Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Jul;49(3):766-777. 10.4143/crt.2016.457.
FGFR4 Arg388 Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Resected Colon Cancer Promoting Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hemato-Oncology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. hwacnuhd@gmail.com
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Chonnam National Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2388322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.457
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) plays an important role in cancer progression during tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. This study evaluated the prognostic role of FGFR4 polymorphism in patients with resected colon cancer, including the underlying mechanism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
FGFR4 polymorphism was characterized in patientswho received curative resection for stage III colon cancer. FGFR4-dependent signal pathways involving cell proliferation, invasion, and migration according to genotypes were also evaluated in transfected colon cancer cell lines.
RESULTS
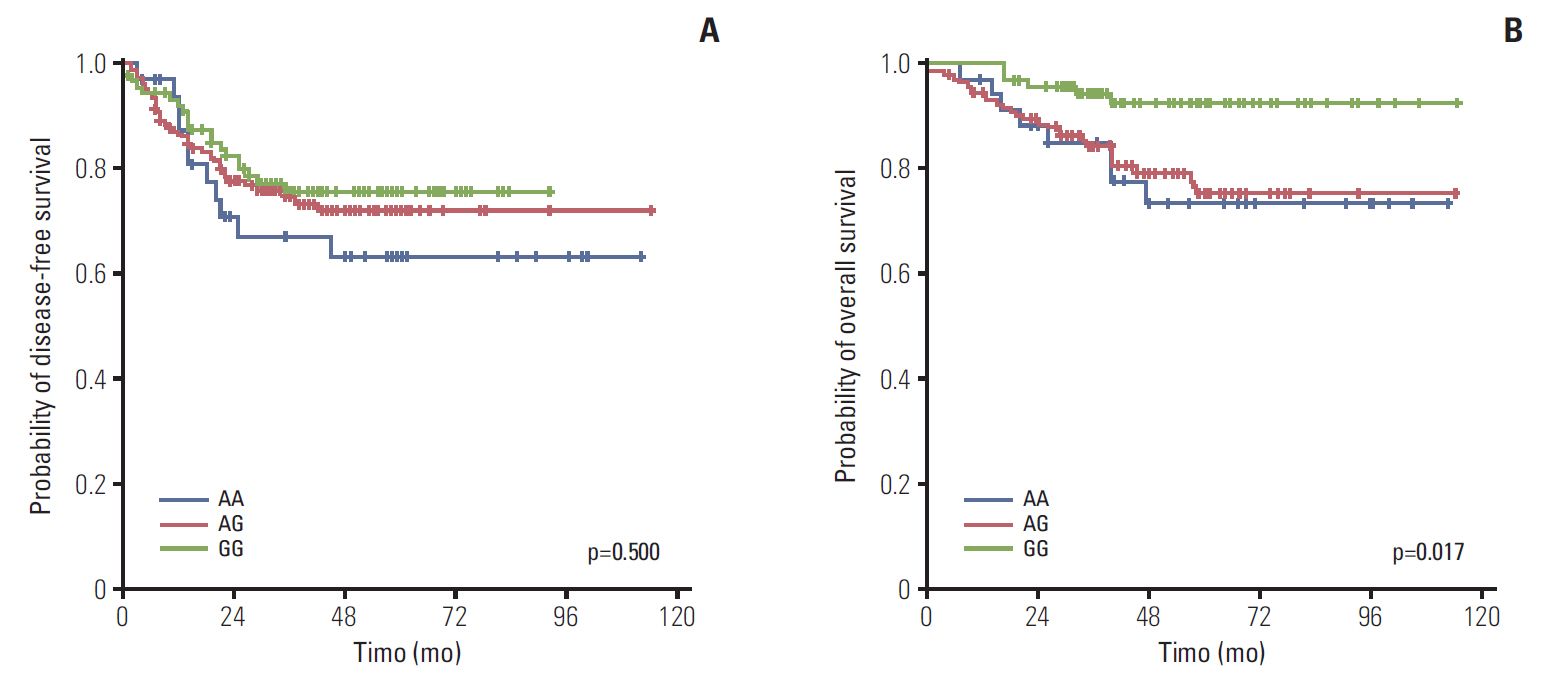
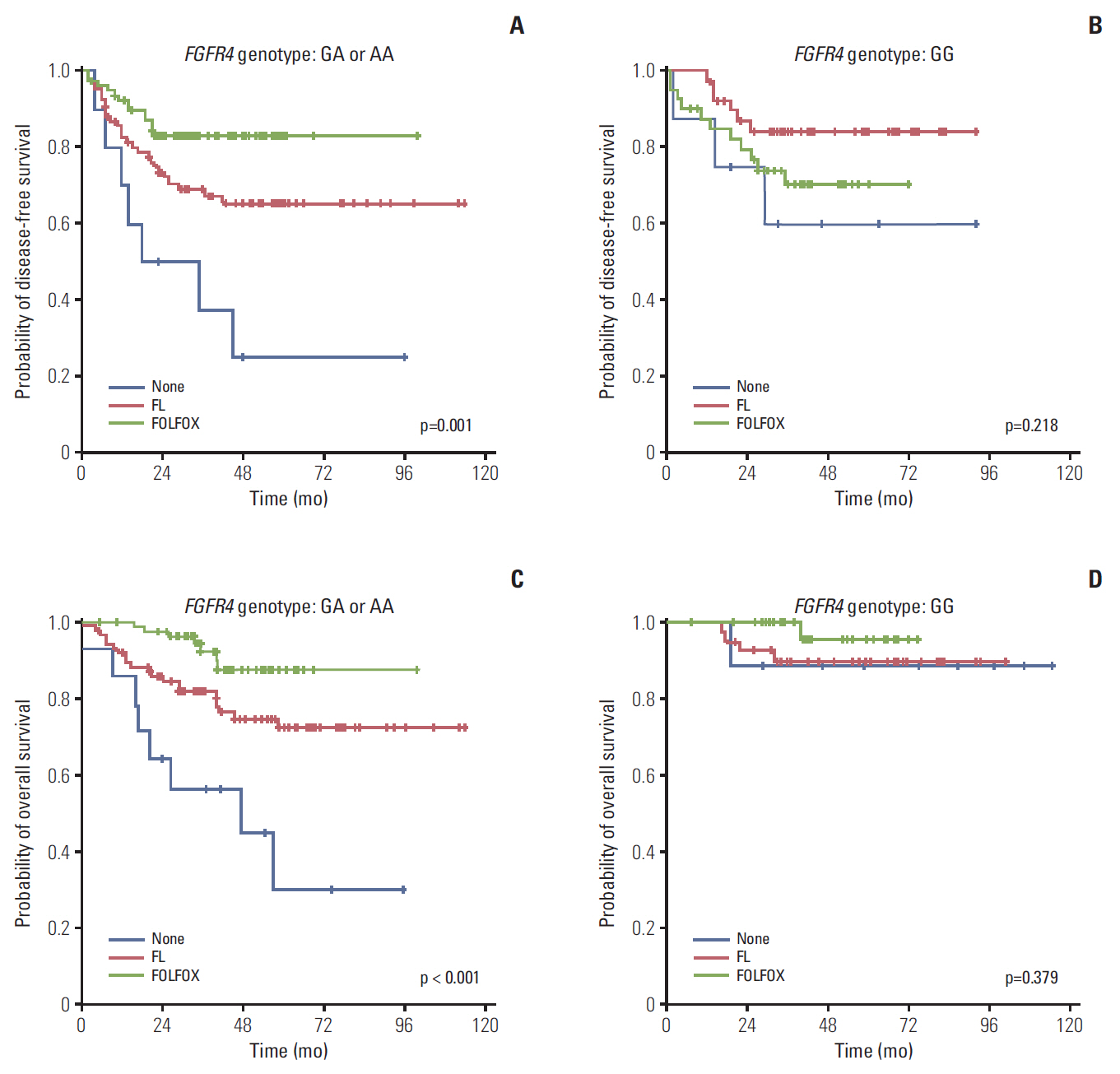
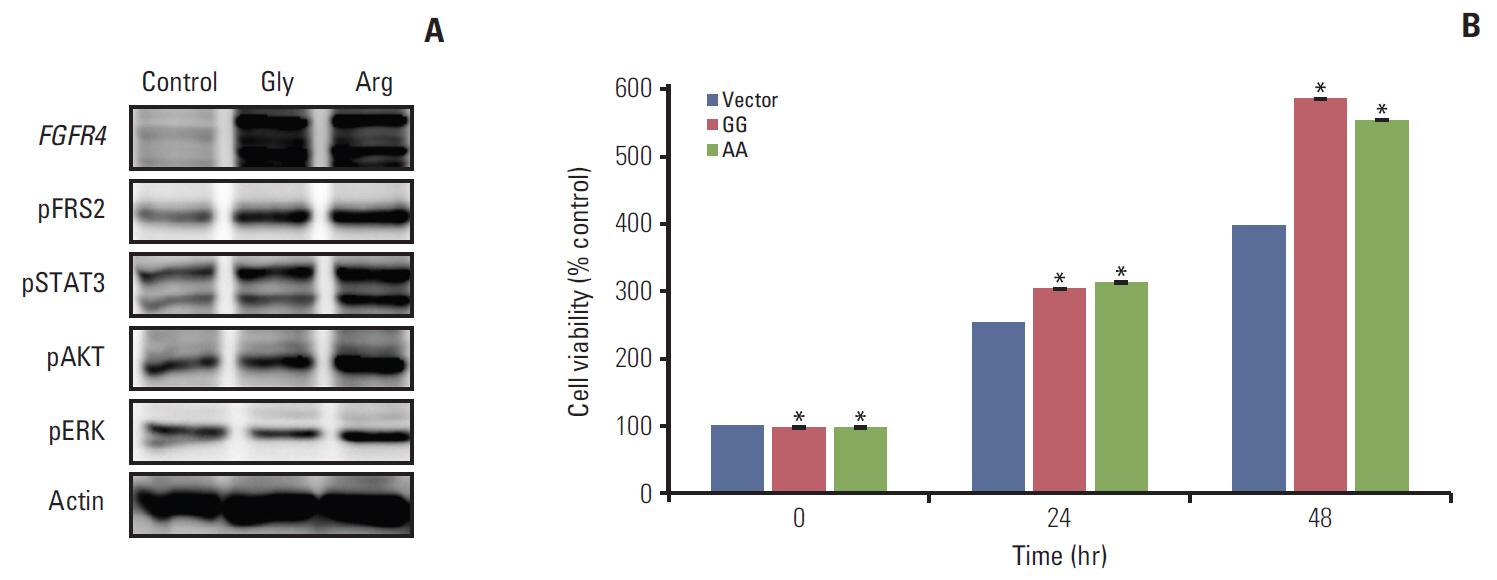
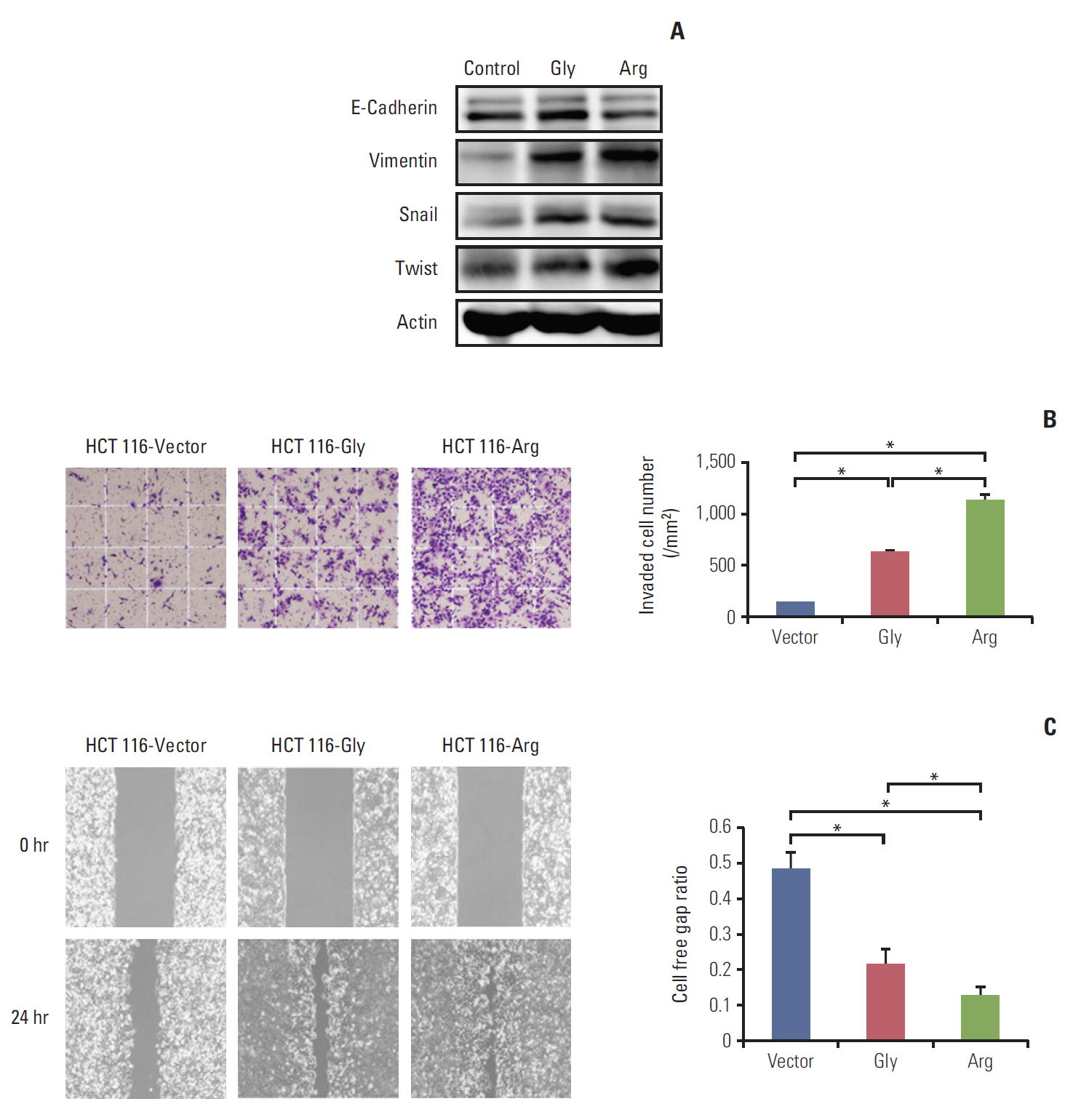
Among a total of 273 patients, the GG of FGFR4 showed significantly better overall survival than the AG or AA, regardless of adjuvant treatment. In the group of AG or AA, combination of folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) resulted in better survival than fluorouracil/leucovorin or no adjuvant chemotherapy. However, in GG, there was no difference among treatment regimens. Using multivariate analyses, the Arg388 carriers, together with age, N stage, poor differentiation, absence of a lymphocyte response, and no adjuvant chemotherapy, had a significantly worse OS than patients with the Gly388 allele. In transfected colon cancer cells, overexpression of Arg388 significantly increased cell proliferation and changes in epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers compared with cells overexpressing the Gly388 allele.
CONCLUSION
The Arg388 allele of FGFR4 may be a biomarker and a candidate target for adjuvant treatment of patients with resected colon cancer.
MeSH Terms
-
Alleles
Biomarkers
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Chemotherapy, Adjuvant
Colon*
Colonic Neoplasms*
Fluorouracil
Genotype
Humans
Leucovorin
Lymphocytes
Multivariate Analysis
Neoplasm Metastasis
Prognosis
Receptor, Fibroblast Growth Factor, Type 4
Signal Transduction
Biomarkers
Fluorouracil
Leucovorin
Receptor, Fibroblast Growth Factor, Type 4
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
FGFR4 Gly388Arg Polymorphism Affects the Progression of Gastric Cancer by Activating STAT3 Pathway to Induce Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
Yanwei Ye, Jie Li, Dongbao Jiang, Jingjing Li, Chuangfeng Xiao, Yingze Li, Chao Han, Chunlin Zhao
Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52(4):1162-1177. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.138.
Reference
-
References
1. Turner N, Grose R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10:116–29.
Article2. Burke D, Wilkes D, Blundell TL, Malcolm S. Fibroblast growth factor receptors: lessons from the genes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998; 23:59–62.
Article3. Brooks AN, Kilgour E, Smith PD. Molecular pathways: fibroblast growth factor signaling: a new therapeutic opportunity in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:1855–62.
Article4. Dieci MV, Arnedos M, Andre F, Soria JC. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors as a cancer treatment: from a biologic rationale to medical perspectives. Cancer Discov. 2013; 3:264–79.
Article5. Spinola M, Leoni V, Pignatiello C, Conti B, Ravagnani F, Pastorino U, et al. Functional FGFR4 Gly388Arg polymorphism predicts prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:7307–11.
Article6. Thussbas C, Nahrig J, Streit S, Bange J, Kriner M, Kates R, et al. FGFR4 Arg388 allele is associated with resistance to adjuvant therapy in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3747–55.
Article7. Shen YY, Lu YC, Shen DP, Liu YJ, Su XY, Zhu GS, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 Gly388Arg polymorphism in Chinese gastric cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4568–75.
Article8. Liu R, Li J, Xie K, Zhang T, Lei Y, Chen Y, et al. FGFR4 promotes stroma-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:5926–35.
Article9. Heinzle C, Gsur A, Hunjadi M, Erdem Z, Gauglhofer C, Stattner S, et al. Differential effects of polymorphic alleles of FGF receptor 4 on colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012; 72:5767–77.
