Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jan;57(1):22-32. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.22.
Intestinal Behcet's Disease: A True Inflammatory Bowel Disease or Merely an Intestinal Complication of Systemic Vasculitis?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. geniushee@yuhs.ac
- 2Digestive Disease Center, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2466348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.22
Abstract
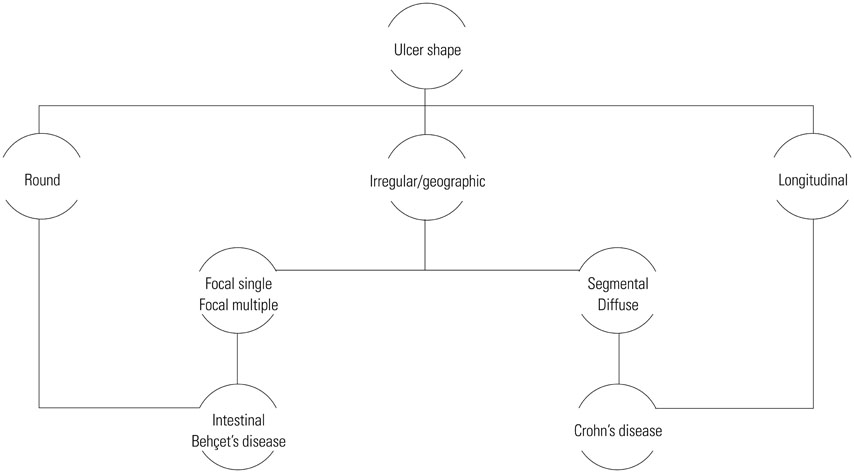
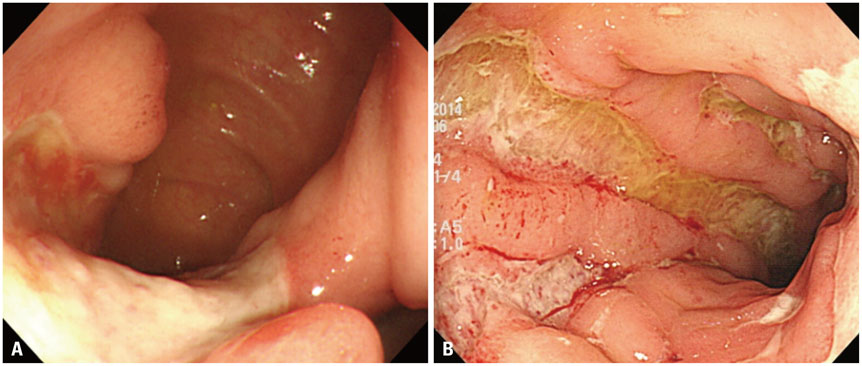
- Behcet's disease (BD) is a multi-systemic inflammatory disorder of an unknown etiology and shows a chronic recurrent clinical course. When the disease involves the alimentary tract, it is called intestinal BD because of its clinical importance. Intestinal BD is more frequently reported in East Asian countries than in Western or Middle Eastern countries. While any part of the gastrointestinal tract can be involved, the most common location of intestinal BD is the ileocecal area. A few, large, deep ulcerations with discrete border are characteristic endoscopic findings of intestinal BD. Currently, there is no single gold standard test or pathognomonic finding of intestinal BD. However, recently developed novel diagnostic criteria and a disease activity index have helped in assessing intestinal BD. As intestinal BD shares a lot of characteristics with inflammatory bowel disease, including genetic background, clinical manifestations, and therapeutic strategies, distinguishing between the two diseases in clinical practice is quite difficult. However, biologic agents such as anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody shows a considerable efficacy similar to inflammatory bowel disease cases. It is important to distinguish and treat those two disease entities separately from the standpoint of precise medicine. Clinicians should require comprehensive knowledge regarding the similarities and differences between intestinal BD and inflammatory bowel disease for making an accurate clinical decision.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Magnetic resonance enterography predicts the prognosis of Crohn's disease
Ji Hoon Lee, Yong Eun Park, Nieun Seo, Hyun Jung Lee, Soo Jung Park, Tae Il Kim, Won Ho Kim, Joon Seok Lim, Jae Hee Cheon
Intest Res. 2018;16(3):445-457. doi: 10.5217/ir.2018.16.3.445.Could adalimumab be used safely and effectively in intestinal Behçet's disease refractory to conventional therapy?
Jihye Park, Jae Hee Cheon
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):263-265. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.263.Optimal diagnosis and disease activity monitoring of intestinal Behçet's disease
Hyun Jung Lee, Jae Hee Cheon
Intest Res. 2017;15(3):311-317. doi: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.311.
Reference
-
1. James DG. Behcet's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1979; 301:431–432.2. Kaklamani VG, Vaiopoulos G, Kaklamanis PG. Behçet's Disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 27:197–217.
Article3. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–1291.
Article4. Dilşn N, Koniçe M, Aral O, Ocal L, Inanç M, Gül A. Comparative study of the skin pathergy test with blunt and sharp needles in Behçet's disease: confirmed specificity but decreased sensitivity with sharp needles. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993; 52:823–825.5. Bayraktar Y, Ozaslan E, Van Thiel DH. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behcet's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 30:144–154.
Article6. Kasahara Y, Tanaka S, Nishino M, Umemura H, Shiraha S, Kuyama T. Intestinal involvement in Behçet's disease: review of 136 surgical cases in the Japanese literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981; 24:103–106.7. Bradbury AW, Milne AA, Murie JA. Surgical aspects of Behçet's disease. Br J Surg. 1994; 81:1712–1721.
Article8. Hatemi G, Seyahi E, Fresko I, Talarico R, Hamuryudan V. Behçet's syndrome: a critical digest of the 2013-2014 literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014; 32:4 Suppl 84. S112–S122.9. Verity DH, Marr JE, Ohno S, Wallace GR, Stanford MR. Behçet's disease, the Silk Road and HLA-B51: historical and geographical perspectives. Tissue Antigens. 1999; 54:213–220.
Article10. Ohno S, Ohguchi M, Hirose S, Matsuda H, Wakisaka A, Aizawa M. Close association of HLA-Bw51 with Behçet's disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982; 100:1455–1458.11. Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T, et al. Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:703–706.
Article12. Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MHC class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet's disease. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:698–702.
Article13. Karasneh J, Gül A, Ollier WE, Silman AJ, Worthington J. Whole-genome screening for susceptibility genes in multicase families with Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1836–1842.
Article14. Direskeneli H. Behçet's disease: infectious aetiology, new autoantigens, and HLA-B51. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:996–1002.15. Hughes T, Coit P, Adler A, Yilmaz V, Aksu K, Düzgün N, et al. Identification of multiple independent susceptibility loci in the HLA region in Behçet's disease. Nat Genet. 2013; 45:319–324.
Article16. Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett JC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:1118–1125.17. Lees CW, Barrett JC, Parkes M, Satsangi J. New IBD genetics: common pathways with other diseases. Gut. 2011; 60:1739–1753.
Article18. Wallace GR, Kondeatis E, Vaughan RW, Verity DH, Chen Y, Fortune F, et al. IL-10 genotype analysis in patients with Behçet's disease. Hum Immunol. 2007; 68:122–127.
Article19. Zou L, Wang L, Gong X, Zhao H, Jiang A, Zheng S. The association between three promoter polymorphisms of IL-10 and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD): a meta-analysis. Autoimmunity. 2014; 47:27–39.
Article20. Cho JH, Brant SR. Recent insights into the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1704–1712.
Article21. Kim ES, Kim SW, Moon CM, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. Interactions between IL17A, IL23R, and STAT4 polymorphisms confer susceptibility to intestinal Behcet's disease in Korean population. Life Sci. 2012; 90:740–746.
Article22. Direskeneli H, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Kibaroglu A, Yavuz S, Ergun T, Akoglu T. Oligoclonal T cell expansions in patients with Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999; 117:166–170.
Article23. Suzuki Y, Hoshi K, Matsuda T, Mizushima Y. Increased peripheral blood gamma delta+ T cells and natural killer cells in Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992; 19:588–592.24. Freysdottir J, Lau S, Fortune F. Gammadelta T cells in Behçet's disease (BD) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). Clin Exp Immunol. 1999; 118:451–457.25. Na SY, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. Up-regulation of Th17 and related cytokines in Behçet's disease corresponding to disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013; 31:3 Suppl 77. 32–40.26. Sugi-Ikai N, Nakazawa M, Nakamura S, Ohno S, Minami M. Increased frequencies of interleukin-2- and interferon-gamma-producing T cells in patients with active Behçet's disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998; 39:996–1004.27. Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI, Ozdemir O, Haznedaroğlu IC, Dündar S, Kirazli S. Cytokines in Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1996; 23:321–322.28. Frassanito MA, Dammacco R, Cafforio P, Dammacco F. Th1 polarization of the immune response in Behçet's disease: a putative pathogenetic role of interleukin-12. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42:1967–1974.
Article29. Dave M, Papadakis KA, Faubion WA Jr. Immunology of inflammatory bowel disease and molecular targets for biologics. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2014; 43:405–424.
Article30. Abraham C, Cho JH. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2066–2078.
Article31. Sartor RB. Mechanisms of disease: pathogenesis of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 3:390–407.
Article32. Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014; 14:329–342.
Article33. Lehner T. The role of heat shock protein, microbial and autoimmune agents in the aetiology of Behçet's disease. Int Rev Immunol. 1997; 14:21–32.
Article34. Sohn S. Etiopathology of Behçet's disease: herpes simplex virus infection and animal model. Yonsei Med J. 1997; 38:359–364.
Article35. Sohn S, Lee ES, Bang D, Lee S. Behçet's disease-like symptoms induced by the Herpes simplex virus in ICR mice. Eur J Dermatol. 1998; 8:21–23.36. Sohn S, Lee ES, Kwon HJ, Lee SI, Bang D, Lee S. Expression of Th2 cytokines decreases the development of and improves Behçet's disease-like symptoms induced by herpes simplex virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 2001; 183:1180–1186.
Article37. Galeone M, Colucci R, D'Erme AM, Moretti S, Lotti T. Potential Infectious Etiology of Behçet's Disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012; 2012:595380.
Article38. Magro F, Santos-Antunes J, Albuquerque A, Vilas-Boas F, Macedo GN, Nazareth N, et al. Epstein-Barr virus in inflammatory bowel disease-correlation with different therapeutic regimens. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1710–1716.
Article39. Dimitroulia E, Pitiriga VC, Piperaki ET, Spanakis NE, Tsakris A. Inflammatory bowel disease exacerbation associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013; 56:322–327.
Article40. Yanai H, Shimizu N, Nagasaki S, Mitani N, Okita K. Epstein-Barr virus infection of the colon with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:1582–1586.
Article41. Goodman AL, Murray CD, Watkins J, Griffiths PD, Webster DP. CMV in the gut: a critical review of CMV detection in the immunocompetent host with colitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015; 34:13–18.
Article42. Iida T, Ikeya K, Watanabe F, Abe J, Maruyama Y, Ohata A, et al. Looking for endoscopic features of cytomegalovirus colitis: a study of 187 patients with active ulcerative colitis, positive and negative for cytomegalovirus. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1156–1163.43. Lehner T, Lavery E, Smith R, van der Zee R, Mizushima Y, Shinnick T. Association between the 65-kilodalton heat shock protein, Streptococcus sanguis, and the corresponding antibodies in Behçet's syndrome. Infect Immun. 1991; 59:1434–1441.
Article44. Hirohata S, Oka H, Mizushima Y. Streptococcal-related antigens stimulate production of IL6 and interferon-gamma by T cells from patients with Behcet's disease. Cell Immunol. 1992; 140:410–419.
Article45. Mendoza-Pinto C, García-Carrasco M, Jiménez-Hernández M, Jiménez-Hernández C, Riebeling-Navarro C, Nava Zavala A, et al. Etiopathogenesis of Behcet's disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2010; 9:241–245.
