J Korean Soc Radiol.
2020 Jan;81(1):157-165. 10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.157.
Application of Point Shearwave Elastography to Breast Ultrasonography: Initial Experience Using “S-Shearwave†in Differential Diagnosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Research Institute of Radiological Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lvjenny@yuhs.ac
- 2Biostatistics Collaboration Unit, Department of Biomedical Systems Informatics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2469189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.157
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the optimal measurement location, cut-off value, and diagnostic performance of S-Shearwave in differential diagnosis of breast masses seen on ultrasonography (US).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
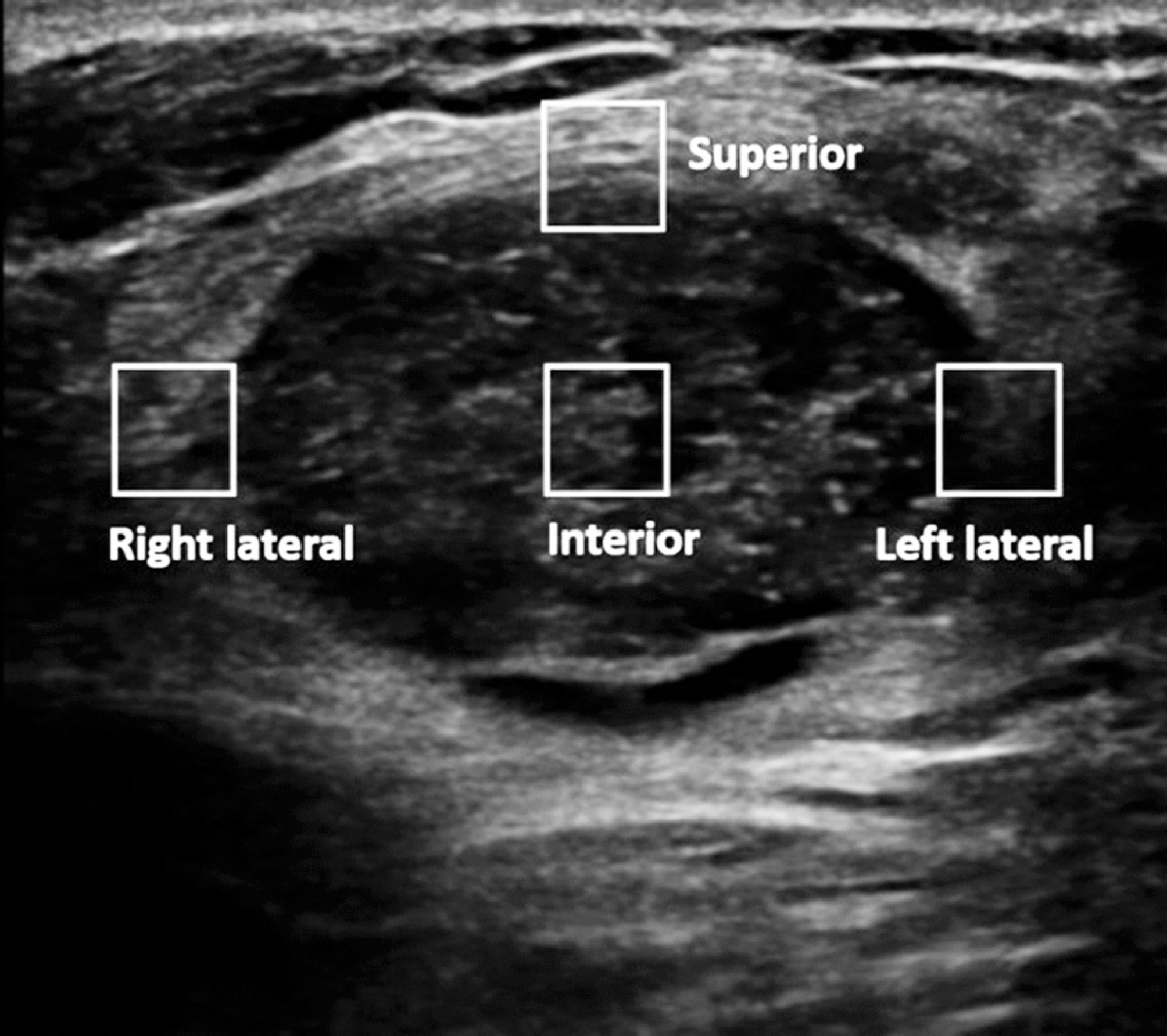
During the study period, 225 breast masses in 197 women were included. S-Shearwave measurements were made by applying a square region-of-interest automatically generated by the US machine. Shearwave elasticity was measured three times at four different locations of the mass, and the highest shearwave elasticity was used for calculating the optimal cut-off value. Diagnostic performance was evaluated by using the area under the receiving operator characteristic curve (AUC).
