Int J Stem Cells.
2019 Jul;12(2):206-217. 10.15283/ijsc18122.
Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cell Therapy for Cavernous Nerve Injury-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in the Rat Model: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Using Methodological Quality Assessment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. Uroljy@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedicine & Health Sciences, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. Suejeong@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Medical Library, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2465892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc18122
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Few studies were evaluated the effect of blindness on outcome in animal models, though a potential effect of blinding has been reported in clinical trials. We evaluated the effects of adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs) on cavernous nerve injury (CNI)-induced erectile dysfunction (ED) in the rat and examined how proper blinding of the outcome assessor affected treatment effect.
METHODS AND RESULTS
We searched in Pubmed, EMBASE, Cochrane and Web of Science databases from inception to January 2019. We included CNI animal model, randomized controlled experiments, and ADSC intervention. Erectile function and structural changes were assessed by intracavernous pressure and mean arterial pressure (ICP/MAP) ratios, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) levels, cavernous smooth muscle and collagen (CSM/collagen) ratios, and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
RESULTS
Nineteen studies were included in the final meta-analysis. The ICP/MAP ratio of the ADSC treatment group increased compared to the control group (SMD=1.33, 95%CI: 1.11~1.56, I²=72%). The nNOS level (SMD=2.29, 95%CI: 1.74~2.84, I²=75%), CSM/collagen (SMD=2.57, 95%CI: 1.62~3.52; I²=85%), and cGMP (SMD=2.96, 95%CI: 1.82~4.10, I²=62%) were also increased in the ADSC treatment group. Preplanned subgroup analysis was conducted to explore the source of heterogeneity. Five studies with blinded outcome assessment were significantly less effective than the unblinded studies (SMD=1.33, 95%CI: 0.86~1.80; SMD=1.81, 95%CI: 1.17~2.46, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
ADSCs might be effective in improving erectile function and structural change in CNI-induced ED. However, non-blinded outcome assessors might cause detection bias and overestimate treatment efficacy. Therefore, the ADSC efficacy must be further evaluated with a rigorous study design to avoid bias.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. PMID: 30207593.
Article2. Li J, Siegel DA, King JB. Stage-specific incidence rates and trends of prostate cancer by age, race, and ethnicity, United States, 2004–2014. Ann Epidemiol. 2018; 28:328–330. DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.03.001. PMID: 29678312. PMCID: PMC6080305.
Article3. Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fossati N, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau S, Lam TB, Mason MD, Matveev VB, Moldovan PC, van den Bergh RCN, Van den Broeck T, van der Poel HG, van der Kwast TH, Rouvière O, Schoots IG, Wiegel T, Cornford P. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2017; 71:618–629. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.003. PMID: 27568654.
Article4. Kang DH, Lee JY, Park SY, Moon HS, Jeong TY, Yoo TK, Choi HY, Park HY, Lee TY, Lee SW. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil 5 mg administered once daily in Korean men with erectile dysfunction: a prospective, multicenter study. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:647–652. DOI: 10.4111/kju.2010.51.9.647. PMID: 20856651. PMCID: PMC2941815.
Article5. Fode M, Ohl DA, Ralph D, Sønksen J. Penile rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy: what the evidence really says. BJU Int. 2013; 112:998–1008. PMID: 23826962.
Article6. Matz EL, Terlecki R, Zhang Y, Jackson J, Atala A. Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Sex Med Rev. 2018; PMID: 29631980.
Article7. Gur S, Abdel-Mageed AB, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG. Advances in stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018; 18:1137–1150. DOI: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1534955. PMID: 30301368.
Article8. Park JS, Suryaprakash S, Lao YH, Leong KW. Engineering mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine and drug delivery. Methods. 2015; 84:3–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.03.002. PMID: 25770356. PMCID: PMC4526354.
Article9. Lin CS. Advances in stem cell therapy for the lower urinary tract. World J Stem Cells. 2010; 2:1–4. DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v2.i1.1. PMID: 21607109. PMCID: PMC3097918.
Article10. Peak TC, Anaissie J, Hellstrom WJ. Current perspectives on stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Sex Med Rev. 2016; 4:247–256. DOI: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2016.02.003. PMID: 27871958.
Article11. Xin ZC, Xu YD, Lin G, Lue TF, Guo YL. Recruiting endogenous stem cells: a novel therapeutic approach for erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2016; 18:10–15. DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.150040. PMID: 25926601. PMCID: PMC4736335.
Article12. Dai R, Wang Z, Samanipour R, Koo KI, Kim K. Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:6737345. DOI: 10.1155/2016/6737345. PMID: 27057174. PMCID: PMC4761677.
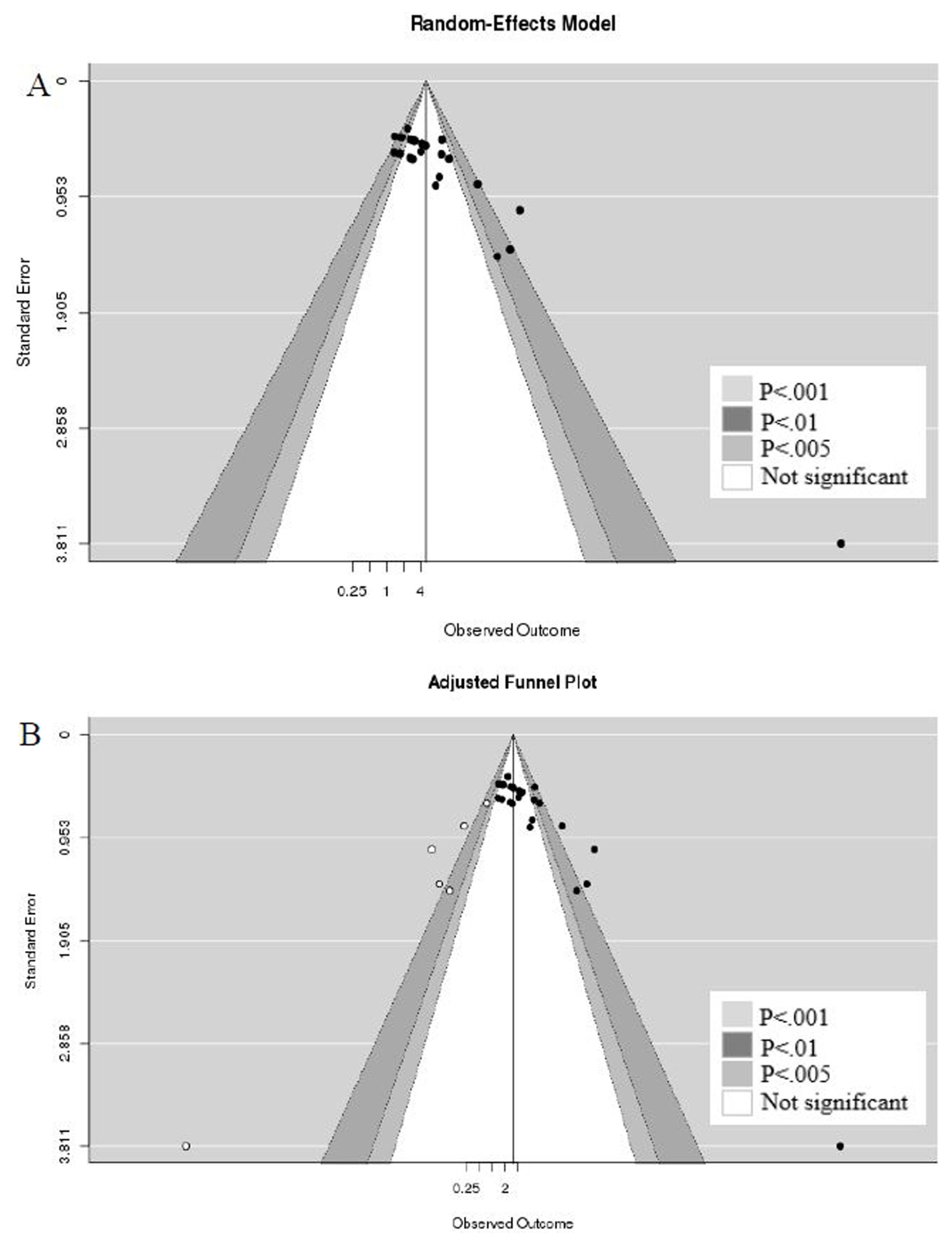
Article13. Hou QL, Ge MY, Zhang CD, Tian DD, Wang LK, Tian HZ, Wang WH, Zhang WD. Adipose tissue-derived stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction in rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017; 49:1127–1137. DOI: 10.1007/s11255-017-1590-2. PMID: 28417342.
Article14. Shan H, Chen F, Zhang T, He S, Xu L, Wei A. Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction of cavernous nerve injury rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0121428. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121428. PMID: 25860455. PMCID: PMC4393097.
Article15. Muhlhausler BS, Bloomfield FH, Gillman MW. Whole animal experiments should be more like human randomized controlled trials. PLoS Biol. 2013; 11:e1001481. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001481. PMID: 23424284. PMCID: PMC3570551.
Article16. Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Langendam MW. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014; 14:43. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43. PMID: 24667063. PMCID: PMC4230647.
Article17. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. PMID: 12958120. PMCID: PMC192859.
Article18. Fandel TM, Albersen M, Lin G, Qiu X, Ning H, Banie L, Lue TF, Lin CS. Recruitment of intracavernously injected adipose-derived stem cells to the major pelvic ganglion improves erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Eur Urol. 2012; 61:201–210. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.07.061. PMID: 21824718. PMCID: PMC3226917.
Article19. Jeon SH, Shrestha KR, Kim RY, Jung AR, Park YH, Kwon O, Kim GE, Kim SH, Kim KH, Lee JY. Combination therapy using human adipose-derived stem cells on the cavernous nerve and low-energy shockwaves on the corpus cavernosum in a rat model of post-prostatectomy erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2016; 88:226.e221–e229. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.10.021. PMID: 26522972.
Article20. Jeong HH, Piao S, Ha JN, Kim IG, Oh SH, Lee JH, Cho HJ, Hong SH, Kim SW, Lee JY. Combined therapeutic effect of udenafil and adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC)/brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-membrane system in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Urology. 2013; 81:1108.e1107–e1114. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.01.022. PMID: 23522997.
Article21. Kim IG, Piao S, Lee JY, Hong SH, Hwang TK, Kim SW, Kim CS, Ra JC, Noh I, Lee JY. Effect of an adipose-derived stem cell and nerve growth factor-incorporated hydrogel on recovery of erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19:14–23. DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2011.0654. PMID: 22834730. PMCID: PMC3530933.
Article22. Lee SH, Kim IG, Jung AR, Shrestha KR, Lee JH, Park KD, Chung BH, Kim SW, Kim KH, Lee JY. Combined effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor immobilized poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid membrane with human adipose-derived stem cells and basic fibroblast growth factor hydrogel on recovery of erectile dysfunction. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014; 20:2446–2454. DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2013.0495. PMID: 24673637. PMCID: PMC4161192.
Article23. Piao S, Kim IG, Lee JY, Hong SH, Kim SW, Hwang TK, Oh SH, Lee JH, Ra JC, Lee JY. Therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells and BDNF-immobilized PLGA membrane in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med. 2012; 9:1968–1979. DOI: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02760.x. PMID: 22642440.
Article24. You D, Jang MJ, Lee J, Suh N, Jeong IG, Sohn DW, Kim SW, Ahn TY, Kim CS. Comparative analysis of periprostatic implantation and intracavernosal injection of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells for erectile function recovery in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Prostate. 2013; 73:278–286. DOI: 10.1002/pros.22567. PMID: 22821215.
Article25. Zheng T, Zhang TB, Wang CL, Zhang WX, Jia DH, Yang F, Sun YY, Ding XJ, Wang R. Icariside II promotes the differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells to Schwann cells to preserve erectile function after cavernous nerve injury. Mol Cells. 2018; 41:553–561. PMID: 29902838. PMCID: PMC6030246.26. Ying C, Yang M, Zheng X, Hu W, Wang X. Effects of intracavernous injection of adipose-derived stem cells on cavernous nerve regeneration in a rat model. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013; 33:233–240. DOI: 10.1007/s10571-012-9890-7. PMID: 23161147.
Article27. Xu Y, Guan R, Lei H, Li H, Wang L, Gao Z, Song W, Xin Z. Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells-based micro-tissues in a rat model of postprostatectomy erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2014; 11:2439–2448. DOI: 10.1111/jsm.12636. PMID: 25042722.
