Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2019 Jul;7(3):158-164. 10.4168/aard.2019.7.3.158.
A case of FLNA gene mutation with respiratory insufficiency and periventricular heterotopia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmaped@skku.edu
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Environmental Health Center for Atopic Diseases, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2461409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2019.7.3.158
Abstract
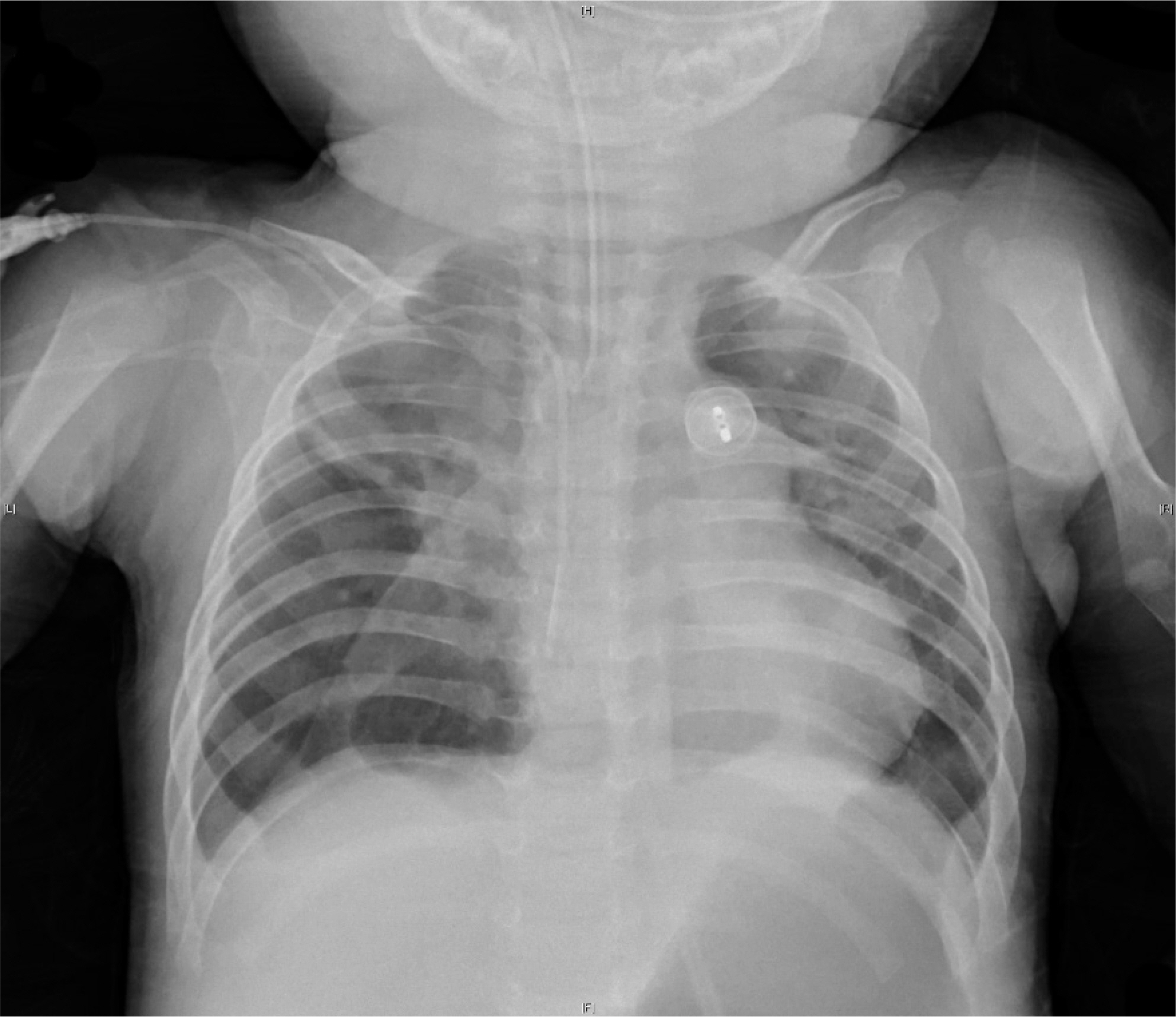
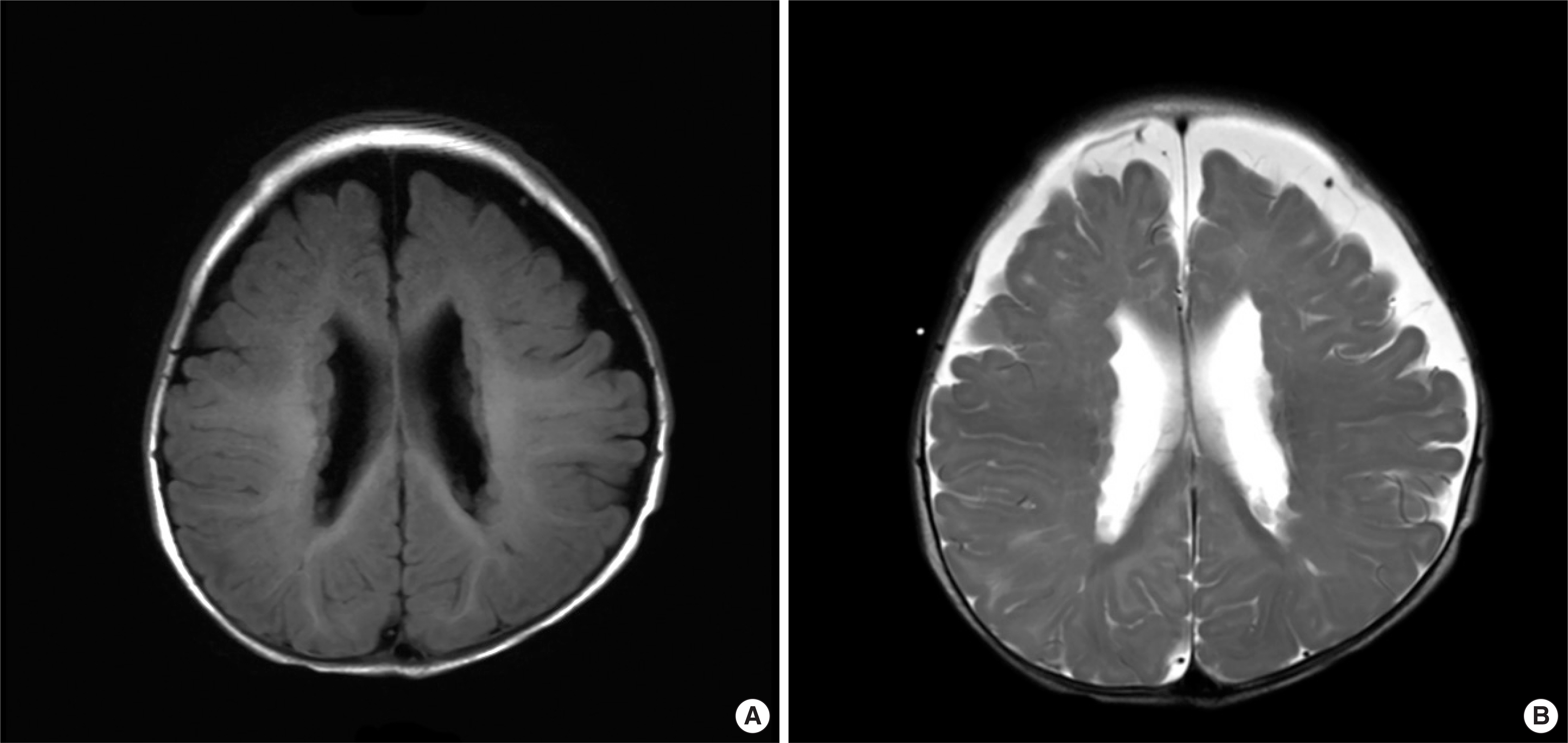
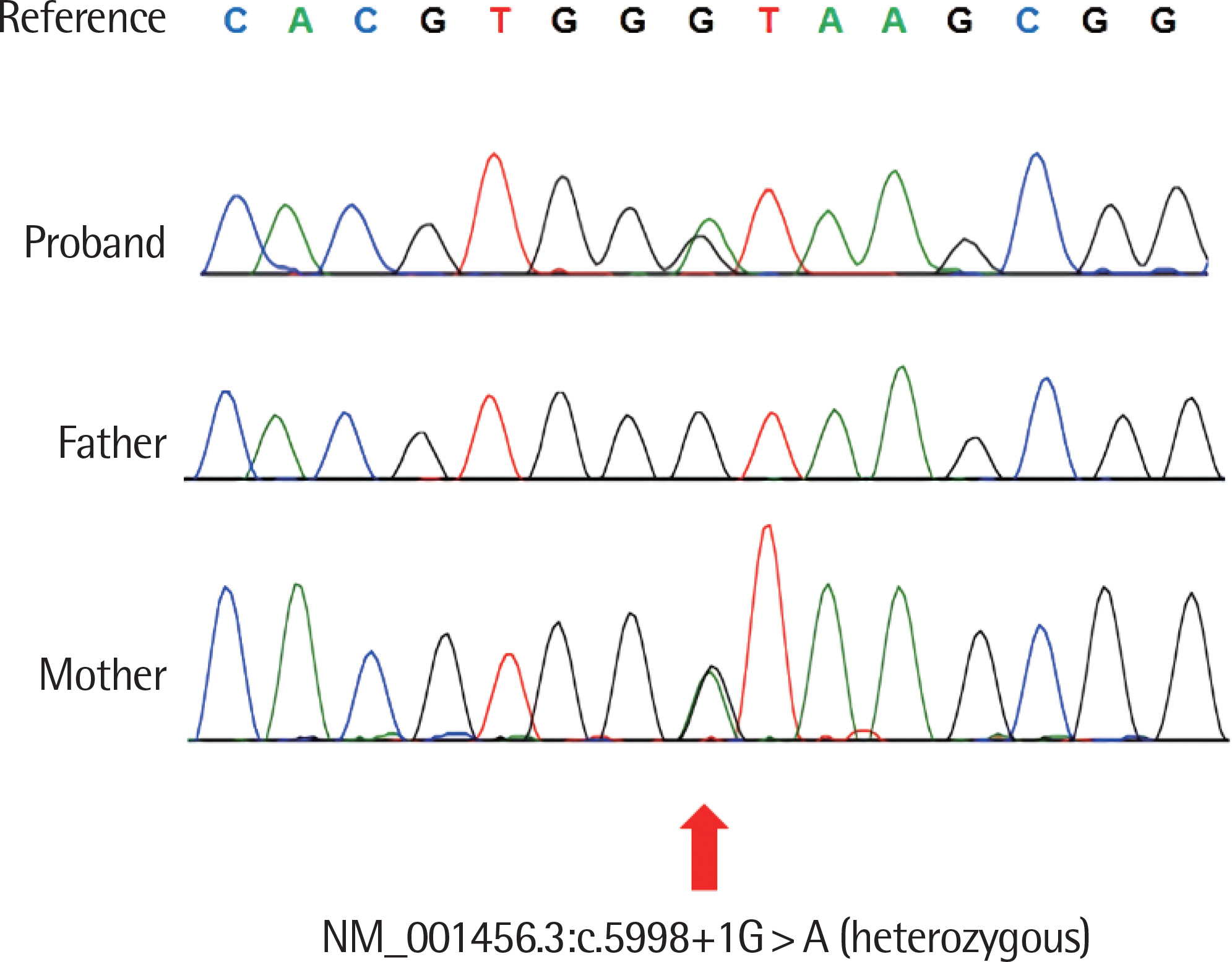
- Filamin A is an actin-binding protein and, in humans, is encoded by FLNA gene in the long arm of X chromosome. Filamin A plays a role in the formation of