Diabetes Metab J.
2020 Feb;44(1):173-185. 10.4093/dmj.2018.0211.
Role of MicroRNA-34a in Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Biomedical Science and Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. kskim@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Jilin Central Hospital, Jilin University, Jilin, China.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Thoracic Surgery, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2470965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0211
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recent studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in the process of cardiomyocyte apoptosis. We have previously reported that granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) ameliorated diastolic dysfunction and attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. In this study, we hypothesized a regulatory role of cardiac miRNAs in the mechanism of the anti-apoptotic effect of G-CSF in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model.
METHODS
Rats were given a high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin injection and then randomly allocated to receive treatment with either G-CSF or saline. H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes were cultured under a high glucose (HG) condition to induce diabetic cardiomyopathy in vitro. We examined the extent of apoptosis, miRNA expression, and miRNA target genes in the myocardium and H9c2 cells.
RESULTS
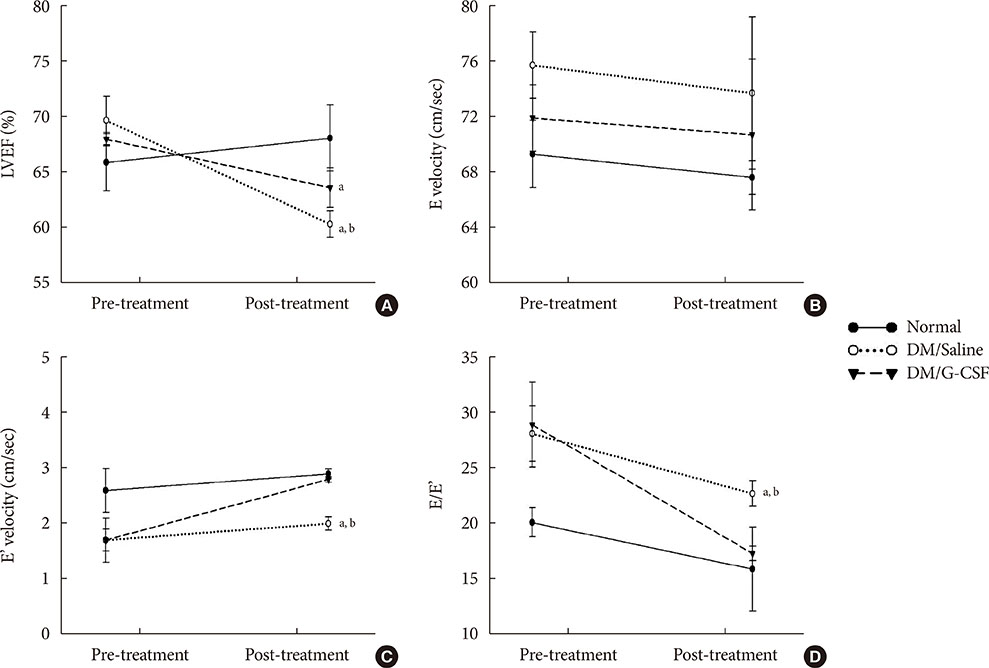
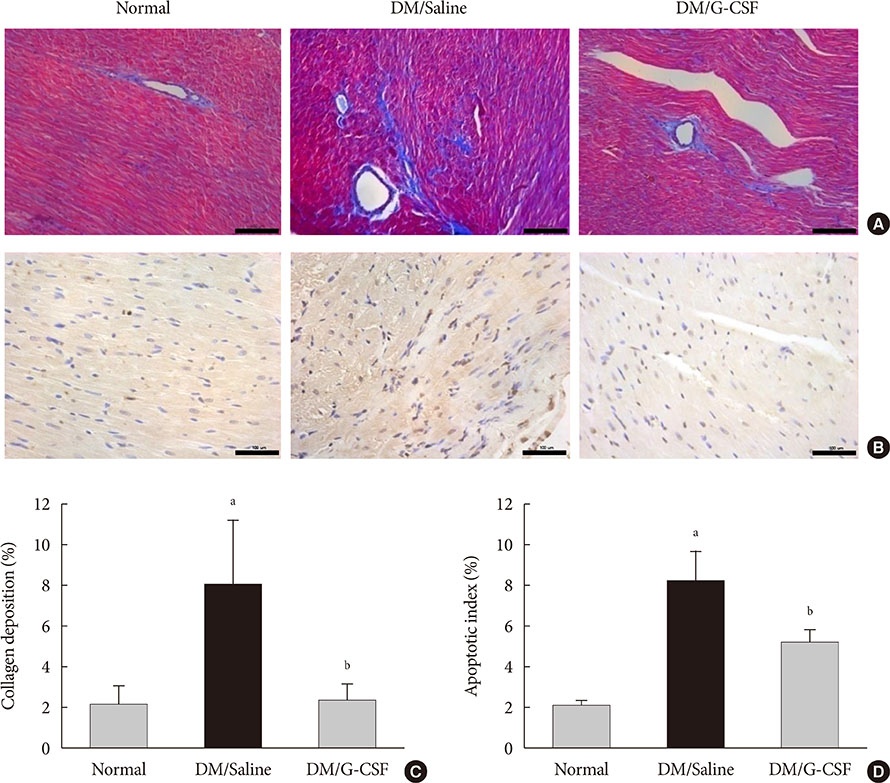
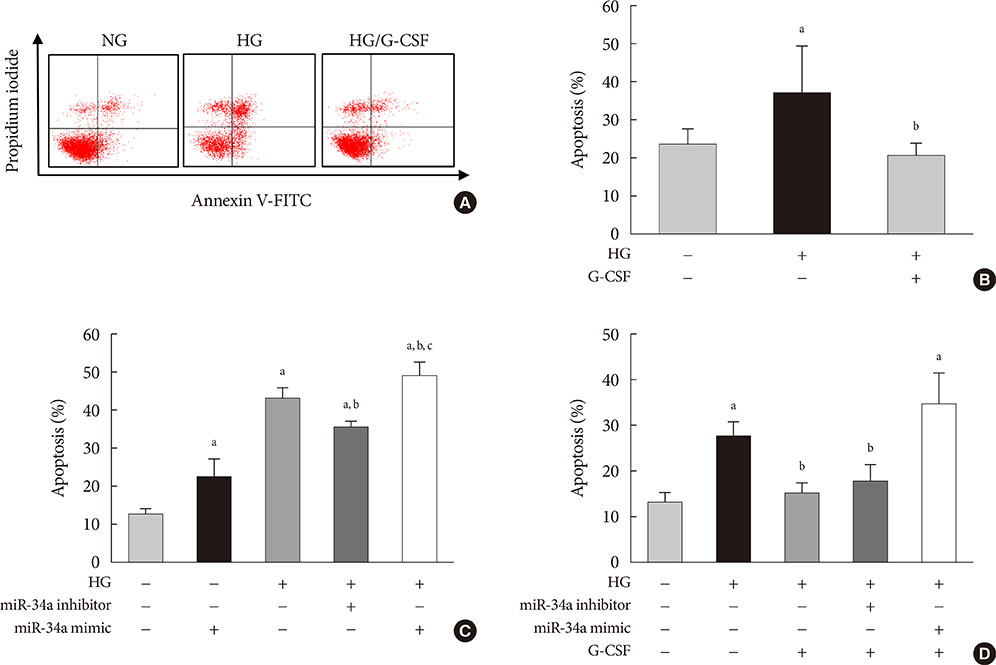
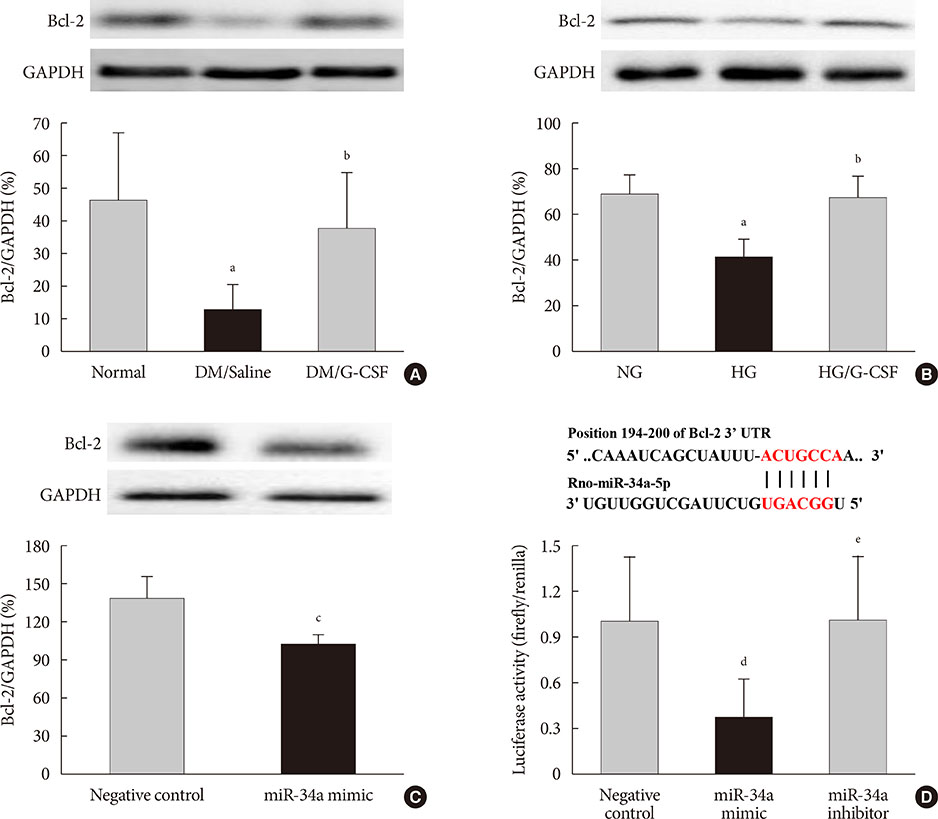
G-CSF treatment significantly decreased apoptosis and reduced miR-34a expression in diabetic myocardium and H9c2 cells under the HG condition. G-CSF treatment also significantly increased B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) protein expression as a target for miR-34a. In addition, transfection with an miR-34a mimic significantly increased apoptosis and decreased Bcl-2 luciferase activity in H9c2 cells.
CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that G-CSF might have an anti-apoptotic effect through down-regulation of miR-34a in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Diabetic Cardiomyopathies*
Diet, High-Fat
Down-Regulation
Glucose
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
In Vitro Techniques
Luciferases
Lymphoma, B-Cell
MicroRNAs
Models, Animal
Myocardium
Myocytes, Cardiac
Rats
Streptozocin
Transfection
Glucose
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
Luciferases
MicroRNAs
Streptozocin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):54-55. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0019.
Reference
-
1. Bugger H, Abel ED. Rodent models of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Dis Model Mech. 2009; 2:454–466.
Article2. Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ. Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes. 2002; 51:1938–1948.
Article3. Zhou Q, Lv D, Chen P, Xu T, Fu S, Li J, Bei Y. MicroRNAs in diabetic cardiomyopathy and clinical perspectives. Front Genet. 2014; 5:185.
Article4. Cheng Y, Liu X, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J, Zhang C. MicroRNA-21 protects against the H(2)O(2)-induced injury on cardiac myocytes via its target gene PDCD4. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009; 47:5–14.
Article5. Liu Z, Ye P, Wang S, Wu J, Sun Y, Zhang A, Ren L, Cheng C, Huang X, Wang K, Deng P, Wu C, Yue Z, Xia J. MicroRNA-150 protects the heart from injury by inhibiting monocyte accumulation in a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015; 8:11–20.
Article6. Zhu K, Liu D, Lai H, Li J, Wang C. Developing miRNA therapeutics for cardiac repair in ischemic heart disease. J Thorac Dis. 2016; 8:E918–E927.
Article7. Tang Y, Zheng J, Sun Y, Wu Z, Liu Z, Huang G. MicroRNA-1 regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2. Int Heart J. 2009; 50:377–387.
Article8. Flemming A. Heart failure: targeting miRNA pathology in heart disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:336.9. Liu L, Zhang G, Liang Z, Liu X, Li T, Fan J, Bai J, Wang Y. MicroRNA-15b enhances hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via a mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis. 2014; 19:19–29.
Article10. Mao J, Lv Z, Zhuang Y. MicroRNA-23a is involved in tumor necrosis factor-α induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells and myocardial infarction. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014; 97:23–30.
Article11. Song CL, Liu B, Diao HY, Shi YF, Zhang JC, Li YX, Liu N, Yu YP, Wang G, Wang JP, Li Q. Down-regulation of microRNA-320 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis and protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by targeting IGF-1. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:39740–39757.
Article12. Xie Q, Zhao C, Ye Z, Yang F, Ruan Q, Xie W. Effects of microRNA-21 on the myocardial cell apoptosis induced by ischemia and hypoxia in rat. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2014; 30:153–157.13. Zhang B, Zhou M, Li C, Zhou J, Li H, Zhu D, Wang Z, Chen A, Zhao Q. MicroRNA-92a inhibition attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardiocyte apoptosis by targeting Smad7. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e100298.
Article14. Zhao F, Li B, Wei YZ, Zhou B, Wang H, Chen M, Gan XD, Wang ZH, Xiong SX. MicroRNA-34a regulates high glucose-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013; 33:834–839.
Article15. Demetri GD, Griffin JD. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood. 1991; 78:2791–2808.
Article16. Harada M, Qin Y, Takano H, Minamino T, Zou Y, Toko H, Ohtsuka M, Matsuura K, Sano M, Nishi J, Iwanaga K, Akazawa H, Kunieda T, Zhu W, Hasegawa H, Kunisada K, Nagai T, Nakaya H, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Komuro I. G-CSF prevents cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by activating the Jak-Stat pathway in cardiomyocytes. Nat Med. 2005; 11:305–311.