Article28. Ying C, Hu W, Cheng B, Yang M, Zheng X, Wang X. Erectile function restoration after repair of resected cavernous nerves by adipose-derived stem cells combined with autologous vein graft in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 34:393–402. DOI: 10.1007/s10571-013-0024-7. PMID: 24398902.
Article29. Yang R, Fang F, Wang J, Guo H. Adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction after cavernous nerve cryoinjury. Andrology. 2015; 3:694–701. DOI: 10.1111/andr.12047. PMID: 26198799.
Article30. Chen X, Yang Q, Zheng T, Bian J, Sun X, Shi Y, Liang X, Gao G, Liu G, Deng C. Neurotrophic effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on erectile function recovery by pigment epithelium-derived factor secretion in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:5161248. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5161248. PMID: 26783403. PMCID: PMC4691496.
Article31. Lin H, Dhanani N, Tseng H, Souza GR, Wang G, Cao Y, Ko TC, Jiang H, Wang R. Nanoparticle improved stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Urol. 2016; 195:788–795. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.10.129. PMID: 26519654.
Article32. Wu H, Tang WH, Zhao LM, Liu DF, Yang YZ, Zhang HT, Zhang Z, Hong K, Lin HC, Jiang H. Nanotechnology-assisted adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) therapy for erectile dysfunction of cavernous nerve injury: in vivo cell tracking, optimized injection dosage, and functional evaluation. Asian J Androl. 2018; 20:442–447. DOI: 10.4103/aja.aja_48_18. PMID: 30004040. PMCID: PMC6116694.
Article33. Albersen M, Fandel TM, Lin G, Wang G, Banie L, Lin CS, Lue TF. Injections of adipose tissue-derived stem cells and stem cell lysate improve recovery of erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med. 2010; 7:3331–3340. DOI: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01875.x. PMID: 20561166. PMCID: PMC3885341.
Article34. Lin G, Albersen M, Harraz AM, Fandel TM, Garcia M, McGrath MH, Konety BR, Lue TF, Lin CS. Cavernous nerve repair with allogenic adipose matrix and autologous adipose-derived stem cells. Urology. 2011; 77:1509.e1501–e1508. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2010.12.076. PMID: 21492917. PMCID: PMC3158137.
Article35. You D, Jang MJ, Kim BH, Song G, Lee C, Suh N, Jeong IG, Ahn TY, Kim CS. Comparative study of autologous stromal vascular fraction and adipose-derived stem cells for erectile function recovery in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015; 4:351–358. DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0161. PMID: 25792486. PMCID: PMC4367505.
Article36. Bae JH, Shrestha KR, Park YH, Kim IG, Piao S, Jung AR, Jeon SH, Park KD, Lee JY. Comparison between subcutaneous injection of basic fibroblast growth factor-hydrogel and intracavernous injection of adipose-derived stem cells in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Urology. 2014; 84:1248.e1241–e1247. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.07.028. PMID: 25443945.
Article37. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000; 56:455–463. DOI: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x. PMID: 10877304.
Article38. Hallén K, Gustafsson LE, Wiklund NP. Nerve-induced release of nitric oxide from the rabbit corpus cavernosum is modulated by cyclic GMP. Faseb J. 2005; 19:A1205. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.02.015. PMID: 15893640.
Article39. Jeong H, Yim HW, Cho Y, Park HJ, Jeong S, Kim HB, Hong W, Kim H. The effect of rigorous study design in the research of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell transfer in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013; 4:82. DOI: 10.1186/scrt233. PMID: 23849537. PMCID: PMC3854784.
Article40. Conradi U, Joffe AR. Publication bias in animal research presented at the 2008 Society of Critical Care Medicine Conference. BMC Res Notes. 2017; 10:262. DOI: 10.1186/s13104-017-2574-0. PMID: 28683761. PMCID: PMC5501347.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Mitochondria Transplantation Ameliorated Erectile Dysfunction Induced by Cavernous Nerve Injury
- Repeated Injections of Mesenchymal Stem CellDerived Exosomes Ameliorate Erectile Dysfunction in a Cavernous Nerve Injury Rat Model
- L-Theanine-Treated Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate the Cytotoxicity Induced by N-Nitrosodiethylamine in Liver
- Treatment of Bladder Dysfunction Using Stem Cell or Tissue Engineering Technique
- The neural mechanism of apomorphine-induced erection: an experimental study by the comparison with electrostimulation-induced erection of the rat model