J Breast Cancer.
2019 Dec;22(4):661-666. 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e44.
Ribociclib-Related Stevens–Johnson Syndrome: Oncologic Awareness, Case Report, and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Oncology, University Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain. r.y.barrio@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, University Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain.
- 3Department of Pathology, University Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain.
- 4Department of Clinical Oncology, Getafe Hospital, Madrid, Spain.
- 5Department of Dermatology, Getafe Hospital, Madrid, Spain.
- 6Division of Gyneco-Oncology, Breast Cancer Unit, University Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain.
- KMID: 2470903
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e44
Abstract
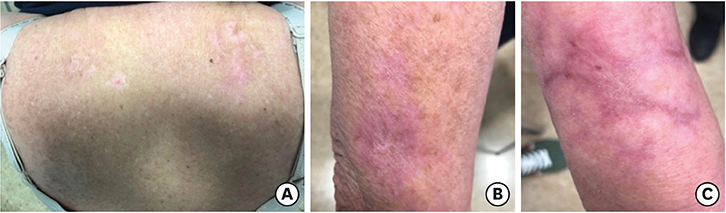
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis belong to a severe dermatopathic spectrum that includes frequently fatal mucocutaneous manifestations consisting of whole epidermal necrosis and sloughing with bullous transformation, blistering, and further skin detachment. Notably, cancer patients are at higher risk of developing SJS than the general population as a consequence of both the nature of neoplastic disease and frequent exposure to anticancer drugs. Ribociclib is a newly approved cycline-dependent kinase inhibitor that has been recently associated with a single case of SJS. We hereby present a case of ribociclib-related SJS. Early detection of threatening skin lesions is crucial to permit the immediate discontinuation of ribociclib given the predictable and unacceptable risk level. In cases of established SJS, early aggressive support should be initiated, ribociclib should be abruptly discontinued, and specific treatment based on actual evidence should be started.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stern RS, Divito SJ. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: associations, outcomes, and pathobiology-thirty years of progress but still much to be done. J Invest Dermatol. 2017; 137:1004–1008.
Article2. Sekula P, Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Halevy S, et al. Comprehensive survival analysis of a cohort of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2013; 133:1197–1204.
Article3. Widmer S, Grossman M. Chemotherapy patient with Stevens-Johnson syndrome presents to the emergency department: a case report. Am J Emerg Med. 2018; 36:1325.e3–1325.e4.
Article4. Karagounis T, Vallurupalli M, Nathan N, Nazarian R, Vedak P, Spring L, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome-like eruption from palbociclib in a patient with metastatic breast cancer. JAAD Case Rep. 2018; 4:452–454.
Article5. Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:1738–1748.
Article6. Harris V, Jackson C, Cooper A. Review of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:E2135.
Article7. Zimmermann S, Sekula P, Venhoff M, Motschall E, Knaus J, Schumacher M, et al. Systemic immunomodulating therapies for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017; 153:514–522.
Article8. Faye O, Roujeau JC. Treatment of epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IV Ig): clinical experience to date. Drugs. 2005; 65:2085–2090.
Article9. González-Herrada C, Rodríguez-Martín S, Cachafeiro L, Lerma V, González O, Lorente JA, et al. Cyclosporine use in epidermal necrolysis is associated with an important mortality reduction: evidence from three different approaches. J Invest Dermatol. 2017; 137:2092–2100.
Article10. Ng QX, De Deyn ML, Venkatanarayanan N, Ho CY, Yeo WS. A meta-analysis of cyclosporine treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Inflamm Res. 2018; 11:135–142.11. Wang CW, Yang LY, Chen CB, Ho HC, Hung SI, Yang CH, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of TNF-α antagonist in CTL-mediated severe cutaneous adverse reactions. J Clin Invest. 2018; 128:985–996.
Article12. Gillis NK, Hicks JK, Bell GC, Daly AJ, Kanetsky PA, McLeod HL. Incidence and triggers of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in a large cancer patient cohort. J Invest Dermatol. 2017; 137:2021–2023.
Article13. Gravante G, Delogu D, Marianetti M, Esposito G, Montone A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Steven-Johnson syndrome in oncologic patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2007; 11:269–274.14. Rosen AC, Balagula Y, Raisch DW, Garg V, Nardone B, Larsen N, et al. Life-threatening dermatologic adverse events in oncology. Anticancer Drugs. 2014; 25:225–234.
Article15. Ng CY, Chen CB, Wu MY, Wu J, Yang CH, Hui RC, et al. Anticancer drugs induced severe adverse cutaneous drug reactions: an updated review on the risks associated with anticancer targeted therapy or immunotherapies. J Immunol Res. 2018; 2018:5376476.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Plus Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome Associated with Ibuprofen Use
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome with Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in a Hypoxic Brain Injury Patient Treated with Carbamazepine
- A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Which Was Misdiagnosed as Sepsis and Infectious Skin Disease
- Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome