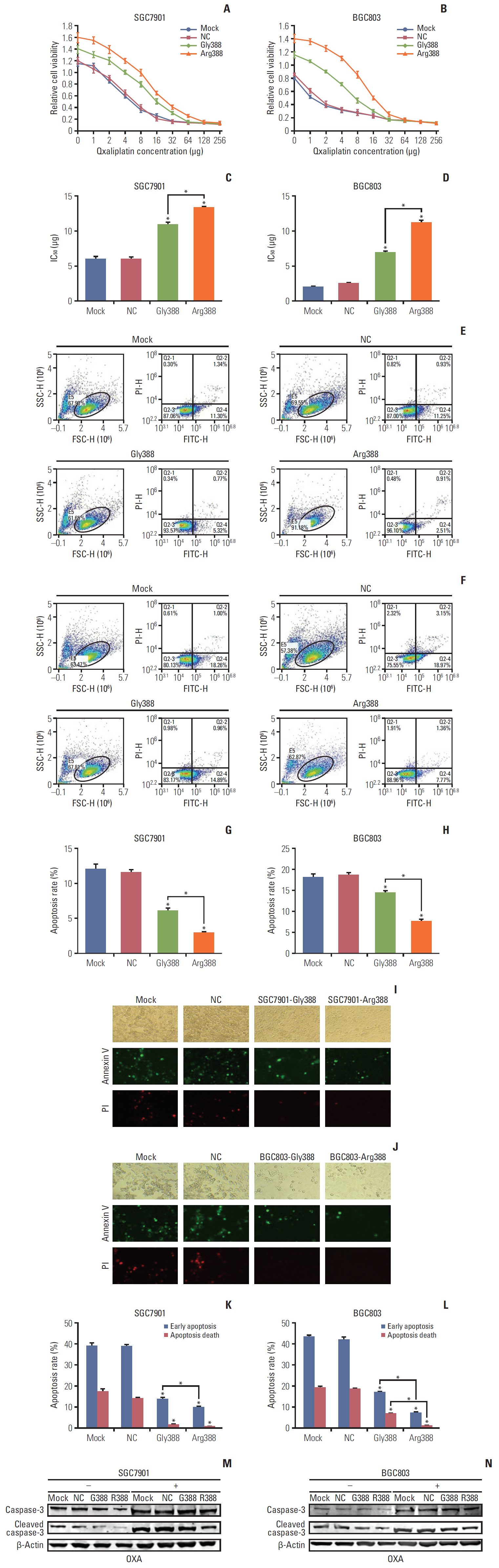
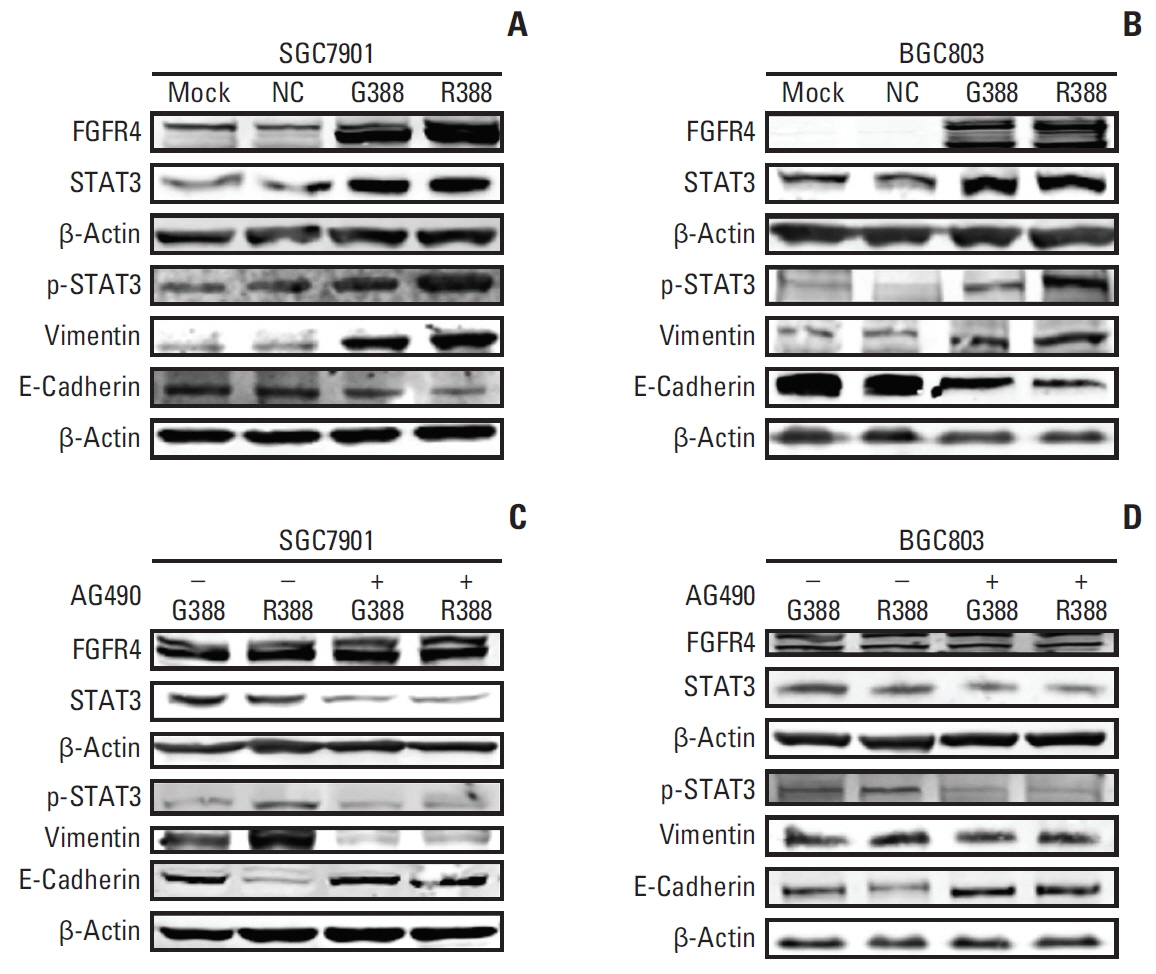
Among 102 GC patients, the FGFR4-Arg388 patients showed significantly higher tumor stage (p=0.047) and worse overall survival (p=0.033) than the Gly388 patients. Immunohistochemical results showed that FGFR4-Arg388 patients were more likely to have higher vimentin (p=0.025) and p-STAT3 (p=0.009) expression compared with FGFR4-Gly388 patients. In transfected GC cells, the overexpression of FGFR4-Arg388 variant increased proliferation and invasion of GC cells, increasing resistance of GC cells to OXA compared with cells overexpressing the Gly388 allele.
Conclusion
The exploration mechanism may be through FGFR4-Arg388/STAT3/epithelial to mesenchymal transition axis regulating pivotal oncogenic properties of GC cells. The FGFR4-Arg388 variant may be a biomarker and a candidate target for adjuvant treatment of GC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Katoh M. Genetic alterations of FGF receptors: an emerging field in clinical cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010; 10:1375–9.
Article2. Li J, Ye Y, Wang M, Lu L, Han C, Zhou Y, et al. The overexpression of FGFR4 could influence the features of gastric cancer cells and inhibit the efficacy of PD173074 and 5-fluorouracil towards gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:6881–91.
Article3. Ye Y, Jiang D, Li J, Wang M, Han C, Zhang X, et al. Silencing of FGFR4 could influence the biological features of gastric cancer cells and its therapeutic value in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:3185–95.
