Investig Clin Urol.
2020 Jan;61(1):81-87. 10.4111/icu.2020.61.1.81.
Treatment persistence with a fixed-dose combination of tadalafil (5 mg) and tamsulosin (0.4 mg) and reasons for early discontinuation in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. dgmoon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2466796
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2020.61.1.81
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The primary aim of this study was to assess treatment persistence with a fixed-dose combination (FDC) of tadalafil (5 mg) and tamsulosin (0.4 mg). This study also evaluated the reasons for early treatment discontinuation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective observational study included patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction who started an FDC treatment of tadalafil (5 mg) and tamsulosin (0.4 mg) between July 2017 and February 2018. Treatment persistence and reasons for early discontinuation were evaluated during the first 6 months. The cumulative discontinuation rate and differences in various parameters were assessed using Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test, respectively. Factors related to persistence were analyzed using a Cox proportional hazard model.
RESULTS
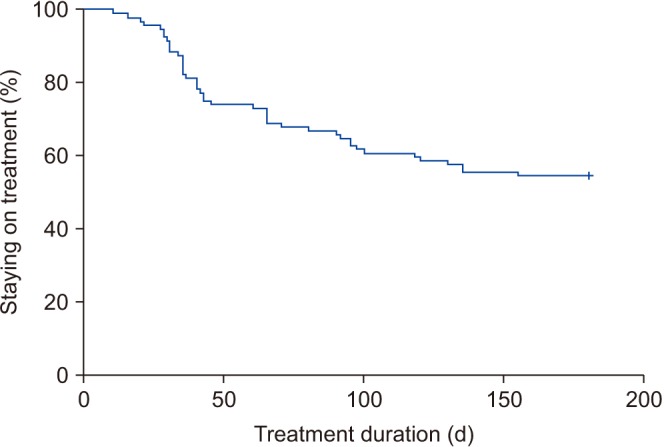
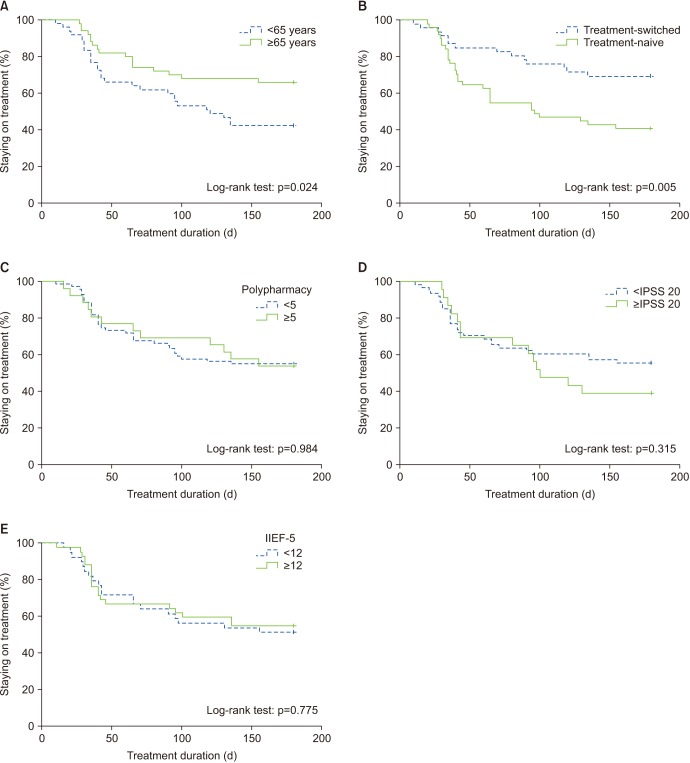
Overall, 97 patients were included in the study. The cumulative persistence rate at 30, 90, and 180 days was 88.7%, 66.0%, and 54.6%, respectively. The cumulative persistence over 6 months differed significantly according to the administration of FDC therapy (log-rank p=0.005) and age (log-rank p=0.024). Younger patients (odds ratio, 2.049; p=0.021) and treatment-naive patients (odds ratio, 2.461; p=0.006) were more likely to discontinue therapy within 6 months. The common reasons for discontinuing therapy were side effects (63.6%) and perceived poor efficacy (22.7%).
CONCLUSIONS
Side effects were reported to be the main reason for treatment discontinuation. Thus, to improve compliance for a once-daily FDC of tadalafil (5 mg) and tamsulosin (0.4 mg), it is recommended to select patients who show adaptation to a combination of α-blockers and phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors prior to FDC treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seftel AD, de la Rosette J, Birt J, Porter V, Zarotsky V, Viktrup L. Coexisting lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review of epidemiological data. Int J Clin Pract. 2013; 67:32–45. PMID: 23082930.
Article2. Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs R, Fourcade R, et al. The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int. 2003; 92:719–725. PMID: 14616454.
Article3. Braun MH, Sommer F, Haupt G, Mathers MJ, Reifenrath B, Engelmann UH. Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: co-morbidity or typical “Aging Male” symptoms? Results of the “Cologne Male Survey”. Eur Urol. 2003; 44:588–594. PMID: 14572759.
Article4. Brookes ST, Link CL, Donovan JL, McKinlay JB. Relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: results from the Boston Area Community Health Survey. J Urol. 2008; 179:250–255. discussion 255. PMID: 18001787.
Article5. Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E, et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol. 2003; 44:637–649. PMID: 14644114.
Article6. Oelke M, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A, Emberton M, Gravas S, Michel MC, et al. ; European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol. 2013; 64:118–140. PMID: 23541338.7. Song WH, Park J, Yoo S, Oh S, Cho SY, Cho MC, et al. Changes in the prevalence and risk factors of erectile dysfunction during a decade: the Korean Internet Sexuality Survey (KISS), a 10-year-interval web-based survey. World J Mens Health. 2019; 37:199–209. PMID: 30588782.
Article8. Hovstadius B, Petersson G. Factors leading to excessive polypharmacy. Clin Geriatr Med. 2012; 28:159–172. PMID: 22500536.
Article9. Sergi G, De Rui M, Sarti S, Manzato E. Polypharmacy in the elderly: can comprehensive geriatric assessment reduce inappropriate medication use? Drugs Aging. 2011; 28:509–518. PMID: 21721596.10. Kim SW, Park NC, Lee SW, Yang DY, Park JK, Moon DG, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination therapy of tamsulosin and tadalafil for patients with lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction: results of a randomized, double-blinded, active-controlled trial. J Sex Med. 2017; 14:1018–1027. PMID: 28760246.
Article11. National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation. “Gugutams 0.4/5 mg®” approval report [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2016. 10. 20. cited 2019 Sep 23. Available from: http://www.nifds.go.kr/brd/m_88/down.do?brd_id=board_mfds_191&seq=26016&data_tp=A&file_seq=1.12. Kirby M, Chapple C, Jackson G, Eardley I, Edwards D, Hackett G, et al. Erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms: a consensus on the importance of co-diagnosis. Int J Clin Pract. 2013; 67:606–618. PMID: 23617950.
Article13. Krueger KP, Berger BA, Felkey B. Medication adherence and persistence: a comprehensive review. Adv Ther. 2005; 22:313–356. PMID: 16418141.
Article14. Park HJ. The role of the urologist in men's health. World J Mens Health. 2017; 35:57–58. PMID: 28868815.
Article15. Kim TH, You HW, Park JH, Lee JG, Choo MS, Park WH, et al. Persistence of solifenacin therapy in patients with overactive bladder in the clinical setting: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Int J Clin Pract. 2016; 70:351–357. PMID: 27028673.
Article16. Kim TH, Choo MS, Kim YJ, Koh H, Lee KS. Drug persistence and compliance affect patient-reported outcomes in overactive bladder syndrome. Qual Life Res. 2016; 25:2021–2029. PMID: 26701707.
Article17. Koh JS, Cho KJ, Kim HS, Kim JC. Twelve-month medication persistence in men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Clin Pract. 2014; 68:197–202. PMID: 24372906.
Article18. Hatzichristou D, d'Anzeo G, Porst H, Buvat J, Henneges C, Rossi A, et al. Tadalafil 5 mg once daily for the treatment of erectile dysfunction during a 6-month observational study (EDATE): impact of patient characteristics and comorbidities. BMC Urol. 2015; 15:111. PMID: 26563171.
Article19. Shiovitz TM, Bain EE, McCann DJ, Skolnick P, Laughren T, Hanina A, et al. Mitigating the effects of nonadherence in clinical trials. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 56:1151–1164. PMID: 26634893.
Article20. Abdel-Hamid IA, Ali OI. Delayed ejaculation: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. World J Mens Health. 2018; 36:22–40. PMID: 29299903.
Article21. Lee LK, Goren A, Boytsov NN, Donatucci CF, McVary KT. Treatment satisfaction among men with concurrent benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction treated with tadalafil or other phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor combinations. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016; 10:1205–1215. PMID: 27471377.
Article22. Won JE, Chu JY, Choi HC, Chen Y, Park HJ, Dueñas HJ. Safety and effectiveness of once-daily tadalafil (5 mg) therapy in Korean men with benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms in a real-world clinical setting: results from a post-marketing surveillance study. World J Mens Health. 2018; 36:161–170. PMID: 28879692.
Article23. Porst H, Rajfer J, Casabé A, Feldman R, Ralph D, Vieiralves LF, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of tadalafil 5 mg dosed once daily in men with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2008; 5:2160–2169. PMID: 18557812.
Article24. Rajfer J, Aliotta PJ, Steidle CP, Fitch WP 3rd, Zhao Y, Yu A. Tadalafil dosed once a day in men with erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in the US. Int J Impot Res. 2007; 19:95–103. PMID: 16871272.
Article25. Yu KD, Zhou Y, Liu GY, Li B, He PQ, Zhang HW, et al. A prospective, multicenter, controlled, observational study to evaluate the efficacy of a patient support program in improving patients' persistence to adjuvant aromatase inhibitor medication for postmenopausal, early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 134:307–313. PMID: 22527106.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Tamsulosin, a Selective alpha1A-adrenoreceptor Antagonist, in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Pharmacokinetics and safety profiles of tadalafil/tamsulosin HCl fixed-dose combination capsule under fasted and fed condition in healthy volunteers
- The Effect of Finasteride, Tamsulosin and Doxazosin Therapy on Sexual Function in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Open-label, Intermittent Dose, Prospective Study Evaluating the Effects of Tadalafil on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Function in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Continuation and Durability of Effects
- The Experience with Combination of Finasteride and Tamsulosin on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia