Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2019 Oct;7(4):186-191. 10.4168/aard.2019.7.4.186.
Recent changing pattern of aeroallergen sensitization in children with allergic diseases: A single center study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hbkim@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2461395
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2019.7.4.186
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Allergic diseases have been increasing worldwide over the past few decades. Allergic sensitization is a pivotal risk factor for the development of allergic diseases. The purpose of this study was to examine changes in allergic sensitization patterns of aeroallergens over the last 10 years in children with respiratory allergic diseases.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 12,848 children under the age of 18 years who received skin prick tests (n=3,852) or serum specific IgE tests (n=8,996) to evaluate sensitization from 2007 to 2016 in a single center, Seoul, Korea.
RESULTS
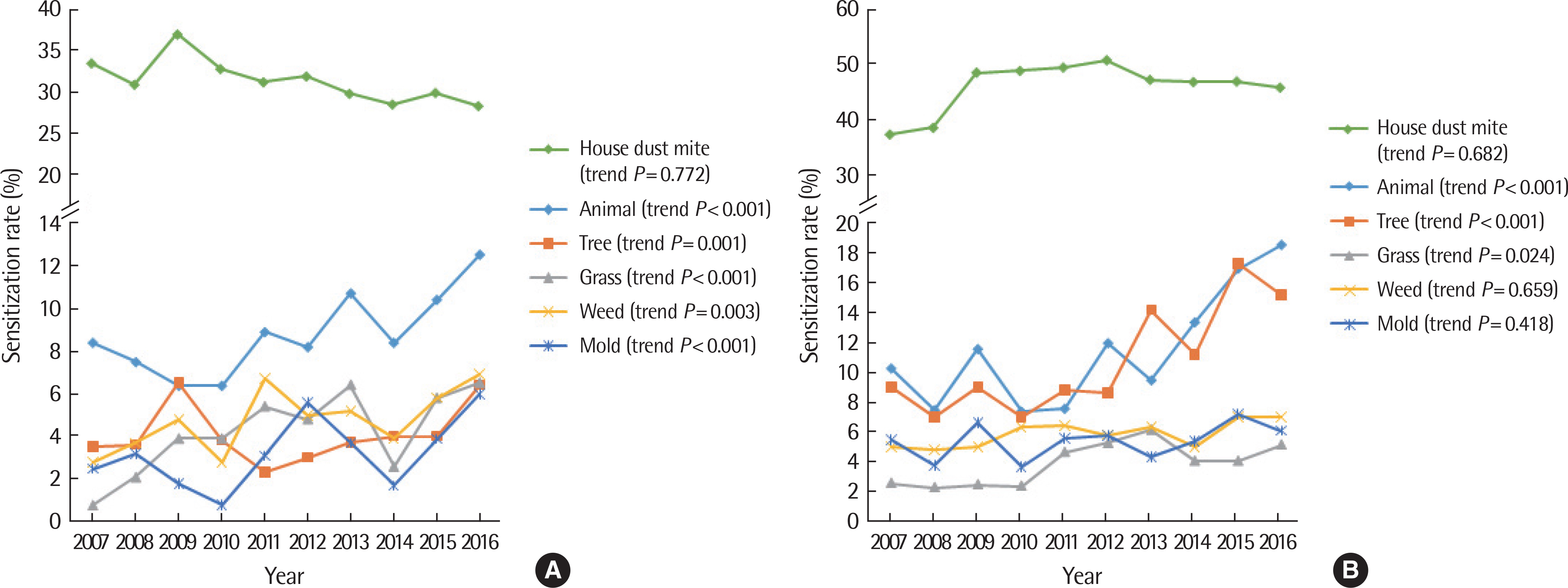
Sensitization rate to house dust mite (Dermatophagoides farinae and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) reached a plateau in preschool (28.3%-32.8%) and schoolchildren (45.8%-47.2%). Sensitization rate to animal dander (cat and dog) was increasing from 8.4% to 12.5% in preschool children and from 10.3% to 18.6% in schoolchildren (trend P<0.001 each). In preschool children, tree (birch, oak, and alder; from 3.5% to 6.4%), grass (timothy; from 0.8% to 6.5%), weed (ragweed and mugwort; from 2.8% to 6.9%) pollens and mold (Alternaria; from 2.5% to 6.0%) were also in similar increasing pattern (trend P=0.001, P<0.001, P=0.003, and P<0.001, respectively). Additionally, tree (from 9.0% to 15.2%), grass (from 2.6% to 5.2%) pollens were also in increasing pattern in schoolchildren (trend P<0.001 and P=0.024, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Over the past 10 years, sensitization patterns of aeroallergen have been changing in Korean children with allergic diseases. We should pay attention to the changing patterns of allergic sensitization to educate and prevent the allergic disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Changes of aeroallergen sensitization in childhood
So-Yeon Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2019;7(4):171-172. doi: 10.4168/aard.2019.7.4.171.
Reference
-
References
1. Suh M, Kim HH, Sohn MH, Kim KE, Kim C, Shin DC. Prevalence of allergic diseases among Korean school-age children: a nationwide cross-sectional questionnaire study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:332–8.
Article2. Eder W, Ege MJ, von Mutius E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2226–35.
Article3. Gupta RS, Springston EE, Warrier MR, Smith B, Kumar R, Pongracic J, et al. The prevalence, severity, and distribution of childhood food allergy in the United States. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:e9–17.
Article4. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:343–50.
Article5. MacIntyre EA, Carlsten C, MacNutt M, Fuertes E, Melén E, Tiesler CM, et al. Traffic, asthma and genetics: combining international birth cohort data to examine genetics as a mediator of traffic-related air pollution's impact on childhood asthma. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013; 28:597–606.
Article6. Calışkan M, Bochkov YA, Kreiner-Møller E, Bønnelykke K, Stein MM, Du G, et al. Rhinovirus wheezing illness and genetic risk of childhood-onset asthma. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:1398–407.
Article7. Cecchi L, D'Amato G, Annesi-Maesano I. External exposome and allergic respiratory and skin diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141:846–57.
Article8. Oh JW. Characteristics of allergic pollens and the recent increase of sensitization rate to weed pollen in childhood in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:355–61.
Article9. Jung YH, Hwang KH, Yang SI, Lee E, Kim KH, Kim MJ, et al. Changes of aeroallergen sensitization in children with asthma or allergic rhinitis from a tertiary referral hospital in Seoul over 10 years. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014; 2:97–102.
Article10. Choi MH, Kwon EM, Kim HB, Kim CK. Sensitization to inhalant allergens and its association with allergic diseases in preschool children. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 32:176–82.11. Na MS, Kim GR, Ha EK, Lee SJ, Sheen YH, Choi SH, et al. Allergen sensitization and clinical characteristics in young children with atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:128–34.
Article12. Kim J, Hahm MI, Lee SY, Kim WK, Chae Y, Park YM, et al. Sensitization to aeroallergens in Korean children: a population-based study in 2010. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1165–72.
Article13. Park SH, Lim DH, Son BK, Kim JH, Song YE, Oh IB, et al. Sensitization rates of airborne pollen and mold in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:322–9.
Article14. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:350–5.
Article15. Kim YJ, Yoon SA, Woo SI. Relation of allergic rhinitis, allergen sensitization, and air pollutants in preschool children. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018; 6:197–205.
Article16. Arbes SJ Jr, Gergen PJ, Vaughn B, Zeldin DC. Asthma cases attributable to atopy: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1139–45.
Article17. Jackson DJ, Gern JE, Lemanske RF Jr. Lessons learned from birth cohort studies conducted in diverse environments. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139:379–86.
Article18. Anderson HR, Ruggles R, Pandey KD, Kapetanakis V, Brunekreef B, Lai CK, et al. Ambient particulate pollution and the worldwide prevalence of asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema in children: Phase One of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Occup Environ Med. 2010; 67:293–300.
Article19. Zahradnik E, Raulf M. Animal allergens and their presence in the environment. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:76.
Article20. Frenguelli G. Interactions between climatic changes and allergenic plants. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2002; 57:141–3.21. Oh JW, Lee HB, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Park KS, Kook MH, et al. The revised edition of korean calendar for allergenic pollens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:5–11.
Article22. Yang HJ, Jeon YH, Min TK, Son BS, Park KJ, Moon JY, et al. The impact of climate change on aeroalleregen and pediatric allergic diseases. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:971–8.
Article23. Katotomichelakis M, Anastassakis K, Gouveris H, Tripsianis G, Paraska-kis E, Maroudias N, et al. Clinical significance of Alternaria alternata sensitization in patients with allergic rhinitis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012; 33:232–8.
Article24. Randriamanantany ZA, Annesi-Maesano I, Moreau D, Raherison C, Charpin D, Kopferschmitt C, et al. Alternaria sensitization and allergic rhinitis with or without asthma in the French Six Cities study. Allergy. 2010; 65:368–75.25. Byeon JH, Ri S, Amarsaikhan O, Kim E, Ahn SH, Choi IS, et al. Association between sensitization to mold and impaired pulmonary function in children with asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:509–16.
Article26. Bush RK, Portnoy JM. The role and abatement of fungal allergens in allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107(3 Suppl):S430–40.
Article27. Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS. House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:313–25.
Article28. Kim KW, Kim EA, Kwon BC, Kim ES, Song TW, Sohn MH, et al. Comparison of allergic indices in monosensitized and polysensitized patients with childhood asthma. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:1012–6.
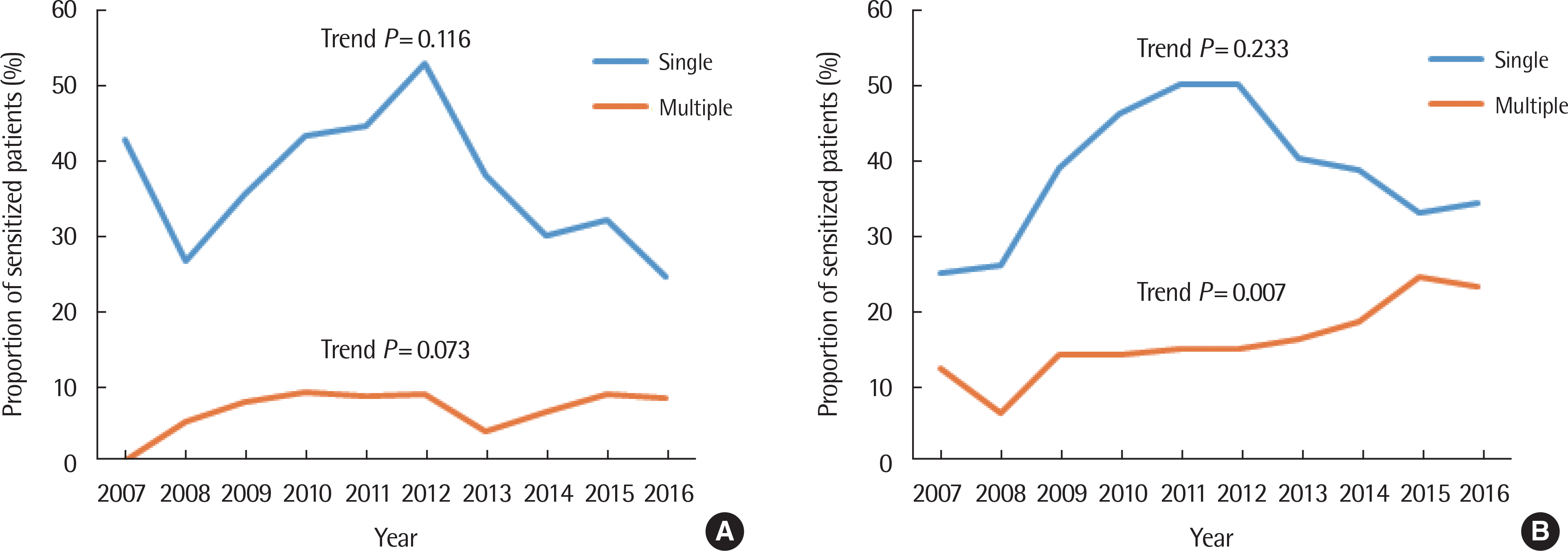
Article29. Ha EK, Baek JH, Lee SY, Park YM, Kim WK, Sheen YH, et al. Association of polysensitization, allergic multimorbidity, and allergy severity: a cross-sectional study of school children. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2016; 171:251–60.
Article30. Cirillo I, Vizzaccaro A, Klersy C, Baiardini I, Marseglia GL, Canonica GW, et al. Quality of life and polysensitization in young men with intermittent asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005; 94:640–3.
Article31. Park KH, Lee J, Lee SC, Son YW, Sim DW, Lee JH, et al. Comparison of the ImmunoCAP assay and advansure alloscreen advanced multiplex specific IgE detection assay. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:786–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Antigen Sensitization and Development of Respiratory Allergy Disease on Severity of Atopic Dermatitis
- Changes in allergen sensitization in children with allergic diseases in the 1980 to 2019
- Allergen sensitization trajectories in children with respiratory and allergic diseases
- Aeroallergen sensitization and associated comorbid diseases of an adult Filipino population with allergic rhinitis
- Association of SCORAD Index and Aeroallergen Sensitization on Urinary Leukotriene E4 in Children with Atopic Dermatitis