Anat Cell Biol.
2023 Mar;56(1):86-93. 10.5115/acb.22.205.
Convolutional neural network of age-related trends digital radiographs of medial clavicle in a Thai population: a preliminary study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 2Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 3Excellence in Osteology Research and Training Center, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 4College of Arts, Media and Technology, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 5Department of Oral Biology and Diagnostic Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- KMID: 2540988
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.205
Abstract
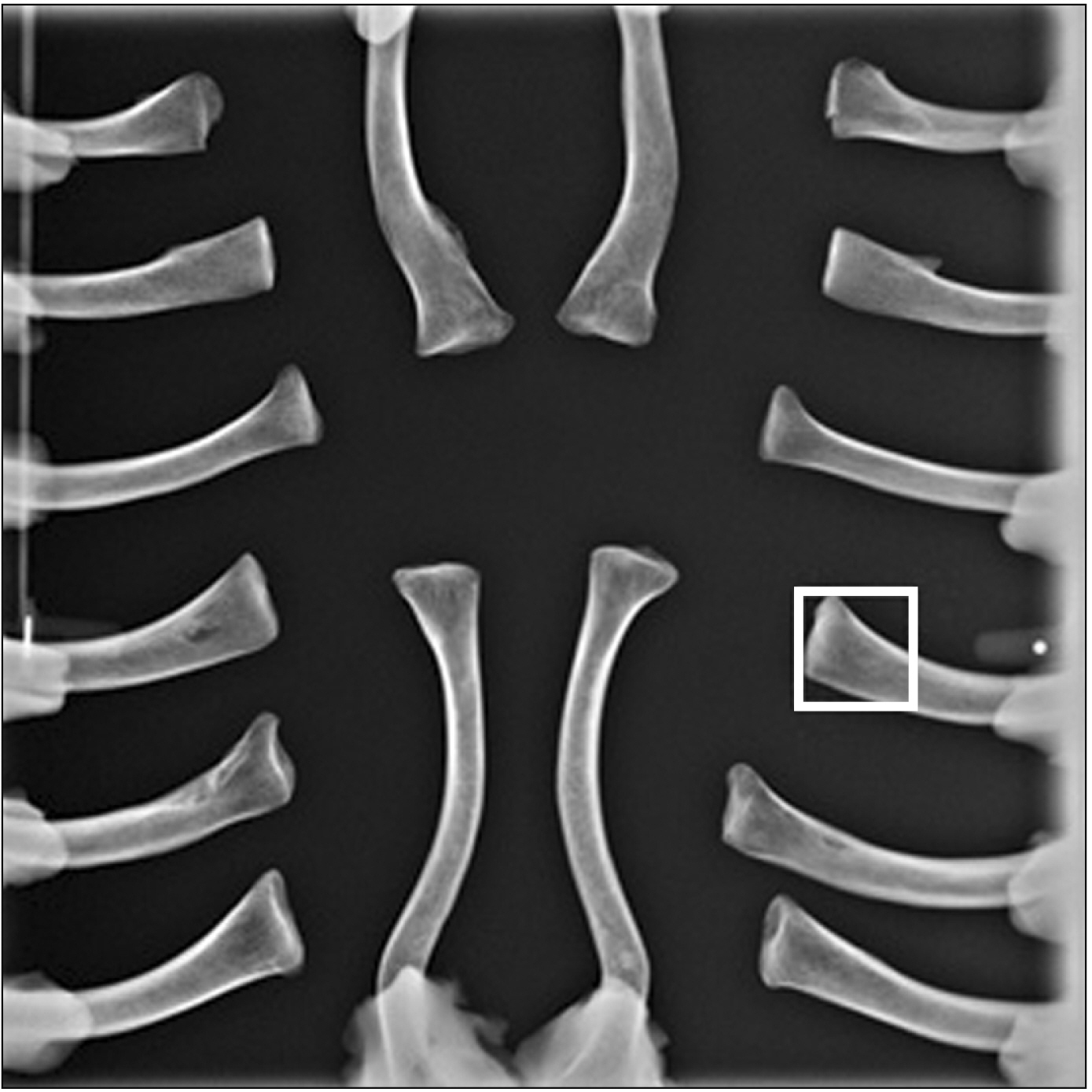
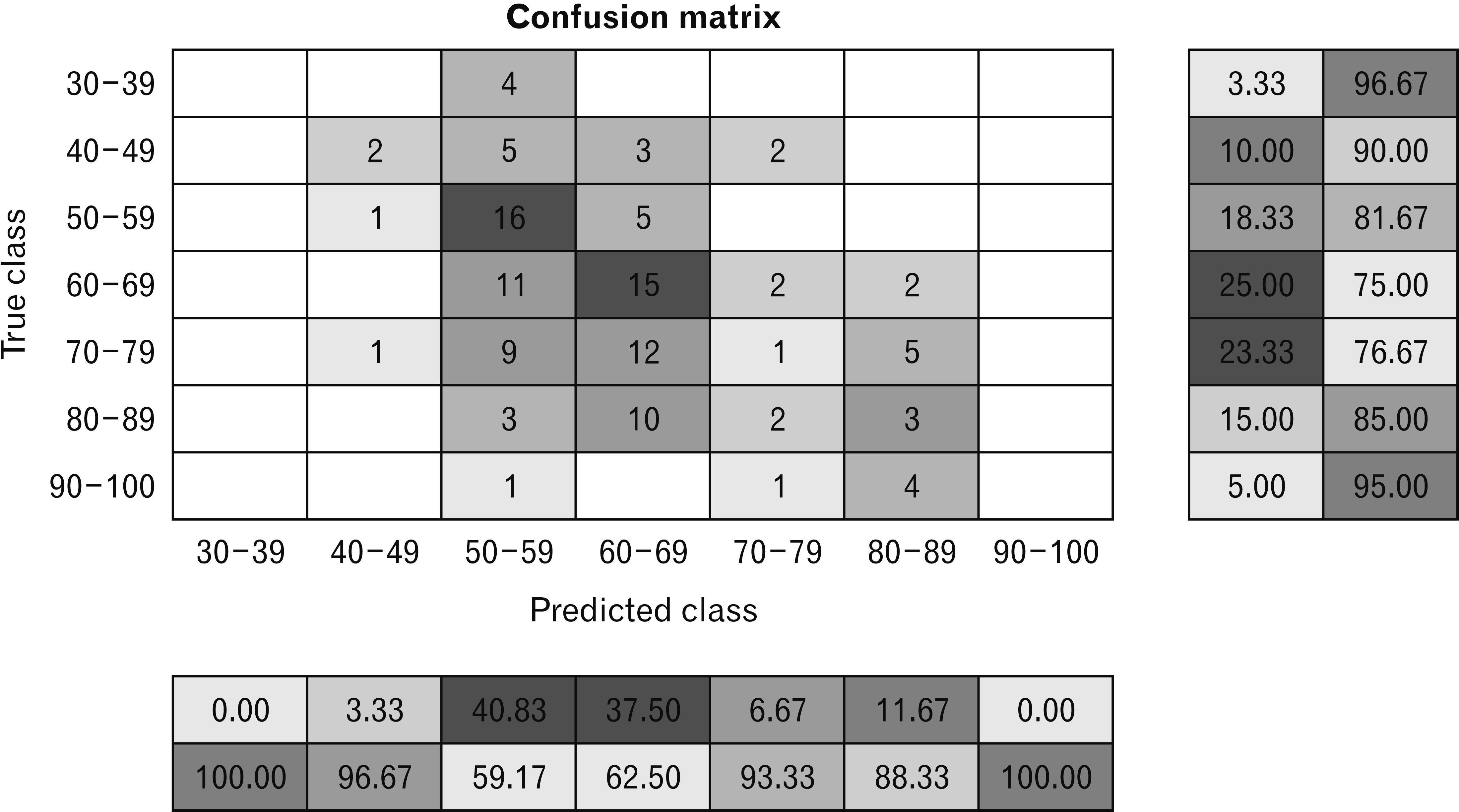
- Age at death estimation has always been a crucial yet challenging part of identification process in forensic field. The use of human skeletons have long been explored using the principle of macro and micro-architecture change in correlation with increasing age. The clavicle is recommended as the best candidate for accurate age estimation because of its accessibility, time to maturation and minimal effect from weight. Our study applies pre-trained convolutional neural network in order to achieve the most accurate and cost effective age estimation model using clavicular bone. The total of 988 clavicles of Thai population with known age and sex were radiographed using Kodak 9000 Extra-oral Imaging System. The radiographs then went through preprocessing protocol which include region of interest selection and quality assessment. Additional samples were generated using generative adversarial network. The total clavicular images used in this study were 3,999 which were then separated into training and test set, and the test set were subsequently categorized into 7 age groups. GoogLeNet was modified at two layers and fine tuned the parameters. The highest validation accuracy was 89.02% but the test set achieved only 30% accuracy. Our results show that the use of medial clavicular radiographs has a potential in the field of age at death estimation, thus, further study is recommended.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Dental characteristics on panoramic radiographs as parameters for non-invasive age estimation: a pilot study
Harin Cheong, Akiko Kumagai, Sehyun Oh, Sang-Seob Lee
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):474-481. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.140.
Reference
-
References
1. Morgan OW, ibanditmongkol P Sr, Perera C, Sulasmi Y, Van Alphen D, Sondorp E. 2006; Mass fatality management following the South Asian tsunami disaster: case studies in Thailand, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka. PLoS Med. 3:e195. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030195. PMID: 16737348. PMCID: PMC1472696. PMID: 1e511fd10cc841c48b386e121b1c27bf.
Article2. inak N Sr. 2020; The study of unclaimed and unidentified bodies management in Thailand and other countries. J Thai Justice Syst. 13:139–52.3. Evert L. 2011. Unidentified bodies in forensic pathology practice in South Africa: demographic and medico-legal perspectives [thesis]. University of Pretoria;Hatfield:4. National Missing and Unidentified Persons System. 2022. The nation's silent mass disaster [Internet]. National Institute of Justice;Washington, D.C.: Available from: https://namus.nij.ojp.gov/. cited 2022 Oct 29.5. Manzoor Mughal A, Hassan N, Ahmed A. 2014; Bone age assessment methods: a critical review. Pak J Med Sci. 30:211–5. DOI: 10.12669/pjms.301.4295. PMID: 24639863. PMCID: PMC3955574.
Article6. Hermetet C, Saint-Martin P, Gambier A, Ribier L, Sautenet B, Rérolle C. 2018; Forensic age estimation using computed tomography of the medial clavicular epiphysis: a systematic review. Int J Legal Med. 132:1415–25. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-018-1847-z. PMID: 29713801.
Article7. Shirley NR. 2009. Age and sex estimation from the human clavicle: an investigation of traditional and novel methods [PhD dissertation]. University of Tennessee;Knoxville:8. Schulz R, Mühler M, Mutze S, Schmidt S, Reisinger W, Schmeling A. 2005; Studies on the time frame for ossification of the medial epiphysis of the clavicle as revealed by CT scans. Int J Legal Med. 119:142–5. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-005-0529-9. PMID: 15711799.
Article9. Marera DO, Satyapal KS. 2018; Fusion of the medial clavicular epiphysis in the South African and Kenyan populations. Int J Morphol. 36:1101–7. DOI: 10.4067/S0717-95022018000301101.
Article10. Milenkovic P, Djukic K, Djonic D, Milovanovic P, Djuric M. 2013; Skeletal age estimation based on medial clavicle--a test of the method reliability. Int J Legal Med. 127:667–76. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-012-0791-6. PMID: 23329360.
Article11. Botha D, Lynnerup N, Steyn M. 2019; Age estimation using bone mineral density in South Africans. Forensic Sci Int. 297:307–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.02.020. PMID: 30852414.
Article12. Kranioti EF, Bonicelli A, García-Donas JG. 2019; Bone-mineral density: clinical significance, methods of quantification and forensic applications. Res Rep Forensic Med Sci. 9:9–21. DOI: 10.2147/RRFMS.S164933.13. Rowe P, Koller A, Sharma S. 2022. Physiology, bone remodeling. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing;Treasure Island: DOI: 10.2147/rrfms.s164933.14. Seeman E, Delmas PD. 2006; Bone quality--the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N Engl J Med. 354:2250–61. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra053077. PMID: 16723616.
Article15. Li Y, Huang Z, Dong X, Liang W, Xue H, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Deng Z. 2019; Forensic age estimation for pelvic X-ray images using deep learning. Eur Radiol. 29:2322–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-018-5791-6. PMID: 30402703.
Article16. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. 2015; Deep learning. Nature. 521:436–44. DOI: 10.1038/nature14539. PMID: 26017442. PMCID: PMC9985066.
Article17. Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. 2015. Going deeper with convolutions. Paper presented at: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2015 Jun 7-12; Boston, USA. p. 1–9. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594.
Article18. Benito M, Sánchez JA, Codinha S. 2014; Age-at-death estimation based on radiological and image analysis methods in clavicle in a current Spanish population. Int J Legal Med. 128:523–33. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-014-0989-x. PMID: 24664396.
Article19. Chantharawetchakun T, Vachirawongsakorn V. 2021; Age estimation in the Thai male population using epiphyseal union of the medial clavicle. Chiang Mai Med J. 60:149–55. DOI: 10.12982/CMUMEDJ.2021.13.
Article20. Schulz R, Mühler M, Reisinger W, Schmidt S, Schmeling A. 2008; Radiographic staging of ossification of the medial clavicular epiphysis. Int J Legal Med. 122:55–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-007-0210-6. PMID: 17940787.
Article21. Schmeling A, Grundmann C, Fuhrmann A, Kaatsch HJ, Knell B, Ramsthaler F, Reisinger W, Riepert T, Ritz-Timme S, Rösing FW, Rötzscher K, Geserick G. 2008; Criteria for age estimation in living individuals. Int J Legal Med. 122:457–60. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-008-0254-2. PMID: 18548266.
Article22. Subramanian S, Viswanathan VK. 2022. Bone age. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing;Treasure Island: DOI: 10.1007/s00414-008-0254-2.23. Fourcade A, Khonsari RH. 2019; Deep learning in medical image analysis: a third eye for doctors. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 120:279–88. DOI: 10.1016/j.jormas.2019.06.002. PMID: 31254638.
Article24. Ott SM. 2018; Cortical or trabecular bone: what's the difference? Am J Nephrol. 47:373–5. DOI: 10.1159/000489672. PMID: 29788030.
Article25. Navega D, Coelho JD, Cunha E, Curate F. 2018; DXAGE: a new method for age at death estimation based on femoral bone mineral density and artificial neural networks. J Forensic Sci. 63:497–503. DOI: 10.1111/1556-4029.13582. PMID: 28851106.
Article26. Thurzo A, Kosnáčová HS, Kurilová V, Kosmeľ S, Beňuš R, Moravanský N, Kováč P, Kuracinová KM, Palkovič M, Varga I. 2021; Use of advanced artificial intelligence in forensic medicine, forensic anthropology and clinical anatomy. Healthcare (Basel). 9:1545. DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9111545. PMID: 34828590. PMCID: PMC8619074. PMID: d69c6f7f6c6649efaf105ed423b793e0.
Article27. Guo YC, Han M, Chi Y, Long H, Zhang D, Yang J, Yang Y, Chen T, Du S. 2021; Accurate age classification using manual method and deep convolutional neural network based on orthopantomogram images. Int J Legal Med. 135:1589–97. DOI: 10.1007/s00414-021-02542-x. PMID: 33661340.
Article28. Mutasa S, Sun S, Ha R. 2020; Understanding artificial intelligence based radiology studies: What is overfitting? Clin Imaging. 65:96–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.04.025. PMID: 32387803. PMCID: PMC8150901.
Article29. Chartrand G, Cheng PM, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal CJ, Kadoury S, Tang A. 2017; Deep learning: a primer for radiologists. Radiographics. 37:2113–31. DOI: 10.1148/rg.2017170077. PMID: 29131760.
Article30. Zhang P, Zhong Y, Li X. 2020. ACCL: adversarial constrained-CNN loss for weakly supervised medical image segmentation. arXiv. 2005.00328 [Preprint]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2005.00328. cited 2022 Dec 6.
Article31. Guan S, Loew M. 2019; Breast cancer detection using synthetic mammograms from generative adversarial networks in convolutional neural networks. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 6:031411. DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.6.3.031411. PMID: 30915386. PMCID: PMC6430964.
Article32. Wang Y, Zhou L, Wang M, Shao C, Shi L, Yang S, Zhang Z, Feng M, Shan F, Liu L. 2020; Combination of generative adversarial network and convolutional neural network for automatic subcentimeter pulmonary adenocarcinoma classification. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 10:1249–64. DOI: 10.21037/qims-19-982. PMID: 32550134. PMCID: PMC7276356.
Article33. Dodge S, Karam L. 2016. Understanding how image quality affects deep neural networks. Paper presented at: 2016 Eighth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX). 2016 Jun 6-8; Lisbon, Portugal. p. 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/QoMEX.2016.7498955.
Article34. Aggarwal A, Mittal M, Battineni G. 2021; Generative adversarial network: an overview of theory and applications. Int J Inf Manag Data Insights. 1:100004. DOI: 10.1016/j.jjimei.2020.100004.
Article35. Kazeminia S, Baur C, Kuijper A, van Ginneken B, Navab N, Albarqouni S, Mukhopadhyay A. 2020; GANs for medical image analysis. Artif Intell Med. 109:101938. DOI: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101938. PMID: 34756215.
Article36. Buda M, Maki A, Mazurowski MA. 2018; A systematic study of the class imbalance problem in convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 106:249–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.07.011. PMID: 30092410.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Convolutional Neural Network Based Sinogram Extrapolation for Truncated CT: Preliminary Study
- Deep learning convolutional neural network algorithms for the early detection and diagnosis of dental caries on periapical radiographs: A systematic review
- Dental age estimation using a convolutional neural network algorithm on panoramic radiographs: A pilot study in Indonesia
- Automatic detection of periodontal compromised teeth in digital panoramic radiographs using faster regional convolutional neural networks
- Lesion-Based Convolutional Neural Network in Diagnosis of Early Gastric Cancer