RESULTS
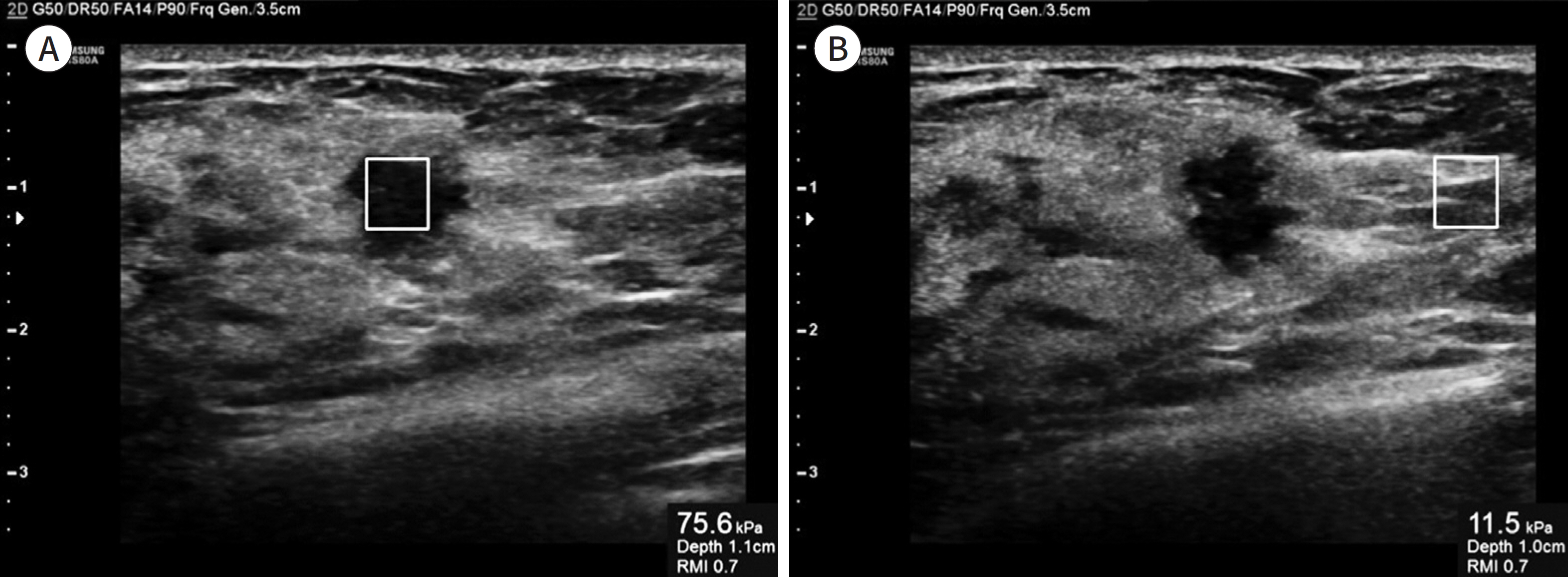
Of the 225 breast masses, 156 (69.3%) were benign and 69 (30.7%) were malignant. Mean S-Shearwave values were significantly higher for malignant masses (108.0 ± 70.0 kPa vs. 43.4 ± 38.3 kPa; p < 0.001). No significant differences were seen among AUC values at different measurement locations. With a cut-off value of 41.9 kPa, S-Shearwave showed 85.7% sensitivity, 63.9% specificity, 70.7% accuracy, and positive and negative predictive values of 51.7% and 90.8%, respectively. The AUCs for US and S-Shearwave did not show significant differences (p = 0.179).
CONCLUSION
S-Shearwave shows comparable diagnostic performance to that of grayscale US that can be applied for differential diagnosis of breast masses seen on US.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American College of Radiology. Breast imaging reporting and data system. 5th ed. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology. 2013.2. Hong AS, Rosen EL, Soo MS, Baker JA. BI-RADS for sonography: positive and negative predictive values of sonographic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1260–1265.
Article3. Kim EK, Ko KH, Oh KK, Kwak JY, You JK, Kim MJ, et al. Clinical application of the BI-RADS final assessment to breast sonography in conjunction with mammography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:1209–1215.
Article4. Costantini M, Belli P, Lombardi R, Franceschini G, Mulè A, Bonomo L. Characterization of solid breast masses: use of the sonographic breast imaging reporting and data system lexicon. J Ultrasound Med. 2006; 25:649–659. quiz 661.5. Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T, et al. Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology. 2006; 239:341–350.
Article6. Lee EJ, Jung HK, Ko KH, Lee JT, Yoon JH. Diagnostic performances of shear wave elastography: which pa-rameter to use in differential diagnosis of solid breast masses? Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1803–1811.
Article7. Yoon JH, Jung HK, Lee JT, Ko KH. Shearwave elastography in the diagnosis of solid breast masses: what leads to false-negative or false-positive results? Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:2432–2440.
Article8. Berg WA, Cosgrove DO, Doré CJ, Schäfer FK, Svensson WE, Hooley RJ, et al. Shearwave elastography im-proves the specificity of breast US: the BE1 multinational study of 939 masses. Radiology. 2012; 262:435–449.
Article9. Burnside ES, Hall TJ, Sommer AM, Hesley GK, Sisney GA, Svensson WE, et al. Differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses with US strain imaging. Radiology. 2007; 245:401–410.
Article10. Cho N, Moon WK, Kim HY, Chang JM, Park SH, Lyou CY. Sonoelastographic strain index for differentiation of benign and malignant nonpalpable breast masses. J Ultrasound Med. 2010; 29:1–7.
Article11. Chang JM, Moon WK, Cho N, Yi A, Koo HR, Han W, et al. Clinical application of shear wave elastography (SWE) in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast diseases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:89–97.
Article12. Choi K, Kong D, Hah Z, Lee HK. A reliability index of shear wave speed measurement for shear wave elastography. Piscataway: IEEE;2015.13. Deffieux T, Gennisson JL, Bercoff J, Tanter M. On the effects of reflected waves in transient shear wave elastography. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2011; 58:2032–2035.
Article14. Tozaki M, Isobe S, Fukuma E. Preliminary study of ultrasonographic tissue quantification of the breast using the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technology. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 80:e182–187.
Article15. Wojcinski S, Brandhorst K, Sadigh G, Hillemanns P, Degenhardt F. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging with Virtual Touch TM tissue quantification: mean shear wave velocity of malignant and benign breast masses. Int J Womens Health. 2013; 5:619–627.16. Tozaki M, Isobe S, Sakamoto M. Combination of elastography and tissue quantification using the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) technology for differential diagnosis of breast masses. Jpn J Radiol. 2012; 30:659–670.
Article17. Teke M, Göya C, Teke F, Uslukaya Ö, Hamidi C, Çetinçakmak MG, et al. Combination of virtual touch tissue imaging and virtual touch tissue quantification for differential diagnosis of breast lesions. J Ultrasound Med. 2015; 34:1201–1208.
Article18. Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K, McLean D, Brauer K, Purdie C, et al. Quantitative shear wave ultrasound elastography: initial experience in solid breast masses. Breast Cancer Res. 2010; 12:R104.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Role of Conventional Ultrasonography and Shearwave Elastography in Asymptomatic Patients with Diffuse Thyroid Disease: Initial Experience with 57 Patients
- EUS Elastography: Advances in Diagnostic EUS of the Pancreas
- Erratum to "Diagnostic Role of Conventional Ultrasonography and Shearwave Elastography in Asymptomatic Patients with Diffuse Thyroid Disease: Initial Experience with 57 Patients" by Kim I, et al. (Yonsei Med J 2014;55:247-53.)
- Which supplementary imaging modality should be used for breast ultrasonography? Comparison of the diagnostic performance of elastography and computer-aided diagnosis
- Shear-wave elastography in breast ultrasonography: the state of the art