J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Apr;35(19):e129. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e129.
Differential Impact of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Levels onthe Prognosis of Patients with LiverCirrhosis According to MELD andChild-Pugh Scores
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500629
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e129
Abstract
- Background
Prognosis of patients with diverse chronic diseases is reportedly associated with 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. In this study, we investigated the potential role of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25[OH]D3) levels in improving the predictive power of conventional prognostic models for patients with liver cirrhosis.
Methods
We investigated clinical findings, including serum 25(OH)D3 levels at admission, of 155 patients with cirrhosis who were followed up for a median of 16.9 months.
Results
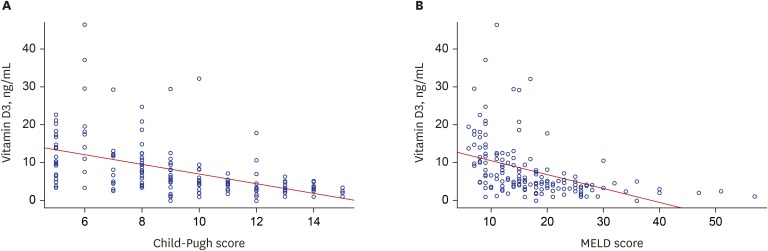
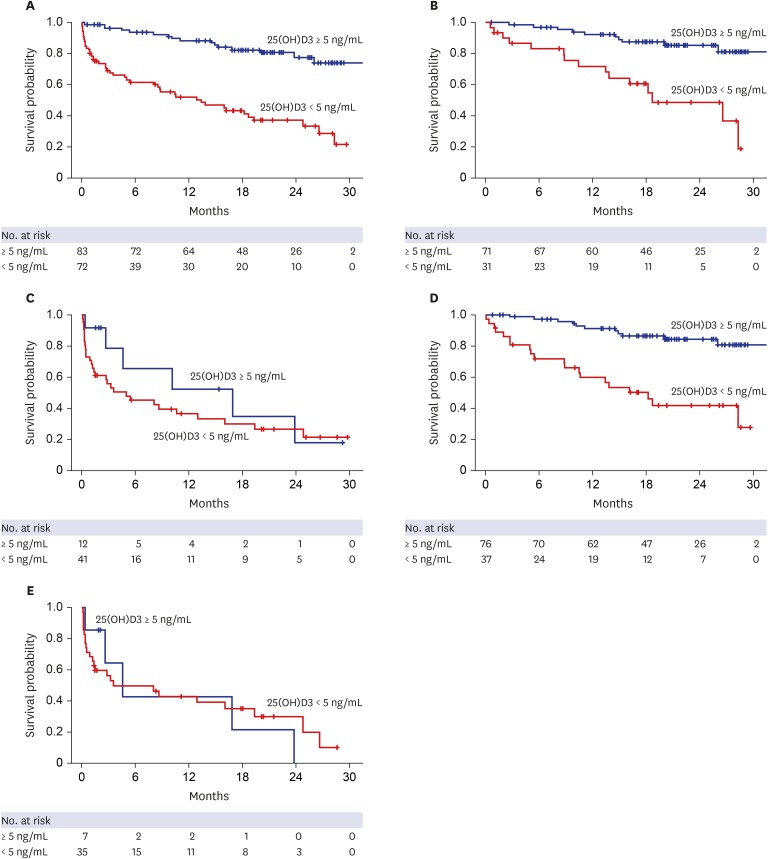
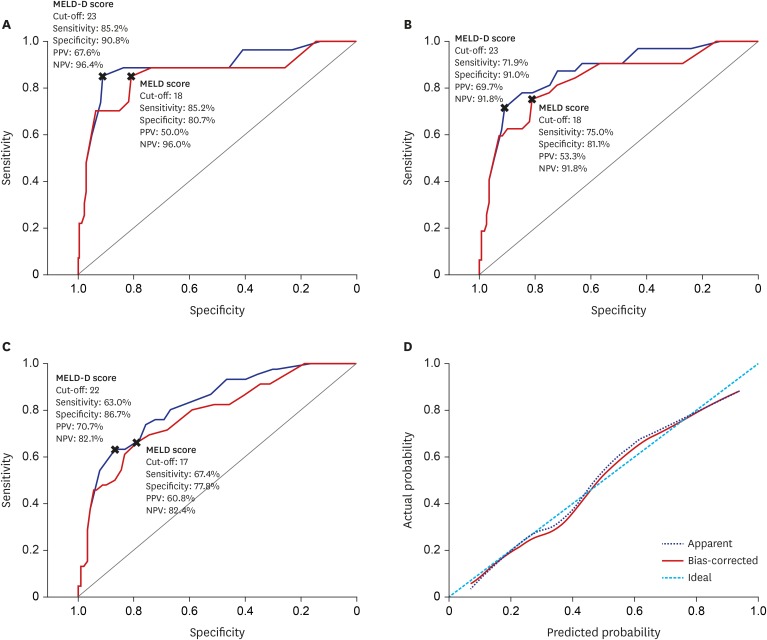
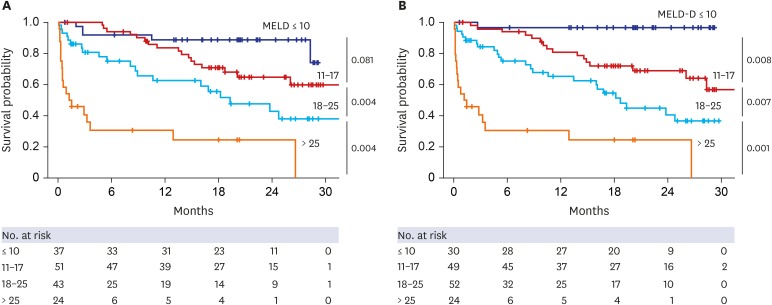
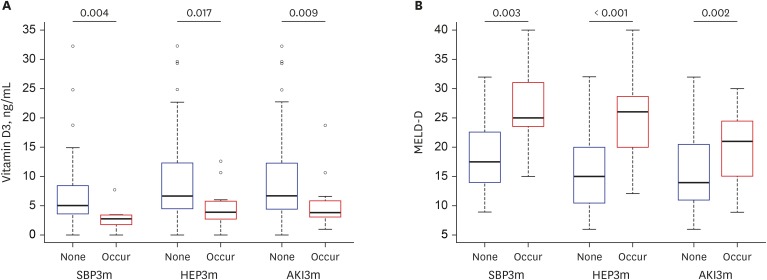
Median 25(OH)D3 levels were significantly different among patients exhibiting Child-Pugh grades A, B, and C. Mortality, including urgent transplantation, was significantly associated with 25(OH)D3 levels in univariate analysis. Severe vitamin-D deficiency (serum 25[OH]D3 level < 5.0 ng/mL) was significantly related to increased mortality, even after adjusting for Child-Pugh and Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores. In particular, the presence of severe vitamin D deficiency clearly defined a subgroup with significantly poorer survival among patients with Child-Pugh scores of 5–10 or MELD scores ≤ 20. A new combination model of MELD score and severe vitamin D deficiency showed significantly more accurate predictive power for short- and long-term mortality than MELD scores alone. Additionally, serum 25(OH)D3 levels and new model scores were significantly associated with the development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, overt encephalopathy, and acute kidney injury.
Conclusion
Serum 25(OH)D3 level is an independent prognostic factor for patients with liver cirrhosis and has a differential impact on disease outcomes according to MELD and Child-Pugh scores.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
동화 남성화스테로이드 유사체 남용 후 발생한 중증 지속 황달
Hyun Gil Goh, Yoo Jin Lee, Tae Hyung Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(3):167-170. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.3.167.
Reference
-
1. Mokdad AA, Lopez AD, Shahraz S, Lozano R, Mokdad AH, Stanaway J, et al. Liver cirrhosis mortality in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. BMC Med. 2014; 12(1):145. PMID: 25242656.
