Clin Orthop Surg.
2017 Dec;9(4):458-464. 10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458.
Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics and Trauma, Hosmat Hospital, Bangalore, India. docmnkumar@gmail.com
- KMID: 2412246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
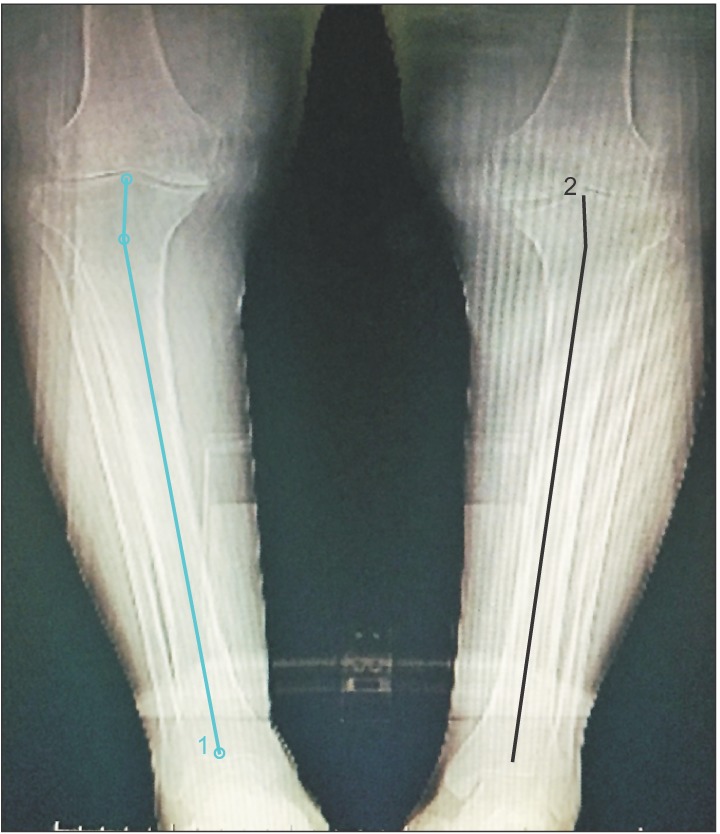
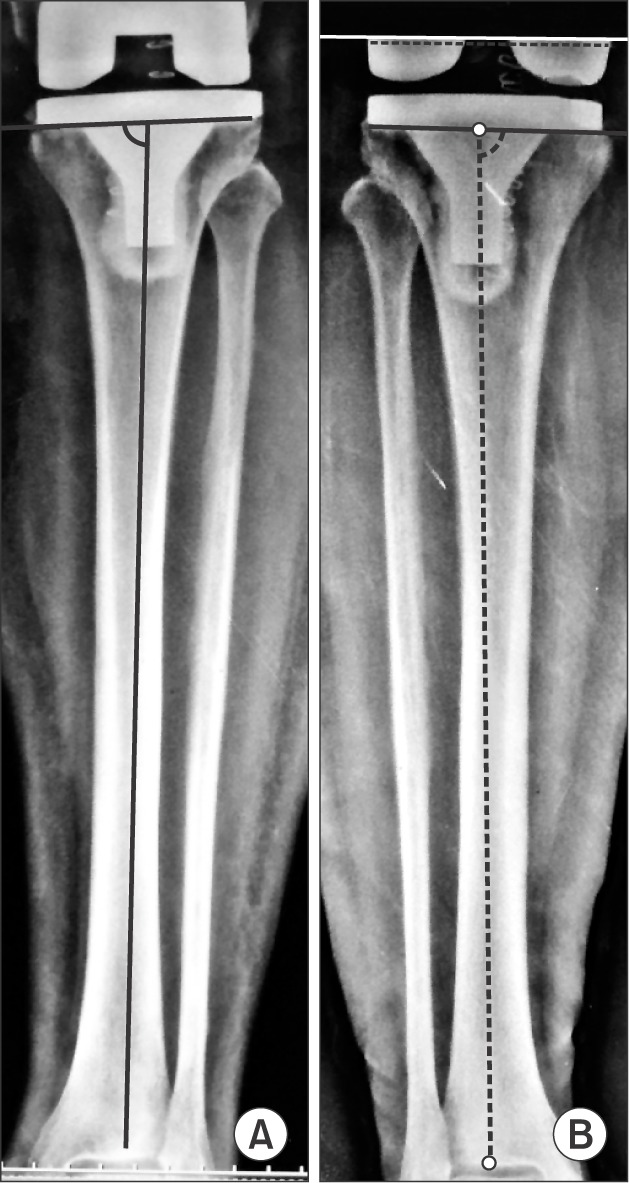
The tibial cut referenced to the center of the intercondylar eminence often leads to varus malalignment in the presence of preexisting proximal tibia vara. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of lateralization of the lateral tibial plateau reference point (based on the amount of proximal tibia vara) on the postoperative coronal plane alignment.
METHODS
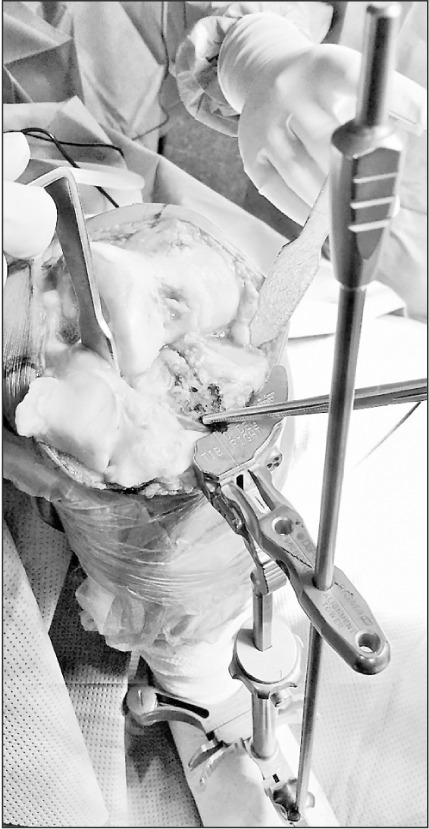
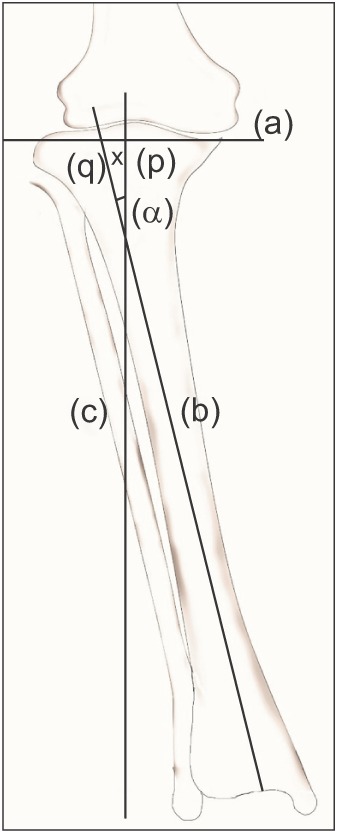
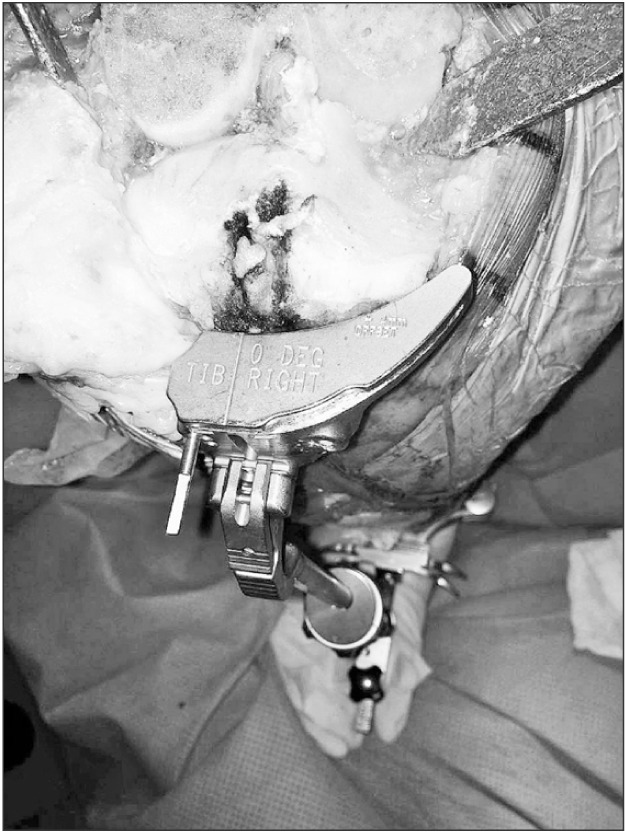
In this prospective cohort study, 62 patients (95 knees) with osteoarthritis and proximal tibia vara underwent primary total knee arthroplasty using a lateral tibial plateau reference point for the extramedullary jig. The pre- and postoperative radiographs were obtained for measurement of mechanical axis deviation, degree of tibia vara, proximal lateral reference point of the tibial condyle, and coronal alignment of the femoral and tibial components. The distance between the tibial reference point and the center of the intercondylar eminence was measured intraoperatively.
RESULTS
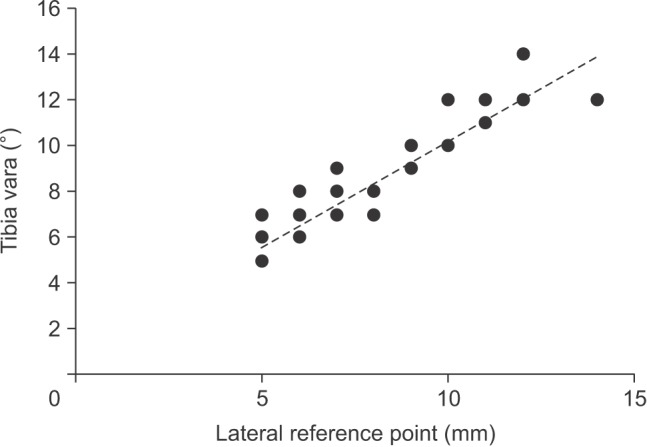
The mean tibia vara was 7.1° (standard deviation [SD], 2.3°). The mean lateral displacement of the reference point was 7 mm (SD, 2.2 mm). Postoperative tibiofemoral angle was 6° to 10° of valgus in 94% of cases. There was a strong correlation between the magnitude of tibia vara and the amount of lateralization of the tibial reference point (R² = 0.79, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
In total knee arthroplasty patients with proximal tibia vara, reasonable accuracy can be achieved with use of the extramedullary jig for tibial component alignment by lateralizing the proximal tibial reference point.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (226):49–64.
