J Rheum Dis.
2020 Oct;27(4):241-246. 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.4.241.
Overview of Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2506977
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2020.27.4.241
Abstract
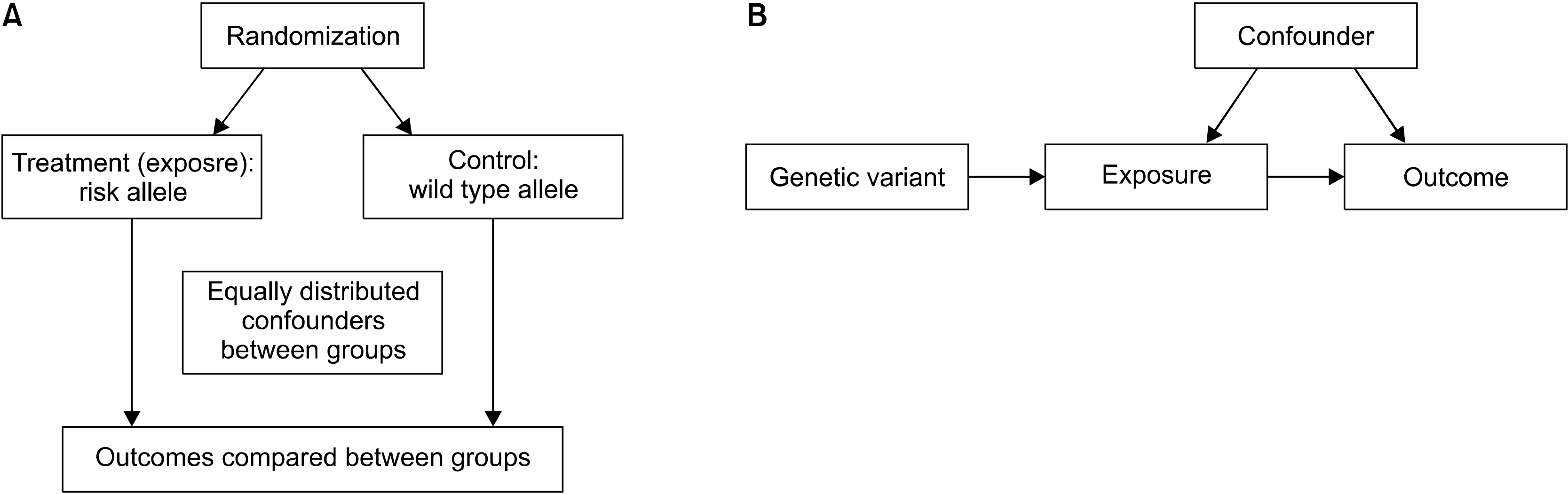
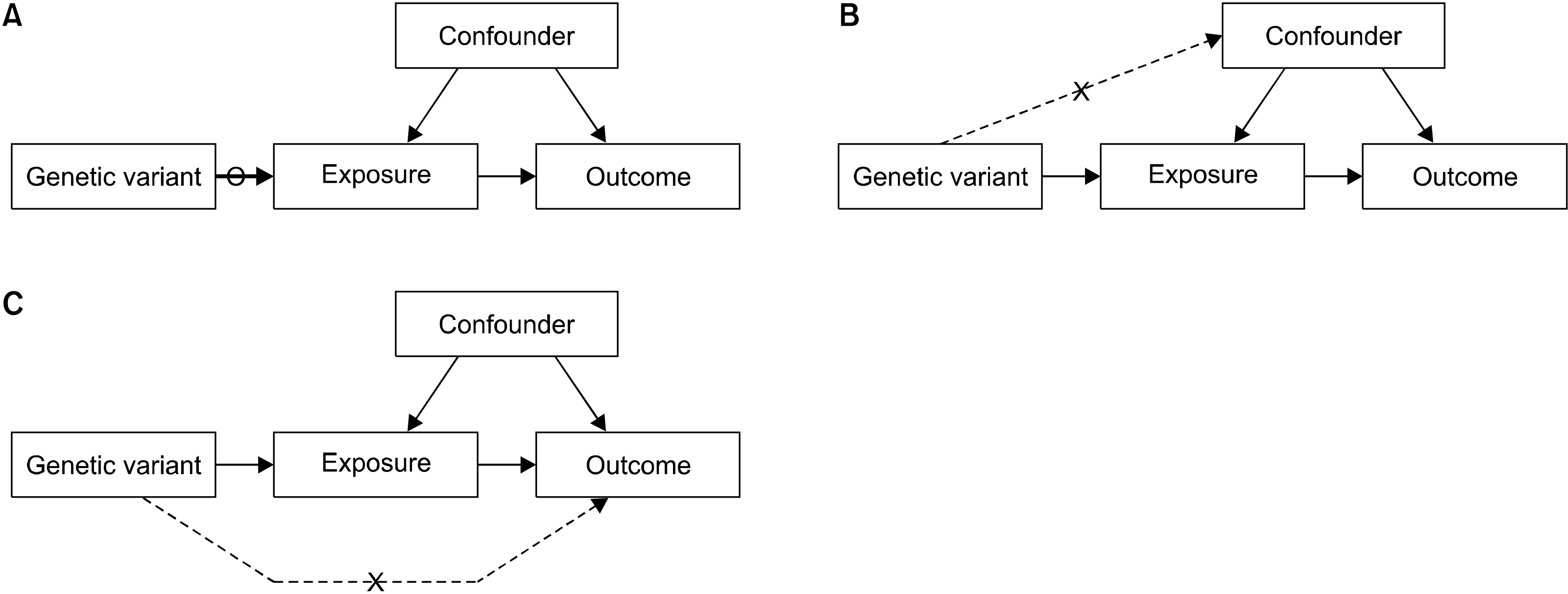
- he inference of causality from observational evidence may be problematic, as observational studies frequently include confounding factors or reverse causation for the identification of associations between exposure and outcome. Thus, in observational studies, the association between a risk factor and a disease of interest may not be causal. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is considered the gold standard, because it has the best possibility to establish a relationship between a risk factor and an outcome. However, RCTs cannot always be performed, because they can be costly, impractical, or even unethical. One of the alternatives is to perform Mendelian randomization (MR) experiments that are similar to RCTs in terms of study design. The MR technique uses genetic variants related to modifiable traits/exposures as tools to detect causal associations with outcomes. MR can provide more credible estimates of the causal effect of a risk factor on an outcome than those obtained in observational studies by overcoming the limitations of observational studies. Therefore, MR can make a substantial contribution to our understanding of complex disease etiology. MR approaches are increasingly being used to evaluate the causality of associations with risk factors, because well-performed MR studies can be a powerful method for exploring causality in complex diseases. However, there are some limitations in MR analyses, and an awareness of these limitations is essential to interpret the results. The validity of results from MR studies depends on three assumptions that should be carefully checked and interpreted in the context of prior biological information.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Greenland S, Robins JM. 1985; Confounding and misclassification. Am J Epidemiol. 122:495–506. DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114131. PMID: 4025298.
Article2. Greenwald P. 2003; Beta-carotene and lung cancer: a lesson for future chemoprevention investigations? J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:E1. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/95.10.e4. PMID: 12759404.3. Lawlor DA, Davey Smith G, Kundu D, Bruckdorfer KR, Ebrahim S. 2004; Those confounded vitamins: what can we learn from the differences between observational versus randomised trial evidence? Lancet. 363:1724–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16260-0. PMID: 15158637.
Article4. Black N. 1996; Why we need observational studies to evaluate the effectiveness of health care. BMJ. 312:1215–8. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.312.7040.1215. PMID: 8634569. PMCID: PMC2350940.
Article5. Wehby GL, Ohsfeldt RL, Murray JC. 2008; 'Mendelian randomization' equals instrumental variable analysis with genetic instruments. Stat Med. 27:2745–9. DOI: 10.1002/sim.3308. PMID: 18509868.
Article6. Zheng J, Baird D, Borges MC, Bowden J, Hemani G, Haycock P, et al. 2017; Recent developments in Mendelian randomization studies. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 4:330–45. DOI: 10.1007/s40471-017-0128-6. PMID: 29226067. PMCID: PMC5711966.
Article7. Angrist JD, Imbens GW, Rubin DB. 1996; Identification of causal effects using instrumental variables. J Am Stat Assoc. 91:444–55. DOI: 10.1002/bimj.201200104. PMID: 23180483.
Article8. Lawlor DA. 2016; Commentary: two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges. Int J Epidemiol. 45:908–15. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyw127. PMID: 27427429. PMCID: PMC5005949.
Article9. Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JA, Timpson N, Davey Smith G. 2008; Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. 27:1133–63. DOI: 10.1002/sim.3213. PMID: 18203119.
Article10. Martens EP, Pestman WR, de Boer A, Belitser SV, Klungel OH. 2006; Instrumental variables: application and limitations. Epidemiology. 17:260–7. DOI: 10.1097/01.ede.0000215160.88317.cb. PMID: 16617274.11. Burgess S, Butterworth A, Thompson SG. 2013; Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 37:658–65. DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21758. PMID: 24114802. PMCID: PMC4377079.
Article12. Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. 2015; Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 44:512–25. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyv080. PMID: 26050253. PMCID: PMC4469799.
Article13. Burgess S, Thompson SG. 2017; Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 32:377–89. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-017-0276-5. PMID: 28664250. PMCID: PMC6828068.
Article14. Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S. 2016; Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 40:304–14. DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21965. PMID: 27061298. PMCID: PMC4849733.
Article15. Davey Smith G, Hemani G. 2014; Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 23:R89–98. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu328. PMID: 25064373. PMCID: PMC4170722.
Article16. Bennett DA, Holmes MV. 2017; Mendelian randomisation in cardiovascular research: an introduction for clinicians. Heart. 103:1400–7. DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310605. PMID: 28596306. PMCID: PMC5574403.
Article17. Swerdlow DI, Kuchenbaecker KB, Shah S, Sofat R, Holmes MV, White J, et al. 2016; Selecting instruments for Mendelian randomization in the wake of genome-wide association studies. Int J Epidemiol. 45:1600–16. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyw088. PMID: 27342221. PMCID: PMC5100611.
Article18. Sekula P, Del Greco MF, Pattaro C, Köttgen A. 2016; Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:3253–65. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016010098. PMID: 27486138. PMCID: PMC5084898.
Article19. Pincus T, Callahan LF. 1985; Formal education as a marker for increased mortality and morbidity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Chronic Dis. 38:973–84. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9681(85)90095-5. PMID: 4066893.
Article20. Kwon JM, Rhee J, Ku H, Lee EK. 2012; Socioeconomic and employment status of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Korea. Epidemiol Health. 34:e2012003. DOI: 10.4178/epih/e2012003. PMID: 22611518. PMCID: PMC3350820.
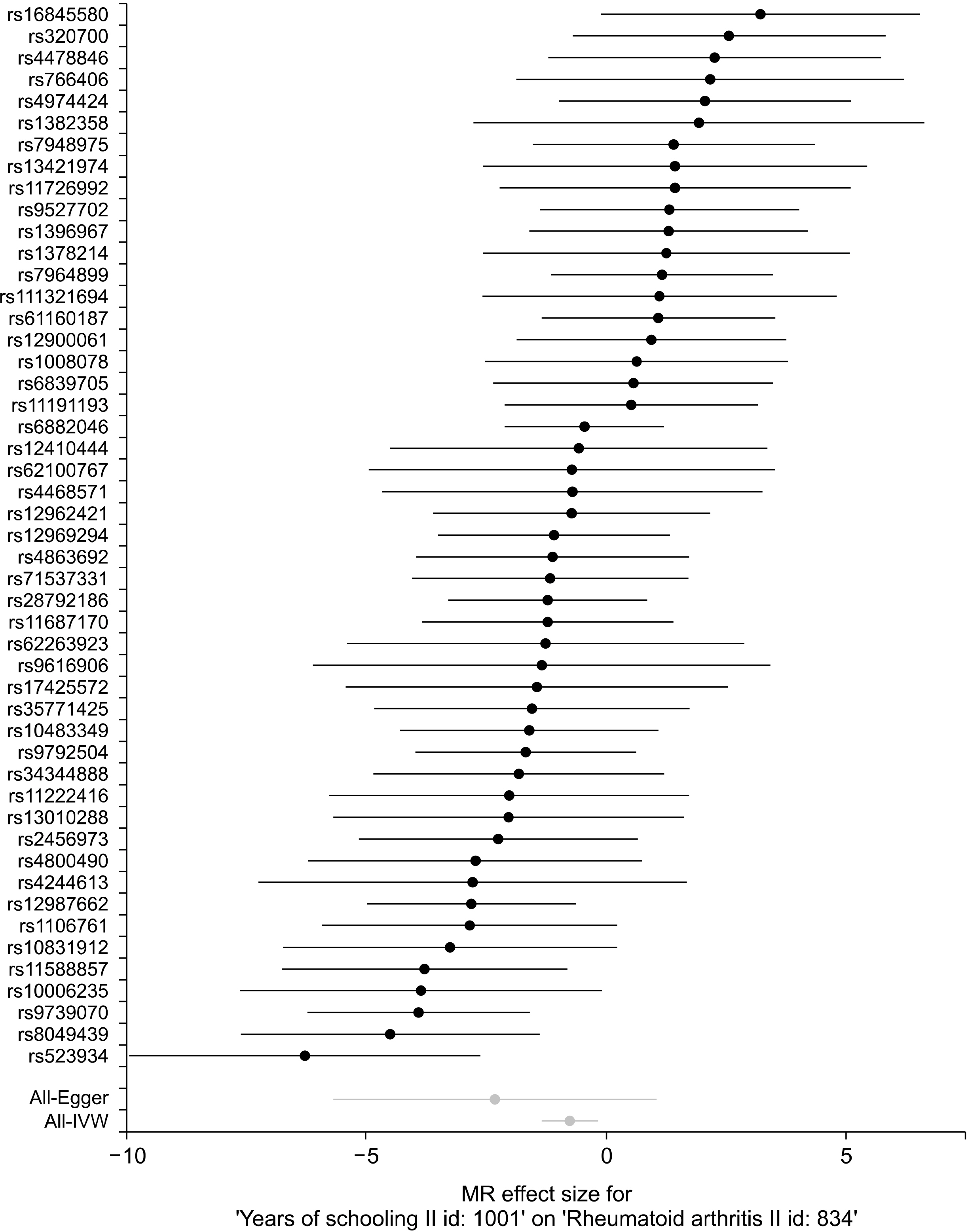
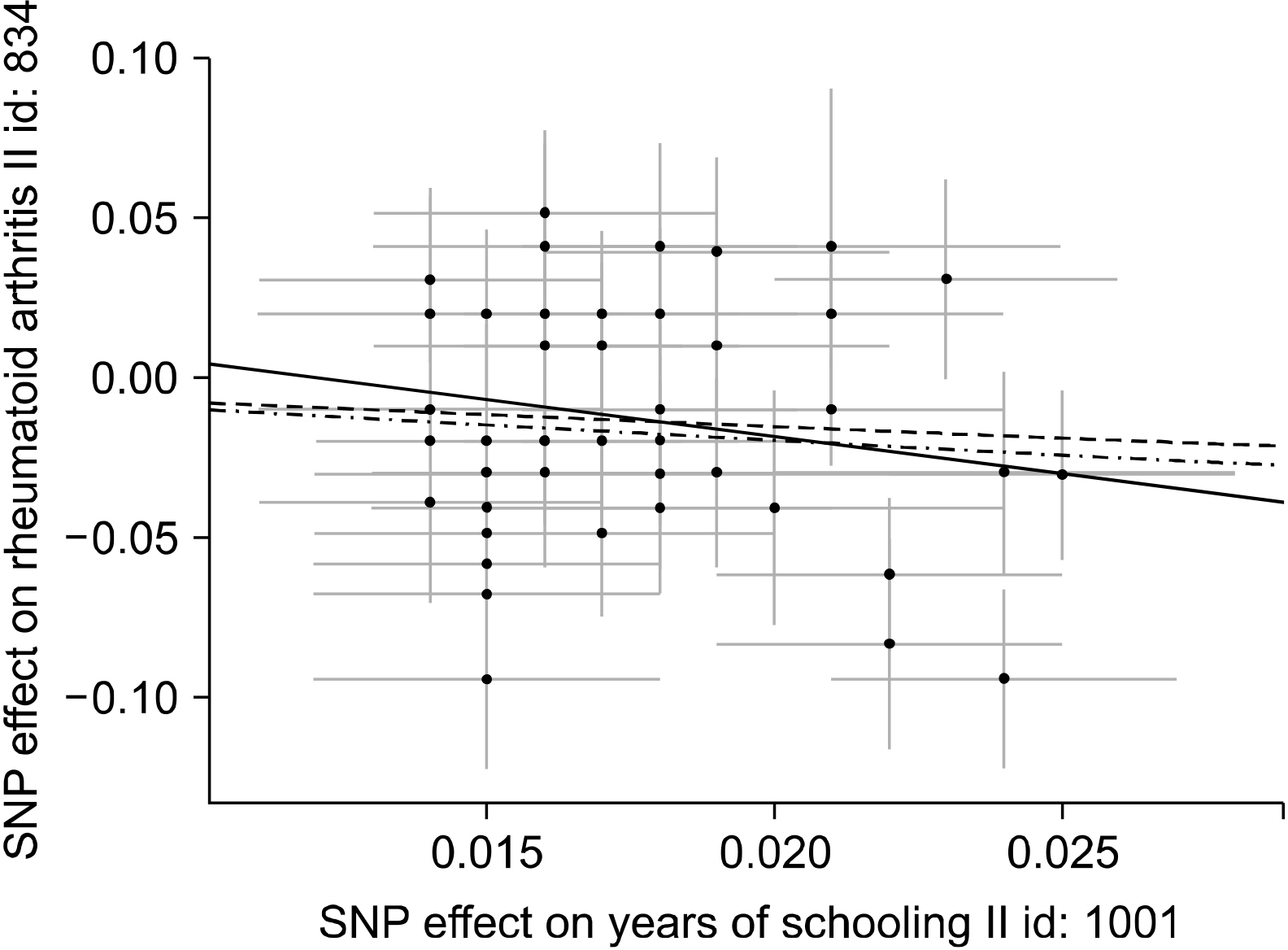
Article21. Uhlig T, Hagen KB, Kvien TK. 1999; Current tobacco smoking, formal education, and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 26:47–54. PMID: 9918239.22. Okbay A, Beauchamp JP, Fontana MA, Lee JJ, Pers TH, Rietveld CA, et al. 2016; Genome-wide association study identifies 74 loci associated with educational attainment. Nature. 533:539–42. DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00023. PMID: 28197077. PMCID: PMC5281599.23. Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP, et al. 2010; Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Nat Genet. 42:508–14. DOI: 10.1038/ng.582. PMID: 20453842. PMCID: PMC4243840.24. Bae SC, Lee YH. 2019; Causal relationship between years of education and the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis. Postgrad Med J. 95:378–81. DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2018-136374. PMID: 31127051.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mendelian Randomization Analysis in Observational Epidemiology
- A Review of Mendelian Randomization: Assumptions, Methods, and Application to Obesity-Related Diseases
- Basic Concepts of a Mendelian Randomization Approach
- Causal association between serum bilirubin and ischemic stroke: multivariable Mendelian randomization
- Exploration of errors in variance caused by using the first-order approximation in Mendelian randomization