Article17. Huttmann A, Duhrsen U, Stypmann J, Noppeney R, Nuckel H, Neumann T, Gutersohn A, Nikol S, Erbel R. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced blood stem cell mobilisation in patients with chronic heart failure: feasibility, safety and effects on exercise tolerance and cardiac function. Basic Res Cardiol. 2006; 101:78–86.18. Lim YH, Joe JH, Jang KS, Song YS, So BI, Fang CH, Shin J, Kim JH, Lim HK, Kim KS. Effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) on diabetic cardiomyopathy in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2011; 10:92.
Article19. Shin JH, Lim YH, Song YS, So BI, Park JY, Fang CH, Lee Y, Kim H, Kim KS. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and ameliorates diastolic dysfunction in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2014; 28:211–220.
Article20. Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P. Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 2005; 52:313–320.
Article21. Sugano M, Yamato H, Hayashi T, Ochiai H, Kakuchi J, Goto S, Nishijima F, Iino N, Kazama JJ, Takeuchi T, Mokuda O, Ishikawa T, Okazaki R. High-fat diet in low-dose-streptozotocin-treated heminephrectomized rats induces all features of human type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a new rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006; 16:477–484.
Article22. Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG. Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2010; 1:94–99.
Article23. Hu M, Ye P, Liao H, Chen M, Yang F. Metformin protects H9C2 cardiomyocytes from high-glucose and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation and inflammatory responses: role of AMPK and JNK. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:2961954.
Article24. Song YS, Fang CH, So BI, Park JY, Lee Y, Shin JH, Jun DW, Kim H, Kim KS. Time course of the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rat. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013; 2013:342648.
Article25. Lee KM, Kang HA, Park M, Lee HY, Choi HR, Yun CH, Oh JW, Kang HS. Interleukin-24 attenuates β-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting apoptosis, the expression of calcification and osteoblastic markers, and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 428:50–55.
Article26. Song YS, Fang CH, So BI, Park JY, Jun DW, Kim KS. Therapeutic effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis in the rat. Ann Hepatol. 2013; 12:115–122.
Article27. Cai L, Kang YJ. Cell death and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2003; 3:219–228.
Article28. Liu X, Liu S. Role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biomed Rep. 2017; 6:140–145.
Article29. Zheng D, Ma J, Yu Y, Li M, Ni R, Wang G, Chen R, Li J, Fan GC, Lacefield JC, Peng T. Silencing of miR-195 reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy in C57BL/6 mice. Diabetologia. 2015; 58:1949–1958.
Article30. Pinti MV, Hathaway QA, Hollander JM. Role of microRNA in metabolic shift during heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017; 312:H33–H45.
Article31. Liu X, Tong Z, Chen K, Hu X, Jin H, Hou M. The role of miRNA-132 against apoptosis and oxidative stress in heart failure. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:3452748.
Article32. Deindl E, Zaruba MM, Brunner S, Huber B, Mehl U, Assmann G, Hoefer IE, Mueller-Hoecker J, Franz WM. G-CSF administration after myocardial infarction in mice attenuates late ischemic cardiomyopathy by enhanced arteriogenesis. FASEB J. 2006; 20:956–958.
Article33. Zhang X, Ma X, An H, Xu C, Cao W, Yuan W, Ma J. Upregulation of microRNA-125b by G-CSF promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:50642–50654.
Article34. Liu Y, Liu D, Guo G, Mao Y, Wang X. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on wound healing and microRNA expression in diabetic rats. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2014; 30:243–250.35. Baez A, Martin-Antonio B, Piruat JI, Prats C, Alvarez-Laderas I, Barbado MV, Carmona M, Urbano-Ispizua A, Perez-Simon JA. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor produces long-term changes in gene and microRNA expression profiles in CD34+ cells from healthy donors. Haematologica. 2014; 99:243–251.
Article36. van Rooij E, Olson EN. MicroRNAs: powerful new regulators of heart disease and provocative therapeutic targets. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:2369–2376.
Article37. Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L, Xiang D, Desano JT, Bommer GT, Fan D, Fearon ER, Lawrence TS, Xu L. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6816.
Article38. Chen Z, Chua CC, Ho YS, Hamdy RC, Chua BH. Overexpression of Bcl-2 attenuates apoptosis and protects against myocardial I/R injury in transgenic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001; 280:H2313–H2320.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sweet Syndrome in a Child with Aplastic Anemia after Receiving Recombinant Granulocyte Colony-stimulating Factor
- Two cases of congenital agranulocytosis treated with recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- Role of Autophagy in Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Induced Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- The effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in chemotherapy of acute myelogenous leukemia
- The effects on the production of platelet activating factor in the cultured human endothelial cells by interleukin-6 and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor