J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Oct;31(10):1538-1545. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1538.
Ossification of the Medial Clavicular Epiphysis on Chest Radiographs: Utility and Diagnostic Accuracy in Identifying Korean Adolescents and Young Adults under the Age of Majority
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Inter-disciplinary Program in Medical Informatics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Medical Examiner's Office, National Forensic Service, Wonju, Korea.
- 6Institute of Forensic Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yoosh@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2468242
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1538
Abstract
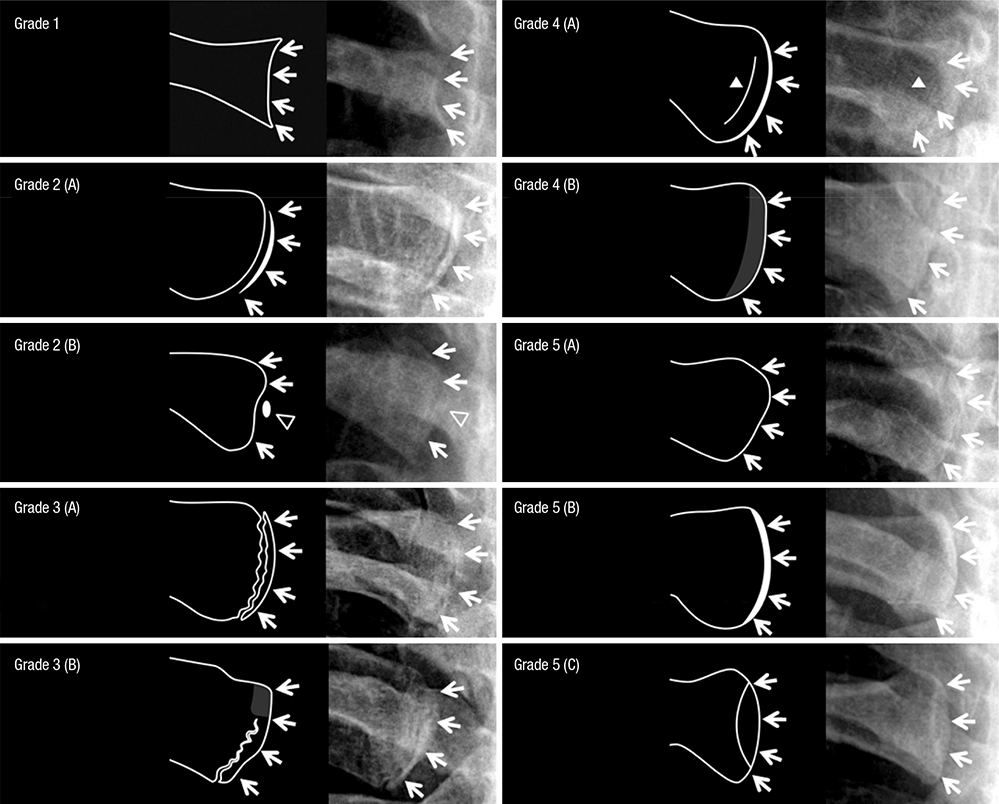
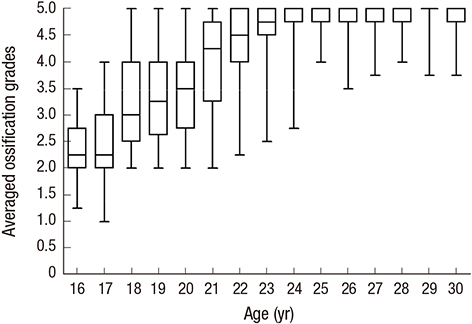
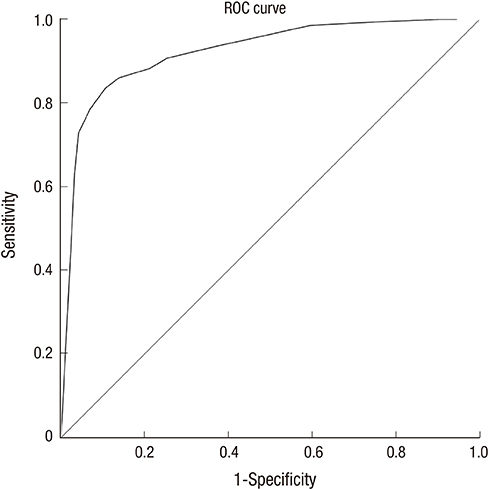
- The aim of our study was to evaluate the utility and diagnostic accuracy of the ossification grade of medial clavicular epiphysis on chest radiographs for identifying Korean adolescents and young adults under the age of majority. Overall, 1,151 patients (age, 16-30) without any systemic disease and who underwent chest radiography were included for ossification grading. Two radiologists independently classified the ossification of the medial clavicular epiphysis from chest radiographs into five grades. The age distribution and inter-observer agreement on the ossification grade were assessed. The diagnostic accuracy of the averaged ossification grades for determining whether the patient is under the age of majority was analyzed by using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Two separate inexperienced radiologists assessed the ossification grade in a subgroup of the patients after reviewing the detailed descriptions and image atlases developed for ossification grading. The median value of the ossification grades increased with increasing age (from 16 to 30 years), and the trend was best fitted by a quadratic function (R-square, 0.978). The inter-observer agreements on the ossification grade were 0.420 (right) and 0.404 (left). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.922 (95% CI, 0.902-0.942). The averaged ossification scores of 2.62 and 4.37 provided 95% specificity for a person < 19 years of age and a person ≥ 19 years of age, respectively. A preliminary assessment by inexperienced radiologists resulted in an AUC of 0.860 (95% CI, 0.740-0.981). The age of majority in Korean adolescents and young adults can be estimated using chest radiographs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schmeling A, Reisinger W, Geserick G, Olze A. The current state of forensic age estimation of live subjects for the purpose of criminal prosecution. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2005; 1:239–246.2. Schmeling A, Olze A, Reisinger W, König M, Geserick G. Statistical analysis and verification of forensic age estimation of living persons in the Institute of Legal Medicine of the Berlin University Hospital Charité. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2003; 5:Suppl 1. S367–71.3. Franklin D. Forensic age estimation in human skeletal remains: current concepts and future directions. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010; 12:1–7.4. Schmeling A, Grundmann C, Fuhrmann A, Kaatsch HJ, Knell B, Ramsthaler F, Reisinger W, Riepert T, Ritz-Timme S, Rösing FW, et al. Criteria for age estimation in living individuals. Int J Legal Med. 2008; 122:457–460.5. Buikstra JE, Ubelaker DH. Standards for Data Collection from Human Skeletal Remains: Proceedings of a Seminar at the Field Museum Of Natural History (Arkansas Archeological Survey Research Series No. 44). Fayetteville, AR: Arkansas Archeological Survey;1994.6. Kreitner KF, Schweden FJ, Riepert T, Nafe B, Thelen M. Bone age determination based on the study of the medial extremity of the clavicle. Eur Radiol. 1998; 8:1116–1122.7. Schmeling A, Schulz R, Reisinger W, Mühler M, Wernecke KD, Geserick G. Studies on the time frame for ossification of the medial clavicular epiphyseal cartilage in conventional radiography. Int J Legal Med. 2004; 118:5–8.8. Meijerman L, Maat GJ, Schulz R, Schmeling A. Variables affecting the probability of complete fusion of the medial clavicular epiphysis. Int J Legal Med. 2007; 121:463–468.9. Schulz R, Mühler M, Reisinger W, Schmidt S, Schmeling A. Radiographic staging of ossification of the medial clavicular epiphysis. Int J Legal Med. 2008; 122:55–58.10. Garamendi PM, Landa MI, Botella MC, Alemán I. Forensic age estimation on digital X-ray images: medial epiphyses of the clavicle and first rib ossification in relation to chronological age. J Forensic Sci. 2011; 56:Suppl 1. S3–12.11. Cameriere R, De Luca S, De Angelis D, Merelli V, Giuliodori A, Cingolani M, Cattaneo C, Ferrante L. Reliability of Schmeling's stages of ossification of medial clavicular epiphyses and its validity to assess 18 years of age in living subjects. Int J Legal Med. 2012; 126:923–932.12. Schmeling A, Reisinger W, Loreck D, Vendura K, Markus W, Geserick G. Effects of ethnicity on skeletal maturation: consequences for forensic age estimations. Int J Legal Med. 2000; 113:253–258.13. Soegiharto BM, Cunningham SJ, Moles DR. Skeletal maturation in Indonesian and white children assessed with hand-wrist and cervical vertebrae methods. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008; 134:217–226.14. Zhang A, Sayre JW, Vachon L, Liu BJ, Huang HK. Racial differences in growth patterns of children assessed on the basis of bone age. Radiology. 2009; 250:228–235.15. Ministry of Unification (KR). Unification White Paper 2010. Seoul: Ministry of Unification;2010.16. Crewson PE. Reader agreement studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1391–1397.17. Park SH, Goo JM, Jo CH. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve: practical review for radiologists. Korean J Radiol. 2004; 5:11–18.18. Jit I, Kulkarni M. Times of appearance and fusion of epiphysis at the medial end of the clavicle. Indian J Med Res. 1976; 64:773–782.19. Schulz R, Mühler M, Mutze S, Schmidt S, Reisinger W, Schmeling A. Studies on the time frame for ossification of the medial epiphysis of the clavicle as revealed by CT scans. Int J Legal Med. 2005; 119:142–145.20. Kellinghaus M, Schulz R, Vieth V, Schmidt S, Schmeling A. Forensic age estimation in living subjects based on the ossification status of the medial clavicular epiphysis as revealed by thin-slice multidetector computed tomography. Int J Legal Med. 2010; 124:149–154.21. Langley-Shirley N, Jantz RL. A Bayesian approach to age estimation in modern Americans from the clavicle. J Forensic Sci. 2010; 55:571–583.22. Bassed RB, Drummer OH, Briggs C, Valenzuela A. Age estimation and the medial clavicular epiphysis: analysis of the age of majority in an Australian population using computed tomography. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2011; 7:148–154.23. Singh J, Chavali KH. Age estimation from clavicular epiphyseal union sequencing in a Northwest Indian population of the Chandigarh region. J Forensic Leg Med. 2011; 18:82–87.24. Brown AA, Derkyi-Kwarteng L, Amonoo-Kuofi HS. Study on the time frame for ossification of the medial clavicular epiphyseal cartilage by X-ray in Ghanaian students. Int J Morphol. 2013; 31:491–496.25. Wittschieber D, Schulz R, Vieth V, Küppers M, Bajanowski T, Ramsthaler F, Püschel K, Pfeiffer H, Schmidt S, Schmeling A. The value of sub-stages and thin slices for the assessment of the medial clavicular epiphysis: a prospective multi-center CT study. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2014; 10:163–169.26. Wittschieber D, Ottow C, Schulz R, Püschel K, Bajanowski T, Ramsthaler F, Pfeiffer H, Vieth V, Schmidt S, Schmeling A. Forensic age diagnostics using projection radiography of the clavicle: a prospective multi-center validation study. Int J Legal Med. 2016; 130:213–219.27. Murata M. Population-specific reference values for bone age. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1997; 423:113–114.28. Wittschieber D, Ottow C, Vieth V, Küppers M, Schulz R, Hassu J, Bajanowski T, Püschel K, Ramsthaler F, Pfeiffer H, et al. Projection radiography of the clavicle: still recommendable for forensic age diagnostics in living individuals? Int J Legal Med. 2015; 129:187–193.29. Schulze D, Rother U, Fuhrmann A, Richel S, Faulmann G, Heiland M. Correlation of age and ossification of the medial clavicular epiphysis using computed tomography. Forensic Sci Int. 2006; 158:184–189.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidence of the Appearance of the Proximal Humeral Ossification Center of the Neonates and Infants on Plain Chest Radiograph
- Convolutional neural network of age-related trends digital radiographs of medial clavicle in a Thai population: a preliminary study
- Atypical Bipolar Segmental Fracture of the Clavicle in an Adolescent: A Case Report
- Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow after Medial Epicondylectomy
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents and Young Adults