Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Sep;53(3):245-251. 10.5115/acb.19.181.
Tumor associated mast cells: biological roles and therapeutic applications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Pathology, RUHS College of Dental Sciences (Government Dental College), Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
- 2Department of Oral Pathology, Saraswati Dental College and Hospital, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
- 3Department of Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Sciences, King George Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
- KMID: 2507636
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.19.181
Abstract
- Mast cells (MCs) are immune cells of the myeloid lineage and are present in connective tissues throughout the body. The activation and degranulation of MCs significantly modulates many aspects of physiological and pathological conditions in various settings. Recent data have expanded the concept that inflammation is a critical component for tumor progression. Interestingly, three of the most aggressive human cancers, malignant melanoma, breast carcinoma and colorectal adenocarcinoma, are commonly associated with a marked host response comprising of various inflammatory cells, but especially MCs around the tumor periphery. A systematic review of the literature was performed based on the English titles listed in the PubMed, EBSCO, Cochrane, Science Direct, ISI web Science, and SciELO databases using the keywords. Abstracts and full-text articles were assessed. This review summarizes the current understanding of the role of MCs in tumor progression.
Keyword
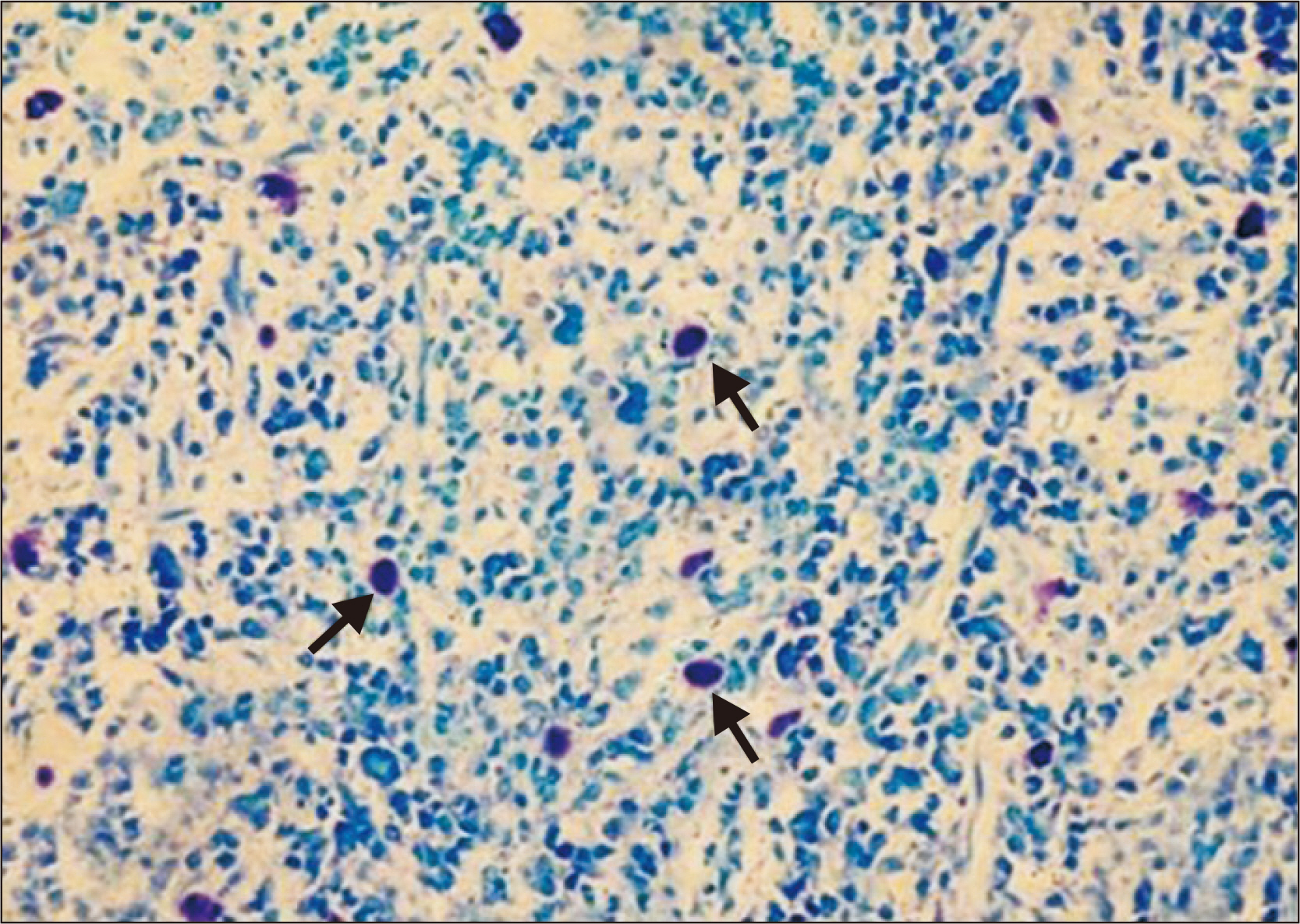
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Walsh LJ. 2003; Mast cells and oral inflammation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 14:188–98. DOI: 10.1177/154411130301400304. PMID: 12799322.
Article2. Ch'ng S, Wallis RA, Yuan L, Davis PF, Tan ST. 2006; Mast cells and cutaneous malignancies. Mod Pathol. 19:149–59. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.3800474. PMID: 16258517.3. Elpek GO, Gelen T, Aksoy NH, Erdoğan A, Dertsiz L, Demircan A, Keleş N. 2001; The prognostic relevance of angiogenesis and mast cells in squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. J Clin Pathol. 54:940–4. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.54.12.940. PMID: 11729214. PMCID: PMC1731336.
Article4. Galli SJ. 1993; New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med. 328:257–65. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280408. PMID: 8418407.
Article5. Galli SJ, Maurer M, Lantz CS. 1999; Mast cells as sentinels of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 11:53–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0952-7915(99)80010-7. PMID: 10047539. PMCID: PMC7477074.
Article6. Grootens J, Ungerstedt JS, Nilsson G, Dahlin JS. 2018; Deciphering the differentiation trajectory from hematopoietic stem cells to mast cells. Blood Adv. 2:2273–81. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018019539. PMID: 30206100. PMCID: PMC6134220.
Article7. Dahlin JS, Hallgren J. 2015; Mast cell progenitors: origin, development and migration to tissues. Mol Immunol. 63:9–17. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.01.018. PMID: 24598075.
Article8. Sawai N, Koike K, Mwamtemi HH, Kinoshita T, Kurokawa Y, Sakashita K, Higuchi T, Takeuchi K, Shiohara M, Kamijo T, Ito S, Kato T, Miyazaki H, Yamashita T, Komiyama A. 1999; Thrombopoietin augments stem cell factor-dependent growth of human mast cells from bone marrow multipotential hematopoietic progenitors. Blood. 93:3703–12. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V93.11.3703. PMID: 10339477.
Article9. Okayama Y, Kawakami T. 2006; Development, migration, and survival of mast cells. Immunol Res. 34:97–115. DOI: 10.1385/IR:34:2:97.
Article10. Joseph S, Das S, Chand R, Roopa R, Thomas IM. 2003; Comparison of toluidine blue Vs thionin for mast cells in rat mesentery using Carnoy's fixative. J Anat Soc India. 52:166–7.11. Moon TC, Befus AD, Kulka M. 2014; Mast cell mediators: their differential release and the secretory pathways involved. Front Immunol. 5:569. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00569. PMID: 25452755. PMCID: PMC4231949.
Article12. Wernersson S, Pejler G. 2014; Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:478–94. DOI: 10.1038/nri3690. PMID: 24903914.
Article13. Yamasaki S, Ishikawa E, Kohno M, Saito T. 2004; The quantity and duration of FcRγ signals determine mast cell degranulation and survival. Blood. 103:3093–101. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2003-08-2944. PMID: 15070690.
Article14. Krishnaswamy G, Kelley J, Johnson D, Youngberg G, Stone W, Huang SK, Bieber J, Chi DS. 2001; The human mast cell: functions in physiology and disease. Front Biosci. 6:D1109–27. DOI: 10.2741/krishnas. PMID: 11532608.
Article15. Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA. 1997; Mast cells. Physiol Rev. 77:1033–79. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.1997.77.4.1033. PMID: 9354811.
Article16. Pejler G, Knight SD, Henningsson F, Wernersson S. 2009; Novel insights into the biological function of mast cell carboxypeptidase A. Trends Immunol. 30:401–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2009.04.008. PMID: 19643669. PMCID: PMC6255860.
Article17. Caughey GH. 2007; Mast cell tryptases and chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol Rev. 217:141–54. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00509.x. PMID: 17498057. PMCID: PMC2275918.
Article18. Huang B, Lei Z, Zhang GM, Li D, Song C, Li B, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Unkeless J, Xiong H, Feng ZH. 2008; SCF-mediated mast cell infiltration and activation exacerbate the inflammation and immunosuppression in tumor microenvironment. Blood. 112:1269–79. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-147033. PMID: 18524989. PMCID: PMC2515142.
Article19. Theoharides TC, Conti P. 2004; Mast cells: the Jekyll and Hyde of tumor growth. Trends Immunol. 25:235–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2004.02.013. PMID: 15099563.
Article20. Rigoni A, Colombo MP, Pucillo C. 2015; The role of mast cells in molding the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 8:167–76. DOI: 10.1007/s12307-014-0152-8. PMID: 25194694. PMCID: PMC4715001.
Article21. Dimitriadou V, Koutsilieris M. 1997; Mast cell-tumor cell interactions: for or against tumour growth and metastasis? Anticancer Res. 17:1541–9.22. Kessler DA, Langer RS, Pless NA, Folkman J. 1976; Mast cells and tumor angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 18:703–9. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.2910180520. PMID: 62725. PMCID: PMC7492388.
Article23. Norrby K. 1997; Mast cells and de novo angiogenesis: angiogenic capability of individual mast-cell mediators such as histamine, TNF, IL-8 and bFGF. Inflamm Res. 46(Suppl 1):7–8. DOI: 10.1007/PL00022372. PMID: 27517977.24. Coussens LM, Raymond WW, Bergers G, Webster LM, Behrendtsen O, Werb Z, Caughey GH, Hanahan D. 1999; Inflammatory mast cells up-regulate angiogenesis during squamous epithelial carcinogenesis. Genes Dev. 13:1382–97. DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.11.1382. PMID: 10364156. PMCID: PMC316772.
Article25. Tomita M, Matsuzaki Y, Edagawa M, Shimizu T, Hara M, Sekiya R, Onitsuka T. 2001; Association of mast cells with tumor angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 14:135–8. DOI: 10.1046/j.1442-2050.2001.00171.x. PMID: 11553224.
Article26. Kwon GY, Lee SD, Park ES. 2005; Mast cell and macrophage counts and microvessel density in invasive breast carcinoma-comparison analysis with clinicopathological parameters. Cancer Res Treat. 37:103–8. DOI: 10.4143/crt.2005.37.2.103. PMID: 19956488. PMCID: PMC2785399.
Article27. Ribatti D, Guidolin D, Marzullo A, Nico B, Annese T, Benagiano V, Crivellato E. 2010; Mast cells and angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol. 91:350–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00714.x. PMID: 20412338. PMCID: PMC2962893.
Article28. Iamaroon A, Pongsiriwet S, Jittidecharaks S, Pattanaporn K, Prapayasatok S, Wanachantararak S. 2003; Increase of mast cells and tumor angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 32:195–9. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00128.x. PMID: 12653857. PMCID: PMC5051296.
Article29. Tomita M, Matsuzaki Y, Onitsuka T. 2000; Effect of mast cells on tumor angiogenesis in lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 69:1686–90. DOI: 10.1016/S0003-4975(00)01160-7. PMID: 10892907.
Article30. Rojas IG, Spencer ML, Martínez A, Maurelia MA, Rudolph MI. 2005; Characterization of mast cell subpopulations in lip cancer. J Oral Pathol Med. 34:268–73. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2004.00297.x. PMID: 15817069. PMCID: PMC7406785.
Article31. Ozdemir O. 2005; Immunosurveillance function of human mast cell? World J Gastroenterol. 11:7054–6. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.7054. PMID: 16437618. PMCID: PMC4717056.32. Amini RM, Aaltonen K, Nevanlinna H, Carvalho R, Salonen L, Heikkilä P, Blomqvist C. 2007; Mast cells and eosinophils in invasive breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 7:165. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-165. PMID: 17727696. PMCID: PMC2048965.
Article33. Takanami I, Takeuchi K, Naruke M. 2000; Mast cell density is associated with angiogenesis and poor prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 88:2686–92. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(20000615)88:12<2686::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-6. PMID: 10870050.
Article34. Ribatti D, Ennas MG, Vacca A, Ferreli F, Nico B, Orru S, Sirigu P. 2003; Tumor vascularity and tryptase-positive mast cells correlate with a poor prognosis in melanoma. Eur J Clin Invest. 33:420–5. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2003.01152.x. PMID: 12760367.
Article35. Peng SH, Deng H, Yang JF, Xie PP, Li C, Li H, Feng DY. 2005; Significance and relationship between infiltrating inflammatory cell and tumor angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. World J Gastroenterol. 11:6521–4. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6521. PMID: 16425427. PMCID: PMC4355797.
Article36. Yodavudh S, Tangjitgamol S, Puangsa-art S. 2008; Prognostic significance of microvessel density and mast cell density for the survival of Thai patients with primary colorectal cancer. J Med Assoc Thai. 91:723–32. PMID: 18672639.37. Tan SY, Fan Y, Luo HS, Shen ZX, Guo Y, Zhao LJ. 2005; Prognostic significance of cell infiltrations of immunosurveillance in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1210–4. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1210. PMID: 15754407. PMCID: PMC4250716.
Article38. Kandhare AD, Aswar UM, Mohan V, Thakurdesai PA. 2017; Ameliorative effects of type-A procyanidins polyphenols from cinnamon bark in compound 48/80-induced mast cell degranulation. Anat Cell Biol. 50:275–83. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2017.50.4.275. PMID: 29354299. PMCID: PMC5768564.
Article39. Khatami M. 2005; Cyclooxygenase inhibitor ketorolac or mast cell stabilizers: immunologic challenges in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1349–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bladder Mucosal Mast Cell Response in Bladder Tumor
- Mast Cells in Allergic Asthma and Beyond
- Histamine and spontaneously released mast cell granules ffect the cell growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Nitric Oxide by Human Mast Cells Incubated with Toxoplasma gondii Lysate
- Bioactive Lipids and Their Derivatives in Biomedical Applications