Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2020 Mar;23(2):174-179. 10.5223/pghn.2020.23.2.174.
Successful Treatment with Rituximab and Immunoadsorption for an Auto-Antibody Induced Bile Salt Export Pump Deficiency in a Liver Transplanted Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pediatric Hepatology and Liver Transplantation Unit, Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain. 38633jqb@gmail.com
- 2Inserm Unité Mixte de Recherche 1193, Université Paris-Saclay, Orsay France.
- 3Department of Immunology, Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- 4Department of HPB Surgery and Trasplant, Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
- KMID: 2471627
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2020.23.2.174
Abstract
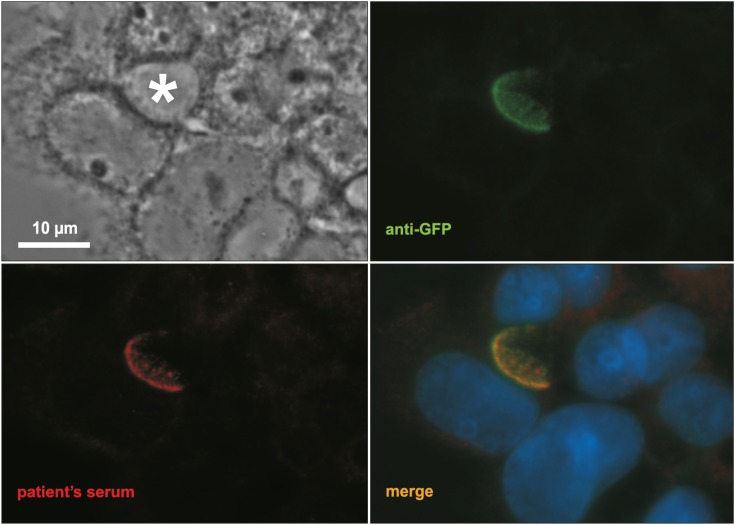
- We present an 8 years old girl who was diagnosed at 6 months of age of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis type 2. Although liver transplantation (LT) was classically considered curative for these patients, cholestasis recurrence with normal gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), mediated by anti-bile salt export pump (BSEP) antibodies after LT (auto-antibody Induced BSEP Deficiency, AIBD) has been recently reported. Our patient underwent LT at 14 months. During her evolution, patient presented three episodes of acute rejection. Seven years after the LT, the patient presented pruritus with cholestasis and elevation of liver enzymes with persistent normal GGT. Liver biopsy showed intrahepatic cholestasis and giant-cell transformation with very low BSEP activity. Auto-antibodies against BSEP were detected therefore an AIBD was diagnosed. She was treated with Rituximab and immunoadsorption with resolution of the AIBD. As a complication of the treatment she developed a pneumocystis infection successfully treated with corticoids, cotrimoxazol and anidulafungin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strautnieks SS, Bull LN, Knisely AS, Kocoshis SA, Dahl N, Arnell H, et al. A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet. 1998; 20:233–238. PMID: 9806540.
Article2. Strautnieks SS, Byrne JA, Pawlikowska L, Cebecauerová D, Rayner A, Dutton L, et al. Severe bile salt export pump deficiency: 82 different ABCB11 mutations in 109 families. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1203–1214. PMID: 18395098.
Article3. Davit-Spraul A, Gonzales E, Baussan C, Jacquemin E. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009; 4:1. PMID: 19133130.
Article4. Jansen PL, Strautnieks SS, Jacquemin E, Hadchouel M, Sokal EM, Hooiveld GJ, et al. Hepatocanalicular bile salt export pump deficiency in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:1370–1379. PMID: 10579978.
Article5. Alissa FT, Jaffe R, Shneider BL. Update on progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 46:241–252. PMID: 18376240.
Article6. Jara P, Hierro L, Martínez-Fernández P, Alvarez-Doforno R, Yánez F, Diaz MC, et al. Recurrence of bile salt export pump deficiency after liver transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:1359–1367. PMID: 19797282.
Article7. Maggiore G, Gonzales E, Sciveres M, Redon MJ, Grosse B, Stieger B, et al. Relapsing features of bile salt export pump deficiency after liver transplantation in two patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2. J Hepatol. 2010; 53:981–986. PMID: 20800306.
Article8. Keitel V, Burdelski M, Warskulat U, Kühlkamp T, Keppler D, Häussinger D, et al. Expression and localization of hepatobiliary transport proteins in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology. 2005; 41:1160–1172. PMID: 15841457.
Article9. Keitel V, Burdelski M, Vojnisek Z, Schmitt L, Häussinger D, Kubitz R. De novo bile salt transporter antibodies as a possible cause of recurrent graft failure after liver transplantation: a novel mechanism of cholestasis. Hepatology. 2009; 50:510–517. PMID: 19642168.
Article10. Davit-Spraul A, Fabre M, Branchereau S, Baussan C, Gonzales E, Stieger B, et al. ATP8B1 and ABCB11 analysis in 62 children with normal gamma-glutamyl transferase progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC): phenotypic differences between PFIC1 and PFIC2 and natural history. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1645–1655. PMID: 20232290.
Article11. Cassio D, Macias RI, Grosse B, Marin JJ, Monte MJ. Expression, localization, and inducibility by bile acids of hepatobiliary transporters in the new polarized rat hepatic cell lines, Can 3-1 and Can 10. Cell Tissue Res. 2007; 330:447–460. PMID: 17909858.
Article12. Gonzales E, Grosse B, Schuller B, Davit-Spraul A, Conti F, Guettier C, et al. Targeted pharmacotherapy in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2: Evidence for improvement of cholestasis with 4-phenylbutyrate. Hepatology. 2015; 62:558–566. PMID: 25716872.
Article13. Tu GW, Ju MJ, Xu M, Rong RM, He YZ, Xue ZG, et al. Combination of caspofungin and low-dose trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole for the treatment of severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in renal transplant recipients. Nephrology (Carlton). 2013; 18:736–742. PMID: 24571744.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Use of Bortezomib for Recurrent Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type II After Liver Transplantation: A Pediatric Case with a 9-Year Follow-Up
- Bipolar and Related Disorders Induced by Sodium 4-Phenylbutyrate in a Male Adolescent with Bile Salt Export Pump Deficiency Disease
- Effect of Thyroid Hormone to the Expression of Bile Salt Export Pump
- Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis in Korea: A Clinicopathological Study of Five Patients
- A Case of Prolonged Hypogammaglobulinemia after Rituximab-Containing Chemotherapy in a Patient with Lymphoma