Article46. Hasan A, Fortune F, Wilson A, Warr K, Shinnick T, Mizushima Y, et al. Role of gamma delta T cells in pathogenesis and diagnosis of Behcet's disease. Lancet. 1996; 347:789–794.47. Sartor RB, Mazmanian SK. Intestinal Microbes in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Am J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2012; 1:15–21.
Article48. Swidsinski A, Ladhoff A, Pernthaler A, Swidsinski S, Loening-Baucke V, Ortner M, et al. Mucosal flora in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2002; 122:44–54.
Article49. Hansen J, Gulati A, Sartor RB. The role of mucosal immunity and host genetics in defining intestinal commensal bacteria. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2010; 26:564–571.
Article50. Frank DN, St Amand AL, Feldman RA, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, Pace NR. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:13780–13785.
Article51. Ott SJ, Musfeldt M, Wenderoth DF, Hampe J, Brant O, Fölsch UR, et al. Reduction in diversity of the colonic mucosa associated bacterial microflora in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2004; 53:685–693.
Article52. Naser SA, Ghobrial G, Romero C, Valentine JF. Culture of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from the blood of patients with Crohn's disease. Lancet. 2004; 364:1039–1044.
Article53. Feller M, Huwiler K, Stephan R, Altpeter E, Shang A, Furrer H, et al. Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and Crohn's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007; 7:607–613.
Article54. Abubakar I, Myhill D, Aliyu SH, Hunter PR. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from patients with Crohn's disease using nucleic acid-based techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:401–410.
Article55. Baumgart M, Dogan B, Rishniw M, Weitzman G, Bosworth B, Yantiss R, et al. Culture independent analysis of ileal mucosa reveals a selective increase in invasive Escherichia coli of novel phylogeny relative to depletion of Clostridiales in Crohn's disease involving the ileum. ISME J. 2007; 1:403–418.
Article56. Issa M, Vijayapal A, Graham MB, Beaulieu DB, Otterson MF, Lundeen S, et al. Impact of Clostridium difficile on inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:345–351.
Article57. Rabizadeh S, Rhee KJ, Wu S, Huso D, Gan CM, Golub JE, et al. Enterotoxigenic bacteroides fragilis: a potential instigator of colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:1475–1483.
Article58. Choi IJ, Kim JS, Cha SD, Jung HC, Park JG, Song IS, et al. Long-term clinical course and prognostic factors in intestinal Behçet's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43:692–700.
Article59. Lee CR, Kim WH, Cho YS, Kim MH, Kim JH, Park IS, et al. Colonoscopic findings in intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2001; 7:243–249.
Article60. Cheon JH, Kim WH. An update on the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015; 27:24–31.
Article61. Jung HC, Rhee PL, Song IS, Choi KW, Kim CY. Temporal changes in the clinical type or diagnosis of Behçet's colitis in patients with aphthoid or punched-out colonic ulcerations. J Korean Med Sci. 1991; 6:313–318.
Article62. Grigg EL, Kane S, Katz S. Mimicry and deception in inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal Behçet disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012; 8:103–112.63. Zou J, Shen Y, Ji DN, Zheng SB, Guan JL. Endoscopic findings of gastrointestinal involvement in Chinese patients with Behcet's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:17171–17178.
Article64. Lee SK, Kim BK, Kim TI, Kim WH. Differential diagnosis of intestinal Behçet's disease and Crohn's disease by colonoscopic findings. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:9–16.
Article65. Cheon JH, Kim ES, Shin SJ, Kim TI, Lee KM, Kim SW, et al. Development and validation of novel diagnostic criteria for intestinal Behçet's disease in Korean patients with ileocolonic ulcers. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:2492–2499.
Article66. Kim JS, Lim SH, Choi IJ, Moon H, Jung HC, Song IS, et al. Prediction of the clinical course of Behçet's colitis according to macroscopic classification by colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:635–640.
Article67. Chung MJ, Cheon JH, Kim SU, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim NK, et al. Response rates to medical treatments and long-term clinical outcomes of nonsurgical patients with intestinal Behçet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44:e116–e122.
Article68. Yim SM, Kim DH, Lee HJ, Jang HW, Park SJ, Hong SP, et al. Mucosal healing predicts the long-term prognosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:2529–2535.
Article69. Kim DH, Chan HC, Lung PFC, Ng SC, Cheon JH. Ileocolonoscopy in Crohn's disease. In : Kim WH, Cheon JH, editors. Atlas of inflammatory bowel diseases. 1st ed. New York: Springer Berlin Heidelberg;2015. p. 31–51.70. Shepherd NA. Pathological mimics of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 1991; 44:726–733.
Article71. Ebert EC. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:201–207.
Article72. Shen B. Endoscopic, Imaging, and Histologic Evaluation of Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:S41–S45.
Article73. Yurdakul S, Tüzüner N, Yurdakul I, Hamuryudan V, Yazici H. Gastrointestinal involvement in Behçet's syndrome: a controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996; 55:208–210.74. Chung JW, Cheon JH, Park JJ, Jung ES, Choi EH, Kim H. Development and validation of a novel prognostic scoring model for ischemic colitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010; 53:1287–1294.
Article75. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976; 70:439–444.76. Turner D, Otley AR, Mack D, Hyams J, de Bruijne J, Uusoue K, et al. Development, validation, and evaluation of a pediatric ulcerative colitis activity index: a prospective multicenter study. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:423–432.
Article77. Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980; 1:514.
Article78. Hyams JS, Ferry GD, Mandel FS, Gryboski JD, Kibort PM, Kirschner BS, et al. Development and validation of a pediatric Crohn's disease activity index. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991; 12:439–447.
Article79. van Hees PA, van Elteren PH, van Lier HJ, van Tongeren JH. An index of inflammatory activity in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980; 21:279–286.
Article80. Lee HJ, Kim YN, Jang HW, Jeon HH, Jung ES, Park SJ, et al. Correlations between endoscopic and clinical disease activity indices in intestinal Behcet's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:5771–5778.
Article81. Fresko I, Ugurlu S, Ozbakir F, Celik A, Yurdakul S, Hamuryudan V, et al. Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA) in Behçet's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005; 23:4 Suppl 38. S67–S70.82. Choi CH, Kim TI, Kim BC, Shin SJ, Lee SK, Kim WH, et al. Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody in intestinal Behçet's disease patients: relation to clinical course. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006; 49:1849–1859.
Article83. Filik L, Biyikoglu I. Differentiation of Behcet's disease from inflammatory bowel diseases: anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody and anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:7271.
Article84. Zeng XJ, Zhu WG, Deng XX, Tang FL, Dong Y. [Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in systemic vasculitis: detection and correlation with disease activity]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004; 84:1629–1632.85. Lee KH, Chung HS, Kim HS, Oh SH, Ha MK, Baik JH, et al. Human alpha-enolase from endothelial cells as a target antigen of anti-endothelial cell antibody in Behçet's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:2025–2035.
Article86. Shin SJ, Kim BC, Kim TI, Lee SK, Lee KH, Kim WH. Anti-alpha-enolase antibody as a serologic marker and its correlation with disease severity in intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:812–818.
Article87. Jung YS, Kim SW, Yoon JY, Lee JH, Jeon SM, Hong SP, et al. Expression of a soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) correlates with clinical disease activity in intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:2130–2137.
Article88. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A, et al. Management of Behçet disease: a systematic literature review for the European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:1528–1534.
Article89. Lee HW, Kim WH, Cheon JH. The medical treatments of intestinal Behcet's disease: an update. Intest Res. 2013; 11:155–160.
Article90. Sawyer A, Walker TM, Terry SI. Behçet's syndrome with ileal involvement--the beneficial effect of sulphasalazine. West Indian Med J. 1978; 27:218–221.91. Kitauchi S, Ohata H, Kuroda R, Hirose M, Sakaguchi A, Nishi S, et al. [Follow-up observation of intestinal Behçet disease treated with salazosulfapyridine and mesalazine for 8 years and 9 months]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1998; 95:140–144.92. Matsukawa M, Yamasaki T, Kouda T, Kurihara M. Endoscopic therapy with absolute ethanol for postoperative recurrent ulcers in intestinal Behçet's disease, and simple ulcers. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:255–258.
Article93. Jung YS, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH, Cheon JH. Long-term clinical outcomes and factors predictive of relapse after 5-aminosalicylate or sulfasalazine therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:e38–e45.
Article94. Fallingborg J, Laustsen J. Colitis of Behçet's syndrome. Acta Med Scand. 1984; 215:397–399.
Article95. Kobayashi K, Ueno F, Bito S, Iwao Y, Fukushima T, Hiwatashi N, et al. Development of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease using a modified Delphi approach. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:737–745.
Article96. Park JJ, Kim WH, Cheon JH. Outcome predictors for intestinal Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54:1084–1090.
Article97. Kim DH, Cheon JH, Park JJ, Yoon JY, Moon CM, Hong SP, et al. Clinical outcomes and predictive factors for response after the first course of corticosteroid therapy in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:58–65.
Article98. Yazici H, Pazarli H, Barnes CG, Tüzün Y, Ozyazgan Y, Silman A, et al. A controlled trial of azathioprine in Behçet's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:281–285.
Article99. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for thiopurine maintenance therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18:750–757.
Article100. Park JJ, Cheon JH, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Outcome predictors for thiopurine maintenance therapy in patients with Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2012; 57:133–141.
Article101. Hamuryudan V, Mat C, Saip S, Ozyazgan Y, Siva A, Yurdakul S, et al. Thalidomide in the treatment of the mucocutaneous lesions of the Behçet syndrome. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128:443–450.
Article102. Yasui K, Uchida N, Akazawa Y, Nakamura S, Minami I, Amano Y, et al. Thalidomide for treatment of intestinal involvement of juvenile-onset Behçet disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:396–400.
Article103. Bariol C, Meagher AP, Vickers CR, Byrnes DJ, Edwards PD, Hing M, et al. Early studies on the safety and efficacy of thalidomide for symptomatic inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17:135–139.
Article104. Travis SP, Czajkowski M, McGovern DP, Watson RG, Bell AL. Treatment of intestinal Behçet's syndrome with chimeric tumour necrosis factor alpha antibody. Gut. 2001; 49:725–728.
Article105. Hassard PV, Binder SW, Nelson V, Vasiliauskas EA. Anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy for gastrointestinal Behçet's disease: a case report. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120:995–999.
Article106. Kram MT, May LD, Goodman S, Molinas S. Behçet's ileocolitis: successful treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody (infliximab) therapy: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:118–121.
Article107. Byeon JS, Choi EK, Heo NY, Hong SC, Myung SJ, Yang SK, et al. Antitumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy for early postoperative recurrence of gastrointestinal Behçet's disease: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007; 50:672–676.
Article108. Lee JH, Kim TN, Choi ST, Jang BI, Shin KC, Lee SB, et al. Remission of intestinal Behçet's disease treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody (Infliximab). Korean J Intern Med. 2007; 22:24–27.
Article109. Naganuma M, Sakuraba A, Hisamatsu T, Ochiai H, Hasegawa H, Ogata H, et al. Efficacy of infliximab for induction and maintenance of remission in intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:1259–1264.
Article110. Iwata S, Saito K, Yamaoka K, Tsujimura S, Nawata M, Suzuki K, et al. Effects of anti-TNF-alpha antibody infliximab in refractory entero-Behcet's disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:1012–1013.
Article111. Kinoshita H, Kunisaki R, Yamamoto H, Matsuda R, Sasaki T, Kimura H, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in patients with intestinal Behçet's disease refractory to conventional medication. Intern Med. 2013; 52:1855–1862.
Article112. Lee JH, Cheon JH, Jeon SW, Ye BD, Yang SK, Kim YH, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in intestinal Behçet's disease: a Korean multicenter retrospective study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1833–1838.113. Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, Mayer LF, Schreiber S, Colombel JF, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1541–1549.
Article114. Rutgeerts P, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, Mayer LF, Schreiber S, Colombel JF, et al. Comparison of scheduled and episodic treatment strategies of infliximab in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:402–413.
Article115. Sands BE, Anderson FH, Bernstein CN, Chey WY, Feagan BG, Fedorak RN, et al. Infliximab maintenance therapy for fistulizing Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:876–885.
Article116. De Cassan C, De Vroey B, Dussault C, Hachulla E, Buche S, Colombel JF. Successful treatment with adalimumab in a familial case of gastrointestinal Behcet's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2011; 5:364–368.
Article117. Ariyachaipanich A, Berkelhammer C, Nicola H. Intestinal Behçet's disease: maintenance of remission with adalimumab monotherapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009; 15:1769–1771.118. van Laar JA, Missotten T, van Daele PL, Jamnitski A, Baarsma GS, van Hagen PM. Adalimumab: a new modality for Behçet's disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:565–566.119. Tanida S, Inoue N, Kobayashi K, Naganuma M, Hirai F, Iizuka B, et al. Adalimumab for the treatment of Japanese patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:940–948.
Article120. Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, Lukas M, MacIntosh D, et al. Human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody (adalimumab) in Crohn's disease: the CLASSIC-I trial. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:323–333.
Article121. Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, Lukas M, MacIntosh DG, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance treatment of Crohn's disease: results of the CLASSIC II trial. Gut. 2007; 56:1232–1239.
Article122. Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, Hanauer SB, Panaccione R, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn's disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:52–65.
Article123. Hisamatsu T, Ueno F, Matsumoto T, Kobayashi K, Koganei K, Kunisaki R, et al. The 2nd edition of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease: indication of anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies. J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:156–162.
Article124. Jung YS, Yoon JY, Lee JH, Jeon SM, Hong SP, Kim TI, et al. Prognostic factors and long-term clinical outcomes for surgical patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1594–1602.
Article125. Lee KS, Kim SJ, Lee BC, Yoon DS, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Surgical treatment of intestinal Behçet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 1997; 38:455–460.
Article126. Moon CM, Cheon JH, Shin JK, Jeon SM, Bok HJ, Lee JH, et al. Prediction of free bowel perforation in patients with intestinal Behçet's disease using clinical and colonoscopic findings. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:2904–2911.
Article127. Naganuma M, Iwao Y, Inoue N, Hisamatsu T, Imaeda H, Ishii H, et al. Analysis of clinical course and long-term prognosis of surgical and nonsurgical patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:2848–2851.
Article128. Lohmuller JL, Pemberton JH, Dozois RR, Ilstrup D, van Heerden J. Pouchitis and extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Ann Surg. 1990; 211:622–627.129. Larson DW, Pemberton JH. Current concepts and controversies in surgery for IBD. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1611–1619.
Article130. Sayek I, Aran O, Uzunalimoglu B, Hersek E. Intestinal Behçet's disease: surgical experience in seven cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 1991; 38:81–83.131. Chou SJ, Chen VT, Jan HC, Lou MA, Liu YM. Intestinal perforations in Behçet's disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:508–514.
Article132. Iida M, Kobayashi H, Matsumoto T, Okada M, Fuchigami T, Yao T, et al. Postoperative recurrence in patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994; 37:16–21.
Article133. Matsumoto T, Uekusa T, Fukuda Y. Vasculo-Behçet's disease: a pathologic study of eight cases. Hum Pathol. 1991; 22:45–51.
Article134. Bozkurt M, Torin G, Aksakal B, Ataoglu O. Behçet's disease and surgical intervention. Int J Dermatol. 1992; 31:571–573.
Article135. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Clinical course of intestinal Behcet's disease during the first five years. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:496–503.
Article136. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Long-term clinical outcomes of Crohn's disease and intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:99–105.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advances in Management of Intestinal Behçet’s Disease: A Perspective From Gastroenterologists
- Intestinal Behcet's disease in a child: a case report
- A Case of Intestinal Behcet's Disease Similar to Crohn's Colitis
- Optimal diagnosis and disease activity monitoring of intestinal Behçet's disease
- The Medical Treatments of Intestinal Behcet's Disease: An Update