cytoskeleton by crosslinking actin filaments in cytoplasm. FLNA mutations affect cytoskeletal regulatory processes and cellular migrating abnormalities that result in periventricular heterotopia. A 5-month-old girl was hospitalized because of breathing difficulty and was diagnosed as having periventricular heterotopia with laryngomalacia, cricopharyngeal incoordination, pulmonary hypertension, and chronic lung disease. A genetic test was performed to find the cause of periventricular heterotopia, and FLNA gene mutation (c.5998+1G>A) was confirmed for the first time in Korea. After discharge, she developed respiratory failure due to a viral infection at 8 months of her age. In spite of management with mechanical ventilation, she died of pneumothorax and pulmonary hemorrhage. Herein, we report a case of FLNA gene mutation who presented with periventricular nodular heterotopia with respiratory insufficiency.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hartwig JH, Stossel TP. Isolation and properties of actin, myosin, and a new actinbinding protein in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1975; 250:5696–705.
Article2. Sheen VL, Dixon PH, Fox JW, Hong SE, Kinton L, Sisodiya SM, et al. Mutations in the X-linked filamin 1 gene cause periventricular nodular heterotopia in males as well as in females. Hum Mol Genet. 2001; 10:1775–83.
Article3. Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Ekşioğlu YZ, Hong SE, Feng Y, Graham DA, et al. Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron. 1998; 21:1315–25.
Article4. Cunningham CC, Gorlin JB, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hartwig JH, Janmey PA, Byers HR, et al. Actinbinding protein requirement for cortical stability and efficient locomotion. Science. 1992; 255:325–7.
Article5. Lange M, Kasper B, Bohring A, Rutsch F, Kluger G, Hoffjan S, et al. 47 patients with FLNA associated periventricular nodular heterotopia. Or-phanet J Rare Dis. 2015; 10:134.
Article6. Singh S, Schecter MG, Guillerman RP, Baker ML, Mallory GB. Case series of four infants with severe infantile respiratory failure associated with filamin A mutation leading to lung transplantation [abstract]. In: American Thoracic Society 2013 International Conference; 2013 May 19; Pennsylvania, USA. Pennsylvania (PA): Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013.7. Masurel-Paulet A, Haan E, Thompson EM, Goizet C, Thauvin-Robinet C, Tai A, et al. Lung disease associated with periventricular nodular heterotopia and an FLNA mutation. Eur J Med Genet. 2011; 54:25–8.
Article8. de Wit MC, Tiddens HA, de Coo IF, Mancini GM. Lung disease in FLNA mutation: confirmatory report. Eur J Med Genet. 2011; 54:299–300.
Article9. Lord A, Shapiro AJ, Saint-Martin C, Claveau M, Melançon S, Wintermark P. Filamin A mutation may be associated with diffuse lung disease mimicking bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature newborns. Respir Care. 2014; 59:e171–7.
Article10. Eltahir S, Ahmad KS, Al-Balawi MM, Bukhamsien H, Al-Mobaireek K, Alotaibi W, et al. Lung disease associated with filamin A gene mutation: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016; 10:97.
Article11. Shelmerdine SC, Semple T, Wallis C, Aurora P, Moledina S, Ashworth MT, et al. Filamin A (FLNA) mutation-A newcomer to the childhood interstitial lung disease (ChILD) classification. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2017; 52:1306–15.
Article12. Bickel S, Siefman M, Eid NS. Interstitial lung disease, bronchiectasis, and asthma in a patient with filamin A, alpha (flna) mutation [abstract]. In: American Thoracic Society 2015 International Conference; 2015 May 20; Debver, USA. Debver (CO): Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015.13. Hehr U, Hehr A, Uyanik G, Phelan E, Winkler J, Reardon W. A filamin A splice mutation resulting in a syndrome of facial dysmorphism, periventricular nodular heterotopia, and severe constipation reminiscent of cere-bro-fronto-facial syndrome. J Med Genet. 2006; 43:541–4.
Article14. Poussaint TY, Fox JW, Dobyns WB, Radtke R, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF, e al. Periventricular nodular heterotopia in patients with filamin-1 gene mutations: neuroimaging findings. Pediatr Radiol. 2000; 30:748–55.
Article15. Robertson SP, Twigg SR, Sutherland-Smith AJ, Biancalana V, Gorlin RJ, Horn D, et al. Localized mutations in the gene encoding the cytoskeletal protein filamin A cause diverse malformations in humans. Nat Genet. 2003; 33:487–91.
Article16. Chen CP, Chern SR, Chiu NC, Liu YP, Chen YN, Chen SW, et al. Detection of a novel c.7106_7110delinsT heterozygous mutation in the FLNA gene in an asymptomatic mother with periventricular nodular heterotopia during prenatal genetic counseling. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2016; 55:897–9.
Article17. Loo DT, Kanner SB, Aruffo A. Filamin binds to the cytoplasmic domain of the beta1-integrin. Identification of amino acids responsible for this interaction. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:23304–12.18. Zhang W, Gunst SJ. Interactions of airway smooth muscle cells with their tissue matrix: implications for contraction. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008; 5:32–9.
Article19. Reinstein E, Frentz S, Morgan T, García-Miñaúr S, Leventer RJ, McGilli-vray G, et al. Vascular and connective tissue anomalies associated with X-linked periventricular heterotopia due to mutations in Filamin A. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013; 21:494–502.
Article20. Hayashi K, Altman A. Filamin A is required for T cell activation mediated by protein kinase C-theta. J Immunol. 2006; 177:1721–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- FLNA Duplication in a Female Infant with Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia
- Periventricular nodular heterotopia in a child with a mild Mowat–Wilson phenotype caused by a novel missense mutation of ZEB2
- Periventricular Heterotopia: A Case Report
- A Case of Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome with Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia Presenting with Status Epilepticus
- Hereditary Myopathy with Early Respiratory Failure with a Heterozygous TTN Gene Missense Mutation