Article2. Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG. Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (299):31–43.
Article3. Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(6 Suppl):39–43. PMID: 19553073.4. Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73(5):709–714. PMID: 1894655.
Article5. Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, et al. Changes in knee alignment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1999; 14(5):566–570. PMID: 10475555.
Article6. Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, Ng TP. Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2007; 15(1):32–36. PMID: 17429114.
Article7. Lasam MP, Lee KJ, Chang CB, Kang YG, Kim TK. Femoral lateral bowing and varus condylar orientation are prevalent and affect axial alignment of TKA in Koreans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(5):1472–1483. PMID: 23011845.
Article8. Kim SM, Kim KW, Cha SM, Han KY. Proximal tibial resection in varus-deformed tibiae during total knee arthroplasty: an in vitro study using sawbone model. Int Orthop. 2015; 39(3):429–434. PMID: 25159008.
Article9. Han KY, Chae WY. The position of proximal reference point of tibia plateau for correct tibial osteotomy in total knee replacement: prospective randomized and 6 years follow-up study. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2011; 23(4):197–202. PMID: 22570834.
Article10. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16(4):494–502. PMID: 13498604.
Article11. Scuderi GR, Bourne RB, Noble PC, Benjamin JB, Lonner JH, Scott WN. The new Knee Society Knee Scoring System. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(1):3–19. PMID: 22045067.
Article12. Brys DA, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Vaughn BK. A comparison of intramedullary and extramedullary alignment systems for tibial component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (263):175–179.
Article13. Maestro A, Harwin SF, Sandoval MG, Vaquero DH, Murcia A. Influence of intramedullary versus extramedullary alignment guides on final total knee arthroplasty component position: a radiographic analysis. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13(5):552–558. PMID: 9726321.14. Simmons ED Jr, Sullivan JA, Rackemann S, Scott RD. The accuracy of tibial intramedullary alignment devices in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1991; 6(1):45–50. PMID: 2016608.
Article15. Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW Jr. Accuracy of intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment cutting systems in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (321):106–110.
Article16. Chiu KY, Yau WP, Ng TP, Tang WM. The accuracy of extramedullary guides for tibial component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008; 32(4):467–471. PMID: 17364176.
Article17. Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM. Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993; 8(4):419–426. PMID: 8409995.
Article18. Dennis DA, Channer M, Susman MH, Stringer EA. Intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment systems in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993; 8(1):43–47. PMID: 8436988.
Article19. Tsukeoka T, Lee TH, Tsuneizumi Y, Suzuki M. The tibial crest as a practical useful landmark in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2014; 21(1):283–289. PMID: 23154034.
Article20. Schneider M, Heisel C, Aldinger PR, Breusch SJ. Use of palpable tendons for extramedullary tibial alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22(2):219–226. PMID: 17275637.
Article21. Fukagawa S, Matsuda S, Mitsuyasu H, et al. Anterior border of the tibia as a landmark for extramedullary alignment guide in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(6):919–924. PMID: 21259337.
Article22. Siston RA, Giori NJ, Goodman SB, Delp SL. Surgical navigation for total knee arthroplasty: a perspective. J Biomech. 2007; 40(4):728–735. PMID: 17317419.
Article23. Stulberg SD, Loan P, Sarin V. Computer-assisted navigation in total knee replacement: results of an initial experience in thirty-five patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A(Suppl 2):90–98.24. Bae DK, Song SJ. Computer assisted navigation in knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011; 3(4):259–267. PMID: 22162787.
Article25. Lustig S, Scholes CJ, Oussedik S, Coolican MR, Parker DA. Unsatisfactory accuracy with VISIONAIRE patient-specific cutting jigs for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(1):249–250. PMID: 23891059.
Article26. Voleti PB, Hamula MJ, Baldwin KD, Lee GC. Current data do not support routine use of patient-specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(9):1709–1712. PMID: 24961893.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Position of Proximal Reference Point of Tibial Plateau to Prevent Varus Tibial Cutting in Total Knee Replacement : Prospective Randomized Study
- Radiographic Analysis of the Tibial Axis on the Antero-posterior and Lateral view of Knee
- The Study of Anatomical Measurement of Proximal tibia and Fitness of tibial Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Three Dimensional Analysis for the Intramedullary Canal Axis of the Proximal Tibia: Clinical Relevance to Total Knee Arthroplasty
- The Position of Proximal Reference Point of Tibia Plateau for Correct Tibial Osteotomy in Total Knee Replacement: Prospective Randomized and 6 Years Follow-up Study