Article4. Ye Y, Shi Y, Zhou Y, Du C, Wang C, Zhan H, et al. The fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 Arg388 allele is associated with gastric cancer progression. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:3354–61.
Article5. Chou CH, Hsieh MJ, Chuang CY, Lin JT, Yeh CM, Tseng PY, et al. Functional FGFR4 Gly388Arg polymorphism contributes to oral squamous cell carcinoma susceptibility. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:96225–38.
Article6. Ezzat S, Wang R, Pintilie M, Asa SL. FGFR4 polymorphic alleles modulate mitochondrial respiration: a novel target for somatostatin analog action in pituitary tumors. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:3481–94.
Article7. Whittle SB, Reyes S, Du M, Gireud M, Zhang L, Woodfield SE, et al. A polymorphism in the FGFR4 gene is associated with risk of neuroblastoma and altered receptor degradation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016; 38:131–8.
Article8. Morimoto Y, Ozaki T, Ouchida M, Umehara N, Ohata N, Yoshida A, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism in fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 at codon 388 is associated with prognosis in high-grade soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer. 2003; 98:2245–50.
Article9. Streit S, Mestel DS, Schmidt M, Ullrich A, Berking C. FGFR4 Arg388 allele correlates with tumour thickness and FGFR4 protein expression with survival of melanoma patients. Br J Cancer. 2006; 94:1879–86.
Article10. Yu W, Feng S, Dakhova O, Creighton CJ, Cai Y, Wang J, et al. FGFR-4 Arg(3)(8)(8) enhances prostate cancer progression via extracellular signal-related kinase and serum response factor signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:4355–66.
Article11. Jalali S, Monsalves E, Tateno T, Zadeh G. Role of mTOR inhibitors in growth hormone-producing pituitary adenomas harboring different FGFR4 genotypes. Endocrinology. 2016; 157:3577–87.
Article12. Ulaganathan VK, Ullrich A. Membrane-proximal binding of STAT3 revealed by cancer-associated receptor variants. Mol Cell Oncol. 2016; 3:e1145176.
Article13. Ezzat S, Zheng L, Florez JC, Stefan N, Mayr T, Hliang MM, et al. The cancer-associated FGFR4-G388R polymorphism enhances pancreatic insulin secretion and modifies the risk of diabetes. Cell Metab. 2013; 17:929–40.14. Sugiyama N, Varjosalo M, Meller P, Lohi J, Chan KM, Zhou Z, et al. FGF receptor-4 (FGFR4) polymorphism acts as an activity switch of a membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-FGFR4 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:15786–91.
Article15. Cho SH, Hong CS, Kim HN, Shin MH, Kim KR, Shim HJ, et al. FGFR4 Arg388 is correlated with poor survival in resected colon cancer promoting epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49:766–77.
Article16. Quintanal-Villalonga A, Ojeda-Marquez L, Marrugal A, Yague P, Ponce-Aix S, Salinas A, et al. The FGFR4-388arg variant promotes lung cancer progression by N-cadherin induction. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:2394.
Article17. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:1471–4.
Article18. Thussbas C, Nahrig J, Streit S, Bange J, Kriner M, Kates R, et al. FGFR4 Arg388 allele is associated with resistance to adjuvant therapy in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3747–55.
Article19. Myoteri D, Dellaportas D, Lykoudis PM, Apostolopoulos A, Marinis A, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A. Prognostic evaluation of vimentin expression in correlation with Ki67 and CD44 in surgically resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017; 2017:9207616.
Article20. Gao H, Lan X, Li S, Xue Y. Relationships of MMP-9, E-cadherin, and VEGF expression with clinicopathological features and response to chemosensitivity in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017; 39:1010428317698368.
Article21. Zhang S, Huang S, Deng C, Cao Y, Yang J, Chen G, et al. Co-ordinated overexpression of SIRT1 and STAT3 is associated with poor survival outcome in gastric cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:18848–60.
Article22. Serra S, Zheng L, Hassan M, Phan AT, Woodhouse LJ, Yao JC, et al. The FGFR4-G388R single-nucleotide polymorphism alters pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor progression and response to mTOR inhibition therapy. Cancer Res. 2012; 72:5683–91.
Article23. Quintanal-Villalonga A, Carranza-Carranza A, Melendez R, Ferrer I, Molina-Pinelo S, Paz-Ares L. Prognostic role of the FGFR4-388Arg variant in lung squamous-cell carcinoma patients with lymph node involvement. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017; 18:667–74.
Article24. Shim HJ, Shin MH, Kim HN, Kim JH, Hwang JE, Bae WK, et al. The prognostic significance of FGFR4 Gly388 polymorphism in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:71–9.25. Gao L, Wang X, Tang Y, Huang S, Hu CA, Teng Y. FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 36:8.
Article26. Calo V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N, et al. STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2003; 197:157–68.27. Okabe M, Miyabe S, Nagatsuka H, Terada A, Hanai N, Yokoi M, et al. MECT1-MAML2 fusion transcript defines a favorable subset of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:3902–7.
Article28. Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F, Raman V, Ramirez N, et al. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2009; 28:2940–7.
Article29. Cheng GZ, Zhang WZ, Sun M, Wang Q, Coppola D, Mansour M, et al. Twist is transcriptionally induced by activation of STAT3 and mediates STAT3 oncogenic function. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:14665–73.
Article30. Zang C, Liu X, Li B, He Y, Jing S, He Y, et al. IL-6/STAT3/TWIST inhibition reverses ionizing radiation-induced EMT and radioresistance in esophageal squamous carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:11228–38.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- RAR-Related Orphan Receptor: An Accelerated Preeclampsia Progression by Activating the JAK/STAT3 Pathway
- FGFR4 Arg388 Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Resected Colon Cancer Promoting Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- Role of Gastric Stem Cells in Gastric Carcinogenesis by Chronic Helicobacter pylori Infection
- Membrane Proteins Involved in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Invasion: Studies on TMPRSS4 and TM4SF5
- Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma