Yonsei Med J.
2020 Jan;61(1):56-63. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.56.
Effect of Dialysis on Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Transactivating Activity in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. leesy1146@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ykpak@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2466336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.56
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Elevated aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) transactivating (AHRT) activity and uremia in chronic kidney disease (CKD) may interact with each other, further complicating the disease course. In this study, we prospectively estimated serum AHRT activity using a highly sensitive cell-based AhR-dependent luciferase activity assay in CKD patients and compared differences therein according to treatment modality.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD) (n=22) and hemodialysis (HD) (n=38) and patients with pre-dialysis CKD stage IV or V (n=28) were included. AHRT activity and intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels were measured. We performed a correlation analysis for AHRT activity, ATP levels, and various clinical parameters.
RESULTS
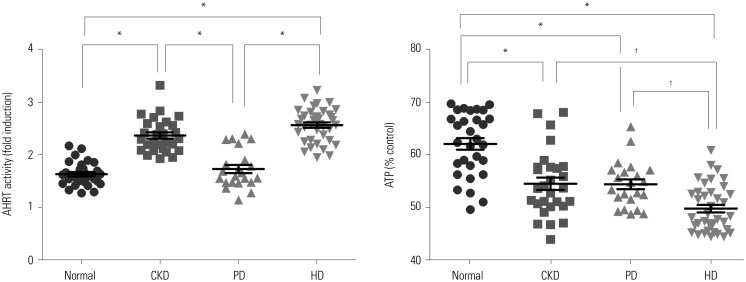
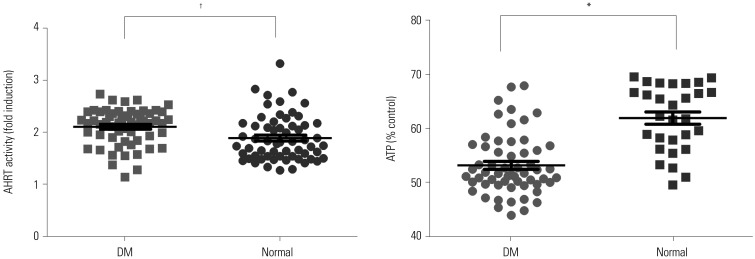
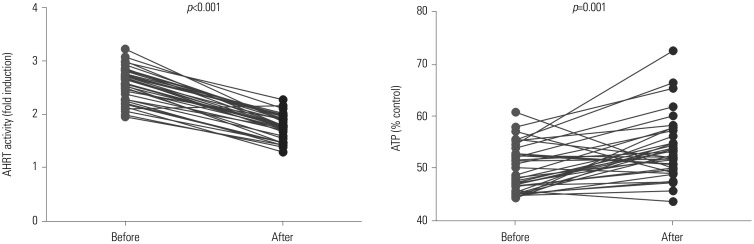
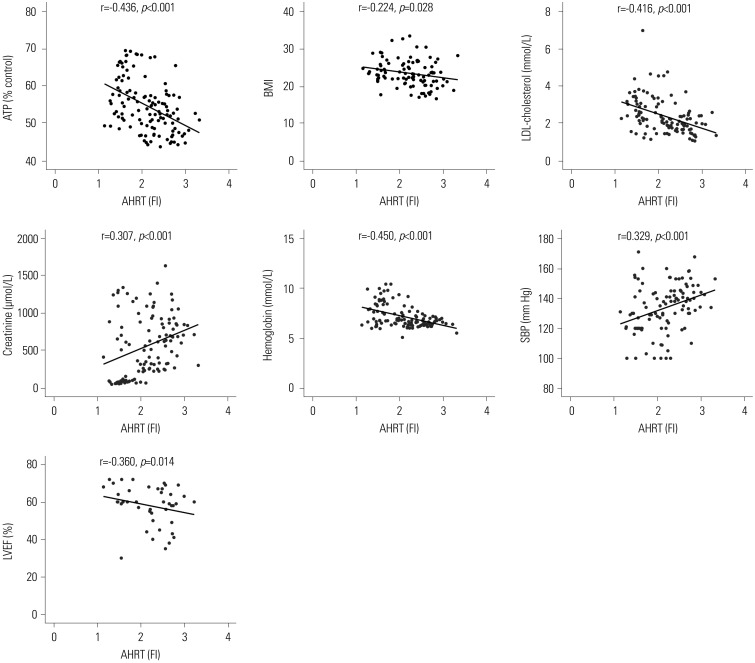
AHRT activity and intracellular ATP levels were inversely correlated and differed according to treatment modalities. AHRT activity was higher in non-dialysis CKD patients than in patients undergoing dialysis and was higher in patients undergoing HD, compared to PD. AHRT activity decreased after HD treatment in HD patients. ATP levels were higher in healthy controls than in patients with pre-dialysis CKD and PD and were further decreased in patients with HD. We noted significant correlations between multiple clinical parameters associated with cardiovascular risk factors and AHRT activity.
CONCLUSION
AHRT activity was elevated in CKD patients, while dialysis treatment reduced AHRT activity. Further studies are warranted to specify AHRT activity and to evaluate the precise roles thereof in patients with CKD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Denison MS, Nagy SR. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003; 43:309–334. PMID: 12540743.
Article2. Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kawajiri K. Molecular mechanisms of the physiological functions of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor, a multifunctional regulator that senses and responds to environmental stimuli. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010; 86:40–53.
Article3. Mackowiak B, Wang H. Mechanisms of xenobiotic receptor activation: direct vs. indirect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1859:1130–1140. PMID: 26877237.
Article4. Nebert DW. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): “pioneer member” of the basic-helix/loop/helix per-Arnt-sim (bHLH/PAS) family of “sensors” of foreign and endogenous signals. Prog Lipid Res. 2017; 67:38–57. PMID: 28606467.5. Park WH, Jun DW, Kim JT, Jeong JH, Park H, Chang YS, et al. Novel cell-based assay reveals associations of circulating serum AhR-ligands with metabolic syndrome and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biofactors. 2013; 39:494–504. PMID: 23361953.
Article6. Park WH, Kang S, Lee HK, Salihovic S, Bavel BV, Lind PM, et al. Relationships between serum-induced AhR bioactivity or mitochondrial inhibition and circulating polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Sci Rep. 2017; 7:9383. PMID: 28839207.
Article7. Kim JT, Kim SS, Jun DW, Hwang YH, Park WH, Pak YK, et al. Serum arylhydrocarbon receptor transactivating activity is elevated in type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2013; 4:483–491.
Article8. Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M, Tritschler I, Trump S, et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 2011; 478:197–203. PMID: 21976023.
Article9. Schroeder JC, Dinatale BC, Murray IA, Flaveny CA, Liu Q, Laurenzana EM, et al. The uremic toxin 3-indoxyl sulfate is a potent endogenous agonist for the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biochemistry. 2010; 49:393–400. PMID: 20000589.
Article10. Vondráček J, Pěnčííková K, Neča J, Ciganek M, Grycová A, Dvořák Z, et al. Assessment of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated activities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a human cell-based reporter gene assay. Environ Pollut. 2017; 220(Pt A):307–316. PMID: 27692884.
Article11. Shah SV, Baliga R, Rajapurkar M, Fonseca VA. Oxidants in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:16–28. PMID: 17167116.
Article12. Chen ZH, Hurh YJ, Na HK, Kim JH, Chun YJ, Kim DH, et al. Resveratrol inhibits TCDD-induced expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 and catechol estrogen-mediated oxidative DNA damage in cultured human mammary epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 2004; 25:2005–2013. PMID: 15142886.
Article13. Sallée M, Dou L, Cerini C, Poitevin S, Brunet P, Burtey S. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-activating effect of uremic toxins from tryptophan metabolism: a new concept to understand cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease. Toxins (Basel). 2014; 6:934–949. PMID: 24599232.14. Brito JS, Borges NA, Esgalhado M, Magliano DC, Soulage CO, Mafra D. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in chronic kidney disease: role of uremic toxins. Nephron. 2017; 137:1–7.
Article15. Leong SC, Sirich TL. Indoxyl sulfate-review of toxicity and therapeutic strategies. Toxins (Basel). 2016; 8:E358. PMID: 27916890.
Article16. Stenvinkel P, Heimbürger O, Paultre F, Diczfalusy U, Wang T, Berglund L, et al. Strong association between malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1999; 55:1899–1911. PMID: 10231453.
Article17. Stenvinkel P, Heimbürger O, Lindholm B, Kaysen GA, Bergström J. Are there two types of malnutrition in chronic renal failure? Evidence for relationships between malnutrition, inflammation and atherosclerosis (MIA syndrome). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000; 15:953–960. PMID: 10862630.
Article18. Annuk M, Fellström B, Akerblom O, Zilmer K, Vihalemm T, Zilmer M. Oxidative stress markers in pre-uremic patients. Clin Nephrol. 2001; 56:308–314. PMID: 11680661.19. Roh E, Kwak SH, Jung HS, Cho YM, Pak YK, Park KS, et al. Serum aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand activity is associated with insulin resistance and resulting type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2015; 52:489–495. PMID: 25385058.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inhibition of indoxyl sulfate-induced intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation: targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- Fluoranthene-Induced Cytotoxicity and Direct Effect of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Antagonist on Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation
- From intestinal dysbiosis to alcohol-associated liver disease
- Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands Indoxyl 3-sulfate and Indole-3-carbinol Inhibit FMS-like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Ligand-induced Bone Marrow-derived plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Differentiation
- Ginsenoside Rb1 Inhibits Doxorubicin-Triggered H9C2 Cell Apoptosis via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor