J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2020 Jan;58(1):30-34. 10.4047/jkap.2020.58.1.30.
Fabrication of closed hollow obturator for hard palate defect patient undergone maxillectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. yhsdent@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2469918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2020.58.1.30
Abstract
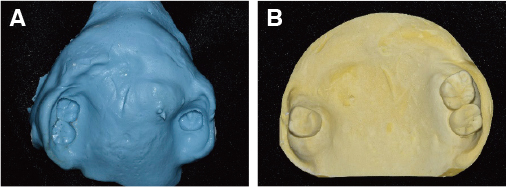
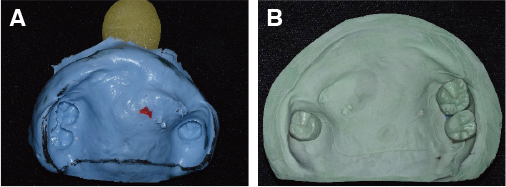
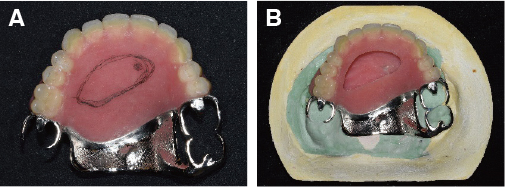
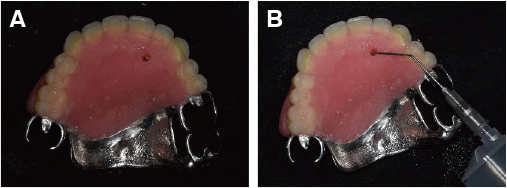
- Maxillectomy is performed to remove the tumor in the palate, maxillary sinus, buccal mucosa or nasal cavity. The resection range depends on the size and the extent of the tumor and it affects speech production or cause nasal regurgitation during feeding. Obturator can occlude an opening such as an oro-nasal fistula and protect the defect area. Successful reconstrucion of the patient's oral cavity who have gone over the maxillectomy is a difficult task. The condition and number of teeth, the remaining support area, and the extent of the defect area have a great influence on manufacturing the obturator. If these factors are disadvantageous, the prognosis of the prosthesis is uncertain. The final obturator must have a sufficient retention in the patient's oral cavity and must not irritate the surrounding tissue and support area where the resection was performed.In this case, a 55 year old female went through the maxillectomy and the only 3 teeth remained. And the retention of the maxillary prosthesis seems to be poor. So that, we fabricated the closed hollow obturator which has reduced weight compared to the conventional obturator. Consequently the closed hollow obturator can give better sealing and the adaptation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Varoujan A. Maxillofacial prosthetics multidisciplinary practice. Baltimore: The Williams & Wilkins Co;1971.2. Minsley GE, Warren DW, Hinton V. Physiologic responses to maxillary resection and subsequent obturation. J Prosthet Dent. 1987; 57:338–344.
Article3. Taylor TD. Clinical maxillofacial prosthetics. Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc.;2000. p. 94–120.4. Jain AR, Philip JM. Cast retainer hollow bulb obturator for a maxillary defect -A case report. Int J Dent Sci Res. 2014; 2:164–167.5. Yalug SH. An alternative method for fabricating a closed hollow obturator: a clinical report. J Oral Sci. 2002; 44:161–164.
Article6. Buzayan MM, Ariffin YT, Yunus N. Closed hollow bulb obturator-one-step fabrication: a clinical report. J Prosthodont. 2013; 22:591–595.
Article7. Shrestha B, Hughes ER, Singh RK, Suwal P, Parajuli PK, Shrestha P, Sharma A, Adhikari G. Fabrication of closed hollow bulb obturator using thermoplastic resin material. Case Rep Dent. 2015; 2015:504561. DOI: 10.1155/2015/504561.
Article8. Chalian VA, Barnett MO. A new technique for constructing a one-piece hollow obturator after partial maxillectomy. J Prosthet Dent. 1972; 28:448–453.
Article9. McAndrew KS, Rothenbergerb S, Minsley GE. An innovative investment method for the fabrication of a closed hollow obturator prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 1998; 80:129–132.
Article10. Elliott DJ. The hollow bulb obturator: its fabrication using one denture flask. Quintessence Dent Technol. 1983; 7:13–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Maxillofacial rehabilitation of hemi-maxillectomy patient using a closed hollow bulb obturator fabricated by one-step polymerization technique: a clinical report
- A hollow definitive obturator fabrication technique for management of partial maxillectomy
- Prosthetic rehabilitation for a maxillectomy patient using 3D printing assisted closed hollow bulb obturator: a case report
- Prosthetic rehabilitation of partially edentulous patient after maxillectomy: A case report
- Use of artificial palate for improving facial support in the fabrication of a maxillary obturator: A case report