J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2020 Feb;55(1):62-70. 10.4055/jkoa.2020.55.1.62.
External Tibial Torsion with Proximal Tibia Vara in Total Knee Arthroplasty of Advanced Osteoarthritis with Severe Varus Deformed Knees
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daejeon Sun Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. mydangjang@naver.com
- KMID: 2470770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2020.55.1.62
Abstract
- PURPOSE
External tibia torsion and proximal tibial vara have been reported in severe varus deformed osteoarthritis, which is a tibio-femoral angle of more than 20°. The radiology measurements were compared with those of control group and the preoperative and follow-up radiology and clinical results were examined.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2007 to March 2016, 43 knees from 37 persons, who underwent total knee arthroplasty for a severe varus deformity of more than 20° on the tibio-femoral angle on the standing radiographs and had a follow-up period more than two years, were examined. The mean follow-up period was 45.7 months. The control group, who underwent conservative treatments, had Kellgren-Lawrence grade three osteoarthritis and a tibio-femoral angle of less than 3° varus. The external tibial torsion of enrolled patients and control group were estimated using the proximal tibio-fibular overlap length and the tibial torsion values on computed tomography. The proximal tibia vara was measured using the proximal tibial tilt angle. The preoperative and postoperative proximal tibio-fibular overlap length, tibial torsion value, proximal tibial tilt angle, and hospital for special surgery (HSS) score were evaluated.
RESULTS
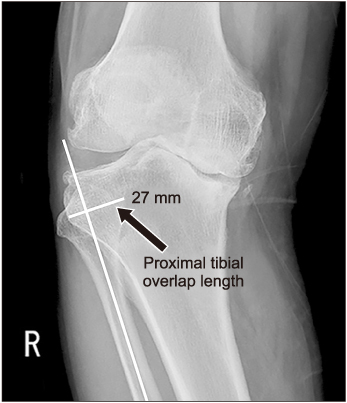
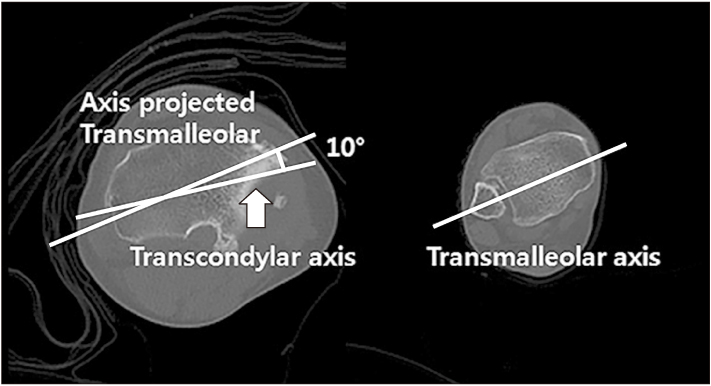
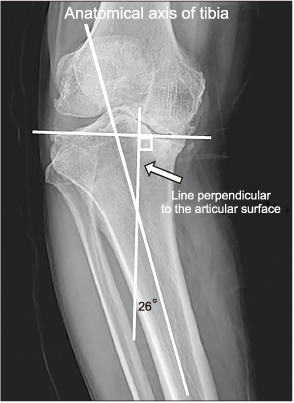
The mean proximal tibio-fibular overlap length was 18.6 mm preoperatively and 11.2 mm (p=0.031) at the follow-up. The control group had a mean proximal tibio-fibular overlap length of 8.7 mm (p=0.024). The mean tibial torsion value was 13.8° preoperatively and 14.0° (p=0.489) at the follow-up. The control group had a mean tibial torsion value of 21.9° (p=0.012). The mean proximal tibial tilt angle was 12.2° preoperatively and 0° (p<0.01) at the follow-up. The control group had a mean proximal tilt angle of 1.2° (p<0.01). The preoperative tibiofemoral angle and mechanical axis deviation were corrected from preoperative 28.3° and medial 68.4 mm to postoperative 0.7° and medial 3.5 mm (p<0.01, p<0.01), respectively. The HSS scores increased from 34 points of preoperatively to 87 points at the last follow-up (p=0.028).