Article2. Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973; 60(8):646–649. PMID: 4541913.
Article3. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000; 31(4):864–871. PMID: 10733541.
Article4. Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, Wiesner RH, Kamath PS, Benson JT, et al. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359(10):1018–1026. PMID: 18768945.
Article5. Kim TH, Ku DH, Um SH, Lee HA, Park SW, Chang JM, et al. How can we improve the performance of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease sodium score in patients with hepatitis B virus-related decompensated liver cirrhosis commencing antiviral treatment? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33(9):1641–1648.
Article6. Matsumura T, Kato T, Sugiyama N, Tasaka-Fujita M, Murayama A, Masaki T, et al. 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses hepatitis C virus production. Hepatology. 2012; 56(4):1231–1239. PMID: 22487892.7. Chan HL, Elkhashab M, Trinh H, Tak WY, Ma X, Chuang WL, et al. Association of baseline vitamin D levels with clinical parameters and treatment outcomes in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2015; 63(5):1086–1092. PMID: 26143444.
Article8. García-Álvarez M, Pineda-Tenor D, Jiménez-Sousa MA, Fernández-Rodríguez A, Guzmán-Fulgencio M, Resino S. Relationship of vitamin D status with advanced liver fibrosis and response to hepatitis C virus therapy: a meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2014; 60(5):1541–1550. PMID: 24975775.
Article9. Arai T, Atsukawa M, Tsubota A, Koeda M, Yoshida Y, Okubo T, et al. Association of vitamin D levels and vitamin D-related gene polymorphisms with liver fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2019; 51(7):1036–1042. PMID: 30683615.
Article10. Ebadi M, Bhanji RA, Mazurak VC, Lytvyak E, Mason A, Czaja AJ, et al. Severe vitamin D deficiency is a prognostic biomarker in autoimmune hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 49(2):173–182. PMID: 30484857.
Article11. Trépo E, Ouziel R, Pradat P, Momozawa Y, Quertinmont E, Gervy C, et al. Marked 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency is associated with poor prognosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2013; 59(2):344–350. PMID: 23557869.
Article12. Putz-Bankuti C, Pilz S, Stojakovic T, Scharnagl H, Pieber TR, Trauner M, et al. Association of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with liver dysfunction and mortality in chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2012; 32(5):845–851. PMID: 22222013.
Article13. Anty R, Tonohouan M, Ferrari-Panaia P, Piche T, Pariente A, Anstee QM, et al. Low levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D are independently associated with the risk of bacterial infection in cirrhotic patients. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2014; 5(5):e56. PMID: 24871371.
Article14. Stokes CS, Krawczyk M, Reichel C, Lammert F, Grünhage F. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with mortality in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014; 44(2):176–183. PMID: 24236541.
Article15. Kubesch A, Quenstedt L, Saleh M, Rüschenbaum S, Schwarzkopf K, Martinez Y, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with hepatic decompensation and inflammation in patients with liver cirrhosis: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e0207162. PMID: 30408125.
Article16. Ramadan HK, Makhlouf NA, Mahmoud AA, Abd Elrhman M, El-Masry MA. Role of vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infections in cirrhotic patients. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019; 43(1):51–57. PMID: 30318356.
Article17. Yousif MM, Sadek AM, Farrag HA, Selim FO, Hamed EF, Salama RI. Associated vitamin D deficiency is a risk factor for the complication of HCV-related liver cirrhosis including hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Intern Emerg Med. 2019; 14(5):753–761. PMID: 30706253.
Article18. Chirumbolo S, Bjørklund G, Sboarina A, Vella A. The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a pro-survival molecule. Clin Ther. 2017; 39(5):894–916. PMID: 28438353.
Article19. Budhathoki S, Hidaka A, Yamaji T, Sawada N, Tanaka-Mizuno S, Kuchiba A, et al. Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and subsequent risk of total and site specific cancers in Japanese population: large case-cohort study within Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study cohort. BMJ. 2018; 360:k671. PMID: 29514781.
Article20. Konstantakis C, Tselekouni P, Kalafateli M, Triantos C. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2016; 29(3):297–306. PMID: 27366029.
Article21. Powe CE, Evans MK, Wenger J, Zonderman AB, Berg AH, Nalls M, et al. Vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D status of black Americans and white Americans. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369(21):1991–2000. PMID: 24256378.
Article22. Robinson-Cohen C, Hoofnagle AN, Ix JH, Sachs MC, Tracy RP, Siscovick DS, et al. Racial differences in the association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration with coronary heart disease events. JAMA. 2013; 310(2):179–188. PMID: 23839752.
Article23. Shah I, Akhtar MK, Hisaindee S, Rauf MA, Sadig M, Ashraf SS. Clinical diagnostic tools for vitamin D assessment. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018; 180:105–117. PMID: 28988826.
Article24. O'Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ; Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2010; 51(1):307–328. PMID: 20034030.25. Córdoba J. New assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2011; 54(5):1030–1040. PMID: 21145874.
Article26. Wong F. Acute kidney injury in liver cirrhosis: new definition and application. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22(4):415–422. PMID: 27987536.
Article27. Ko BJ, Kim YS, Kim SG, Park JH, Lee SH, Jeong SW, et al. Relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and liver fibrosis as assessed by transient elastography in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut Liver. 2016; 10(5):818–825. PMID: 27114415.
Article28. Kwok RM, Torres DM, Harrison SA. Vitamin D and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): is it more than just an association? Hepatology. 2013; 58(3):1166–1174. PMID: 23504808.
Article29. Kitson MT, Roberts SK. D-livering the message: the importance of vitamin D status in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2012; 57(4):897–909. PMID: 22634121.
Article30. Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, Croft JB. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among US adults with hypertension: the NHANES linked mortality study. J Hypertens. 2012; 30(2):284–289. PMID: 22179077.31. Masuda S, Okano T, Osawa K, Shinjo M, Suematsu T, Kobayashi T. Concentrations of vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D metabolites in plasma of patients with liver cirrhosis. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1989; 35(4):225–234. PMID: 2585144.
Article32. Schwartz JB, Lai J, Lizaola B, Kane L, Markova S, Weyland P, et al. A comparison of measured and calculated free 25(OH) vitamin D levels in clinical populations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99(5):1631–1637. PMID: 24483159.
Article33. Lai JC, Bikle DD, Lizaola B, Hayssen H, Terrault NA, Schwartz JB. Total 25(OH) vitamin D, free 25(OH) vitamin D and markers of bone turnover in cirrhotics with and without synthetic dysfunction. Liver Int. 2015; 35(10):2294–2300. PMID: 25757956.
Article34. Petta S, Cammà C, Scazzone C, Tripodo C, Di Marco V, Bono A, et al. Low vitamin D serum level is related to severe fibrosis and low responsiveness to interferon-based therapy in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2010; 51(4):1158–1167. PMID: 20162613.
Article35. Piano S, Tonon M, Angeli P. Management of ascites and hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatol Int. 2018; 12(Suppl 1):122–134. PMID: 28836115.
Article36. Fiati Kenston SS, Song X, Li Z, Zhao J. Mechanistic insight, diagnosis, and treatment of ammonia-induced hepatic encephalopathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 34(1):31–39. PMID: 30070387.
Article37. Vandamme D, Landuyt B, Luyten W, Schoofs L. A comprehensive summary of LL-37, the factotum human cathelicidin peptide. Cell Immunol. 2012; 280(1):22–35. PMID: 23246832.
Article38. Gubatan J, Moss AC. Vitamin D in inflammatory bowel disease: more than just a supplement. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018; 34(4):217–225. PMID: 29762159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and the severity of atopic dermatitis in children with allergic or nonallergenic sensitization
- Important predictor of mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease
- Changes of MELD: Can Exceed Child-Pugh's Authority?
- Measurement of Serum Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D2 Using Diels-Alder Derivatization and Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- New Scoring Systems for Severity Outcome of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Issues Concerning The Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score and The Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score