J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Oct;31(10):1641-1649. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1641.
Effect of Brace to Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture: a Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. spinelee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468257
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1641
Abstract
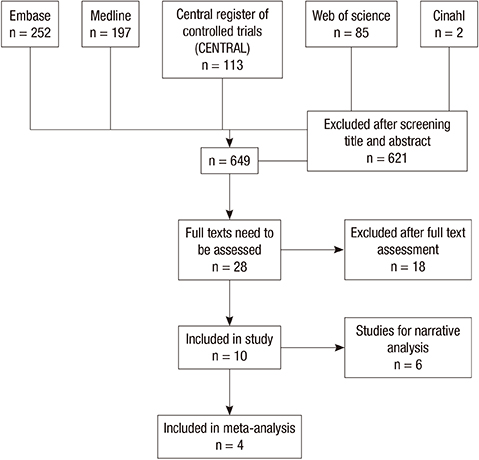
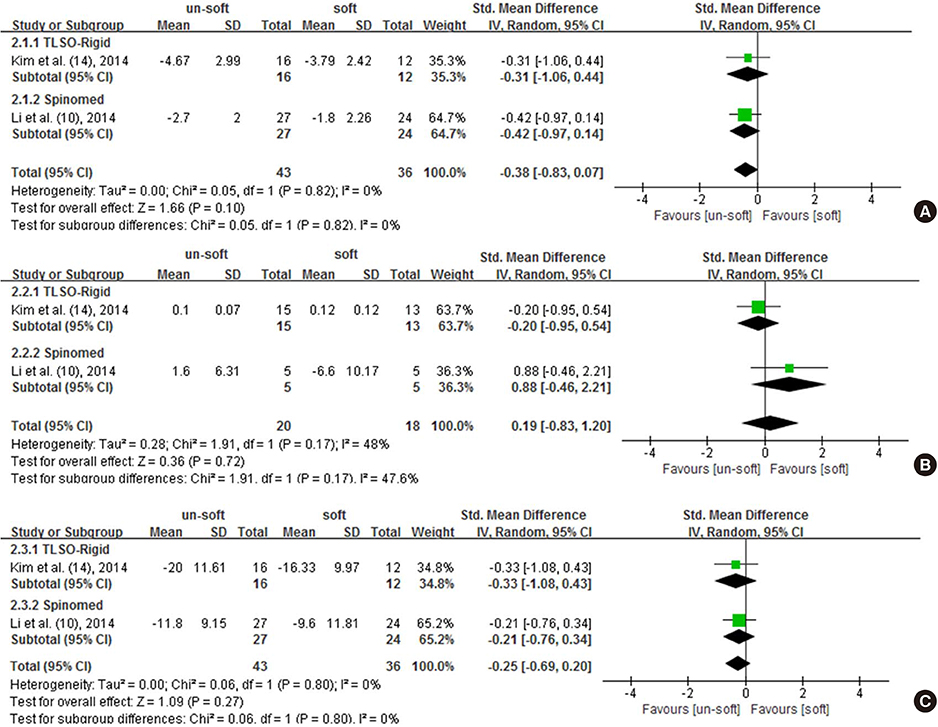
- Brace is one of the most commonly used interventions to manage osteoporotic vertebral fracture. However, its authentic effectiveness remains unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of brace in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. We conducted a literature review and meta-analysis following the guideline and handbook of the Cochrane collaboration. Ten published articles were included in this study and data from 4 randomized controlled trials were analyzed. Low quality evidence proved using Spinomed brace could bring large and significant beneficial effect to patients with sub-acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Very low quality evidence proved no significant difference between Spinomed orthosis, rigid brace and soft brace when they were used in patients with acute fractures. Therefore, it might be applicable to recommend middle term use of Spinomed orthosis to patients with subacute fracture. In addition, this study emphasized the need for high quality randomized controlled trials.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Management of Elderly Patients with Spinal Disease: Interventional Nonsurgical Treatment
Soo-An Park
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2019;54(1):9-17. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.1.9.
Reference
-
1. Gerdhem P. Osteoporosis and fragility fractures: vertebral fractures. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013; 27:743–755.2. Johnell O, Kanis JA, Odén A, Sernbo I, Redlund-Johnell I, Petterson C, De Laet C, Jönsson B. Mortality after osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2004; 15:38–42.3. Newman M, Minns Lowe C, Barker K. Spinal orthoses for vertebral osteoporosis and osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016; 97:1013–1025.4. Rzewuska M, Ferreira M, McLachlan AJ, Machado GC, Maher CG. The efficacy of conservative treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures on acute pain relief: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24:702–714.5. Esses SI, McGuire R, Jenkins J, Finkelstein J, Woodard E, Watters WC 3rd, Goldberg MJ, Keith M, Turkelson CM, Wies JL, et al. The treatment of symptomatic osteoporotic spinal compression fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19:176–182.6. Agabegi SS, Asghar FA, Herkowitz HN. Spinal orthoses. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010; 18:657–667.7. Furlan AD, Malmivaara A, Chou R, Maher CG, Deyo RA, Schoene M, Bronfort G, van Tulder MW; Editorial Board of the Cochrane Back, Neck Group. 2015 updated method guideline for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back and Neck Group. Spine. 2015; 40:1660–1673.8. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: version 5.1.0 [Internet]. updated March 2011. accessed on 2 March 2015. Available at http://handbook.cochrane.org/.9. Chaparro LE, Furlan AD, Deshpande A, Mailis-Gagnon A, Atlas S, Turk DC. Opioids compared with placebo or other treatments for chronic low back pain: an update of the Cochrane Review. Spine. 2014; 39:556–563.10. Li M, Law SW, Cheng J, Kee HM, Wong MS. A comparison study on the efficacy of SpinoMed® and soft lumbar orthosis for osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2015; 39:270–276.11. Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW. Effects of a new spinal orthosis on posture, trunk strength, and quality of life in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:177–186.12. Pfeifer M, Kohlwey L, Begerow B, Minne HW. Effects of two newly developed spinal orthoses on trunk muscle strength, posture, and quality-of-life in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90:805–815.13. Dionyssiotis Y, Trovas G, Thoma S, Lyritis G, Papaioannou N. Prospective study of spinal orthoses in women. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2015; 39:487–495.14. Kim HJ, Yi JM, Cho HG, Chang BS, Lee CK, Kim JH, Yeom JS. Comparative study of the treatment outcomes of osteoporotic compression fractures without neurologic injury using a rigid brace, a soft brace, and no brace: a prospective randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96:1959–1966.15. Sinaki M, Lynn SG. Reducing the risk of falls through proprioceptive dynamic posture training in osteoporotic women with kyphotic posturing: a randomized pilot study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:241–246.16. Valentin GH, Pedersen LN, Maribo T. Wearing an active spinal orthosis improves back extensor strength in women with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2014; 38:232–238.17. Liaw MY, Chen CL, Chen JF, Tang FT, Wong AM, Ho HH. Effects of Knight-Taylor brace on balance performance in osteoporotic patients with vertebral compression fracture. J Back Musculoskeletal Rehabil. 2009; 22:75–81.18. Murata K, Watanabe G, Kawaguchi S, Kanaya K, Horigome K, Yajima H, Morita T, Yamashita T. Union rates and prognostic variables of osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated with a rigid external support. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 17:469–475.19. Talic A, Kapetanovic J, Dizdar A. Effects of conservative treatment for osteoporotic thoracolumbal spine fractures. Mater Sociomed. 2012; 24:16–20.20. Greig AM, Bennell KL, Briggs AM, Hodges PW. Postural taping decreases thoracic kyphosis but does not influence trunk muscle electromyographic activity or balance in women with osteoporosis. Man Ther. 2008; 13:249–257.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- The Efficacy of Bisphosphonates for Prevention of Osteoporotic Fracture: An Update Meta-analysis
- Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Unilateral Biportal Endoscopy as a Treatment for Acute Radiculopathy after Osteoporotic Lumbar Compression Fracture: A Case Report
- Association Between Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture and Body Mass Index