CONCLUSION
Patients with advanced osteoarthritis with a severe varus deformity of more than 20° had significant increases in the external tibial torsion and varus of the proximal tibia. The tibial torsion value before and after surgery in the enrolled patients was not changed statistically, but good clinical results without complications were obtained.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chon JG, Song IS, Kim JB, Jang GI, Ahn CH, Yoon JY. The effects of autologous structural bone graft without internal fixation on posteromedial tibial bone defect in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017; 52:514–520.
Article2. Cooke D, Scudamore A, Li J, Wyss U, Bryant T, Costigan P. Axial lower-limb alignment: comparison of knee geometry in normal volunteers and osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997; 5:39–47.
Article3. Nagamine R, Miyanishi K, Miura H, Urabe K, Matsuda S, Iwamoto Y. Medial torsion of the tibia in Japanese patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (408):218–224.
Article4. Matsui Y, Kadoya Y, Uehara K, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K. Rotational deformity in varus osteoarthritis of the knee: analysis with computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (433):147–151.5. Turner MS. The association between tibial torsion and knee joint pathology. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):47–51.
Article6. Eckhoff DG, Johnston RJ, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RF, Wiedel JD. Version of the osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty. 1994; 9:73–79.
Article7. Yagi T, Sasaki T. Tibial torsion in patients with medial-type osteoarthritic knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (213):177–182.
Article8. Ise N. Torsion of the lower extremity. J Jpn Orthop Assoc. 1976; 50:157–168.9. Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T, et al. Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; (366):155–163.
Article10. Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L. Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (392):46–55.
Article11. Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (356):144–153.
Article12. Nicoll D, Rowley DI. Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:1238–1244.
Article13. Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Mahoney OM, Tullos HS. The effect of femoral component position on patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (260):43–51.
Article14. Jakob RP, Haertel M, Stüssi E. Tibial torsion calculated by computerised tomography and compared to other methods of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980; 62:238–242.
Article15. Madadi F, Madadi F, Maleki A, Shamie AN, Washington ER 3rd, Yazdanshenas H. A new method for tibial torsion measurement by computerized tomography. J Orthop. 2015; 13:43–47.
Article16. Koenig JK, Pring ME, Dwek JR. MR evaluation of femoral neck version and tibial torsion. Pediatr Radiol. 2012; 42:113–115.
Article17. Kharbanda Y, Sharma M. Autograft reconstructions for bone defects in primary total knee replacement in severe varus knees. Indian J Orthop. 2014; 48:313–318.
Article18. Bilgen MS, Eken G, Guney N. Short-term results of the management of severe bone defects in primary TKA with cement and K-wires. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017; 51:388–392.
Article19. Staheli LT, Engel GM. Tibial torsion: a method of assessment and a survey of normal children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972; 86:183–186.20. Turner MS, Smillie IS. The effect of tibial torsion of the pathology of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981; 63:396–398.
Article21. Clementz BG. Assessment of tibial torsion and rotational deformity with a new fluoroscopic technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (245):199–209.
Article22. Fabry G, Cheng LX, Molenaers G. Normal and abnormal torsional development in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):22–26.
Article23. Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR. The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13:812–815.
Article24. Kobayashi A, Himeno R, Uezaki N, Toyonaga T, Mitsuyasu T, Chikama H. Rotation of the leg in osteoarthritis of the knee joint(varus type). Jpn Orthop Surg. 1978; 29:753.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
- Total Knee Arthroplasty in Varus Deformit
- Significant Incidence of Extra-Articular Tibia Vara Affects Radiological Outcome of Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Tibial Torsion and Knee Varus Angle: Are These Aetiologies of Hallux Valgus?
- The Bone Mineral Density of the Proximal Tibia, Lumbar Spine and Proximal Femur and Its Correlation with the Alignment of the Lower Extremity in Knee Osteoarthritic Patients