J Rhinol.
2020 May;27(1):8-15. 10.18787/jr.2018.00277.
Polysaccharide from Hizikia Fusiformis Enhances the Immunomodulatory Activity of Macrophages
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery, Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea
- 2Department of Biochemical and Polymer Engineering, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2502788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2018.00277
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
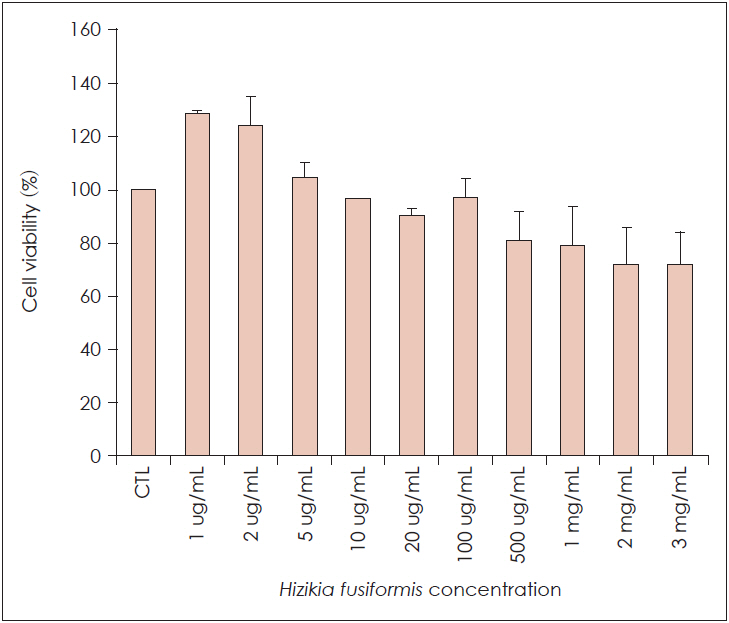
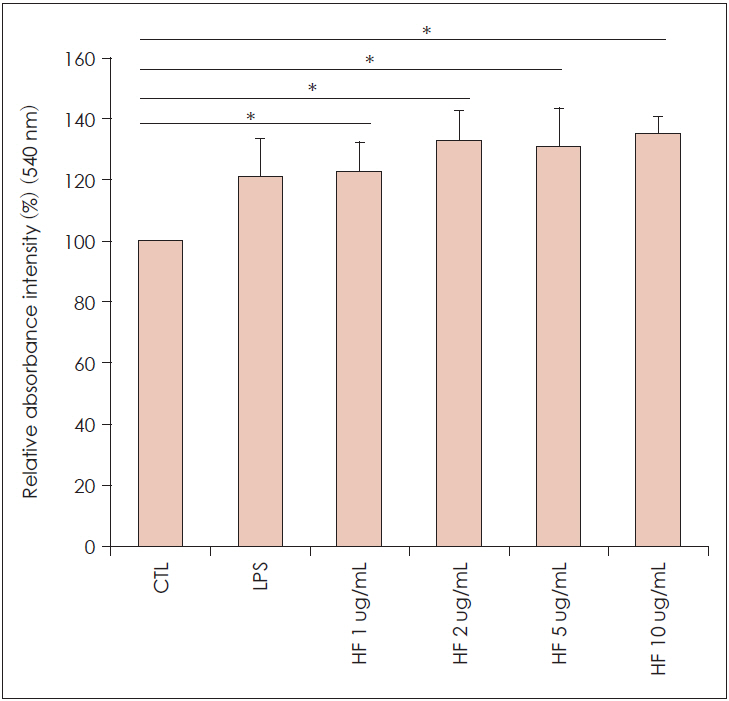
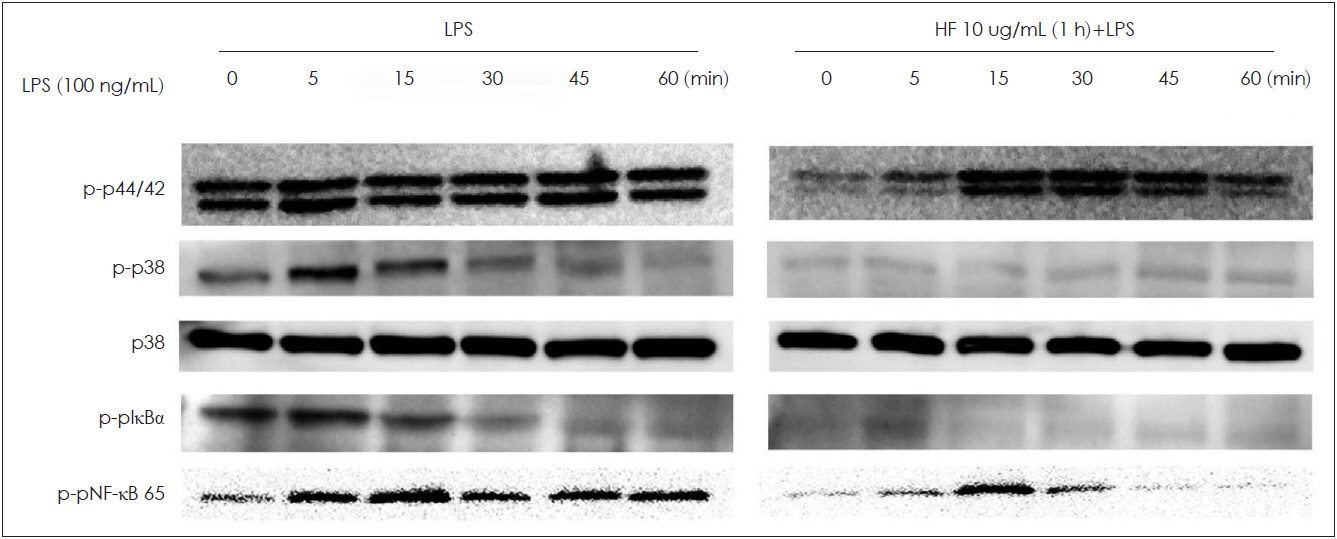
Hizikia fusiformis is widely used in oriental health food in Japan, China, and Korea, and is known for its anti-oxidation properties. Materials and Method: In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory effects and mechanisms of Hizikia fusiformis (H. fusiformis) extracts in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW 264.7 cells. RAW 264.7 cells were incubated in the presence of different concentrations of the viscozyme component of H. fusiformis (1, 2, 5, and 10 μg/mL), and changes in expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (GM-CSF, iNOS, VEGF, and COX-2) were evaluated by real-time PCR and immunoblotting. In addition, the associated signaling pathway including phospho (p)-pNF-κB 65, p-pIkBa, p-p38, and p-p44/42 was also evaluated.
Results
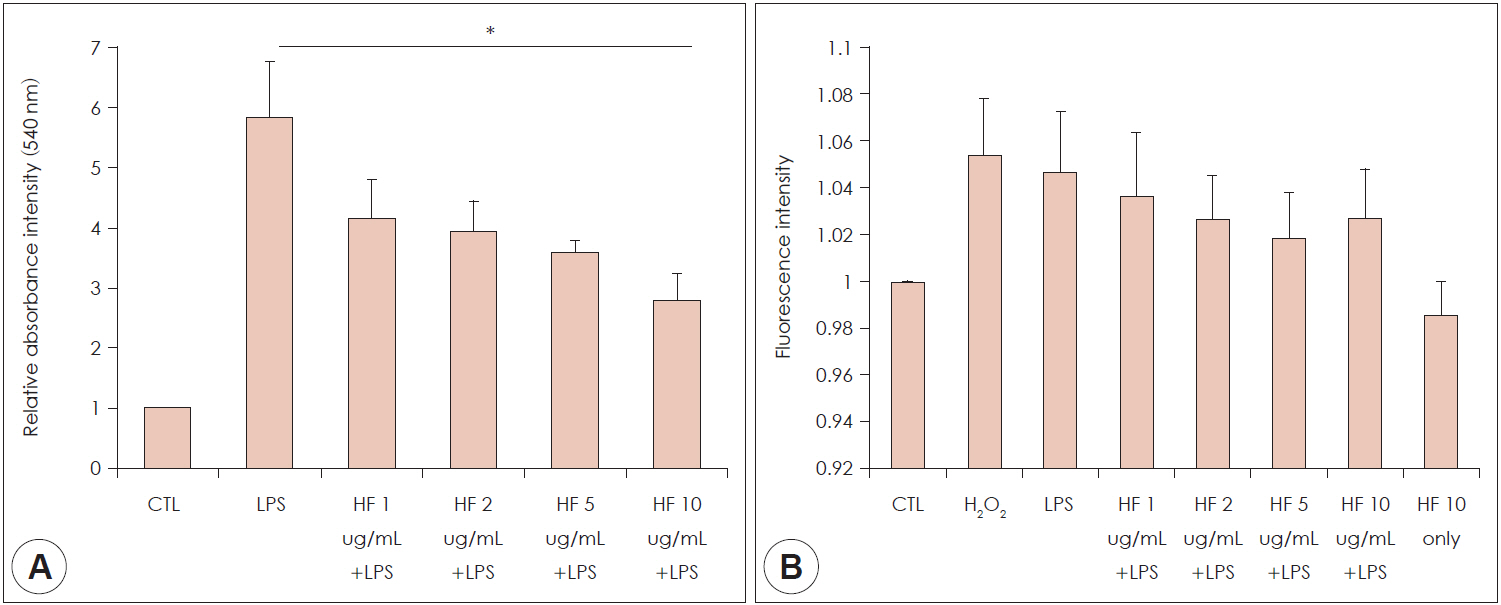
The viscozyme component of H. fusiformis downregulated the expression of GM-CSF, iNOS, VEGF, and COX-2 mRNA. The augmented NO and ROS production was decreased by administration of H. fusiformis. The signal intensity of p-pNF-κB 65, p-pIkBa, p-p38, and p-p44/42 protein activated by LPS was ameliorated by administration of the viscozyme fraction in RAW 264.7 cells.
Conclusion
These results suggest that H. fusiformis has potential as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory diseases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee KY, Jeon YJ. Macrophage activation by polysaccharide isolated from Astragalus membranaceus. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005; 5:1225–33.2. Martinez-Pomares L, Gordon S. Antigen presentation the macrophage way. Cell. 2007; 131:641–3.3. Wang Z, Xie J, Yang Y, Zhang F, Wang S, Wu T, et al. Sulfated Cyclocary apaliurus polysaccharides markedly attenuates inflammation and oxidative damage in lipopolysaccharide-treated macrophage cells and mice. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:40402.4. Kim MS, Kim SH. Inhibitory effect of astragal in on expression of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators through NF-κB in macrophages. Arch Pharm Res. 2011; 34:2101–7.5. Wu M, Wu Y, Qu M, Li W, Yan X. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of water-soluble polysaccharides from brown alga Hizikia fusiformis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013; 56:28–33.6. Shan BE, Yoshida Y, Kuroda E, Yamashita U. Immunomodulating activity of seaweed extract on human lymphocytes in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 1999; 21:59–70.7. Huh GW, Lee DY, In SJ, Lee DG, Park SY, Yi TH, et al. Fucosterols from Hizikia fusiformis and their proliferation activities on osteosarcoma-derived cell MG63. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2012; 55:551–5.8. Lee KH, Kim HJ, Kim HB, Kim ST, Choi YR, Seo DW, et al. Hizikia fusiformis fractions successfully improve atopic dermatitis indices in anti-CD3-stimulated splenocytes and 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzenetreated BALB/c mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014; 66:466–76.9. Yang EJ, Moon JY, Kim MJ, Kim DS, Kim CS, Lee WJ, et al. Inhibitory effect of Jeju endemic seaweeds on the production of proinflammatory mediators in mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010; 11:315–22.10. Kang CH, Kang SH, Boo SH, Pak SY, Choi YH, Moon DO, et al. Ethyl alcohol extract of Hizikia fusiforme induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells by generation of reactive oxygen species. Trop J Pharm Res. 2011; 10:739–46.11. Kim HW, Lee JH. Production and Characterization of β-Glucan Type Oligomer Produced with Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Capsosiphon fulvescens. KSBB Journal. 2013; 28:151–6.12. Siriwardhana N, Jeon YJ, Kim SH, Ha JH, Heo SJ, Lee KW. Enzymatic hydrolysis for effective extraction of antioxidative compounds from Hizikia fusiformis. Algae. 2004; 19:59–68.13. Arango Duque G, Descoteaux A. Macrophage Cytokines: Involvement in Immunity and Infectious Diseases. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:491.14. Denis M. Tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulate human macrophages to restrict growth of virulent Mycobacterium avium and to kill avirulent M. avium: killing effector mechanism depends on the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1991; 49:380–7.15. Hamid Q, Springall DR, Riveros-Moreno V, Chanez P, Howarth P, Redington A, et al. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in asthma. Lancet. 1993; 342:1510–3.16. McInnes IB, Leung BP, Field M, Wei XQ, Huang FP, Sturrock RD, et al. Production of nitric oxide in the synovial membrane of rheumatoid and osteoarthritis patients. J Exp Med. 1996; 184:1519–24.17. Kröncke KD, Kolb-Bachofen V, Berschick B, Burkart V, Kolb H. Activated macrophages kill pancreatic syngeneic islet cells via arginine-dependent nitric oxide generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991; 175:752–2.18. Lander HM, Sehajpal P, Levine DM, Novogrodsky A. Activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by nitric oxide-generating compounds. J Immunol. 1993; 150:1509–6.19. Pilz RB, Suhasini M, Idriss S, Meinkoth JL, Boss GR. Nitric oxide and cGMP analogs activate transcription from AP-1-responsive promoters in mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1995; 9:552–8.20. Sharma BR, Park CS, Ma SJ, Rhyu DY. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of Hizikia fusiformis via multicellular signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017; 30:43–8.21. Fridovich I. Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutases. Annual Review Biochemistry. 1995; 64:97–112.22. Hotta H, Nagano S, Ueda M, Tsujino Y, Koyama J, Osakai T. Higher radical scavenging activities of polyphenolic antioxidants can be ascribed to chemical reactions following their oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 1572:123–32.23. Czochra MP, Widensk A. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity. Journal Anlitica Chemica Acta. 2002; 452:177–84.24. Isaraf DA, Khaizurin TA, Syahida A, Lajis NH, Khozirah S. Cardamonin inhibits COX and iNOS expression via inhibition of p65NF-κB translocation and IκB phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Mol Immunol. 2007; 44:673–9.25. Kaminska B. MAPK signaling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy-from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005; 1754:253–62.26. Hoesel B, Schmid JA. The complexity of NF-kB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013; 12:86.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects on Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity of Hijikia Fusiformis Fraction
- Comparison between Immunostimulatory Activity and Molecular Structure of Different Polysaccharides
- Antiallergic Effect of Hizikia fusiformis in an Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model
- Effect of Hizikia Fusiforme Water Extracts on Mouse Immune Cell Activation
- Dopamine and serotonin alterations by Hizikia fusiformis extracts under in vitro cortical primary neuronal cell cultures