Article10. Bange J, Prechtl D, Cheburkin Y, Specht K, Harbeck N, Schmitt M, et al. Cancer progression and tumor cell motility are associated with the FGFR4 Arg(388) allele. Cancer Res. 2002; 62:840–7.11. Spinola M, Leoni VP, Tanuma J, Pettinicchio A, Frattini M, Signoroni S, et al. FGFR4 Gly388Arg polymorphism and prognosis of breast and colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2005; 14:415–9.
Article12. Wang J, Yu W, Cai Y, Ren C, Ittmann MM. Altered fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 stability promotes prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia. 2008; 10:847–56.
Article13. Streit S, Bange J, Fichtner A, Ihrler S, Issing W, Ullrich A. Involvement of the FGFR4 Arg388 allele in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2004; 111:213–7.
Article14. Shim HJ, Shin MH, Kim HN, Kim JH, Hwang JE, Bae WK, et al. The prognostic significance of FGFR4 Gly388 polymorphism in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:71–9.15. Friedl P, Wolf K. Plasticity of cell migration: a multiscale tuning model. J Cell Biol. 2010; 188:11–9.
Article16. Desnoyers LR, Pai R, Ferrando RE, Hotzel K, Le T, Ross J, et al. Targeting FGF19 inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer xenograft and FGF19 transgenic hepatocellular carcinoma models. Oncogene. 2008; 27:85–97.
Article17. Yu W, Feng S, Dakhova O, Creighton CJ, Cai Y, Wang J, et al. FGFR-4 Arg388 enhances prostate cancer progression via extracellular signal-related kinase and serum response factor signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:4355–66.
Article18. Ulaganathan VK, Sperl B, Rapp UR, Ullrich A. Germline variant FGFR4 p.G388R exposes a membrane-proximal STAT3 binding site. Nature. 2015; 528:570–4.
Article19. Ye Y, Shi Y, Zhou Y, Du C, Wang C, Zhan H, et al. The fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 Arg388 allele is associated with gastric cancer progression. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:3354–61.
Article20. Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW. The epithelialmesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2006; 172:973–81.
Article21. Sanchez-Lopez E, Flashner-Abramson E, Shalapour S, Zhong Z, Taniguchi K, Levitzki A, et al. Targeting colorectal cancer via its microenvironment by inhibiting IGF-1 receptor-insulin receptor substrate and STAT3 signaling. Oncogene. 2016; 35:2634–44.
Article22. Balanis N, Wendt MK, Schiemann BJ, Wang Z, Schiemann WP, Carlin CR. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition promotes breast cancer progression via a fibronectin-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288:17954–67.
Article23. Gavine PR, Mooney L, Kilgour E, Thomas AP, Al-Kadhimi K, Beck S, et al. AZD4547: an orally bioavailable, potent, and selective inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase family. Cancer Res. 2012; 72:2045–56.
Article24. Guagnano V, Kauffmann A, Wohrle S, Stamm C, Ito M, Barys L, et al. FGFR genetic alterations predict for sensitivity to NVPBGJ398, a selective pan-FGFR inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2012; 2:1118–33.
Article25. Lee SH, Lopes de Menezes D, Vora J, Harris A, Ye H, Nordahl L, et al. In vivo target modulation and biological activity of CHIR-258, a multitargeted growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, in colon cancer models. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:3633–41.26. Tan L, Wang J, Tanizaki J, Huang Z, Aref AR, Rusan M, et al. Development of covalent inhibitors that can overcome resistance to first-generation FGFR kinase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:E4869–77.
Article27. Tabernero J, Bahleda R, Dienstmann R, Infante JR, Mita A, Italiano A, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of JNJ-42756493, an oral pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:3401–8.
Article28. Zhao G, Li WY, Chen D, Henry JR, Li HY, Chen Z, et al. A novel, selective inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptors that shows a potent broad spectrum of antitumor activity in several tumor xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011; 10:2200–10.
Article29. Katoh M. FGFR inhibitors: Effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2016; 38:3–15.
Article30. Hagel M, Miduturu C, Sheets M, Rubin N, Weng W, Stransky N, et al. First selective small molecule inhibitor of FGFR4 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas with an activated FGFR4 signaling pathway. Cancer Discov. 2015; 5:424–37.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- FGFR4 Gly388Arg Polymorphism Affects the Progression of Gastric Cancer by Activating STAT3 Pathway to Induce Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- The Prognostic Significance of FGFR4 Gly388 Polymorphism in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
- Consideration of EphA2 in relation to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in uterine endometrial cancer
- Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Drug Resistance and Metastasis of Lung Cancer