Clin Nutr Res.
2019 Oct;8(4):272-283. 10.7762/cnr.2019.8.4.272.
Nutrition Care Management Practices for In-Patients with Dysphagia in Korean Clinical Settings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Major of Food and Nutrition, Seoul Women's University, Seoul 01797, Korea. klee@swu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2461095
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2019.8.4.272
Abstract
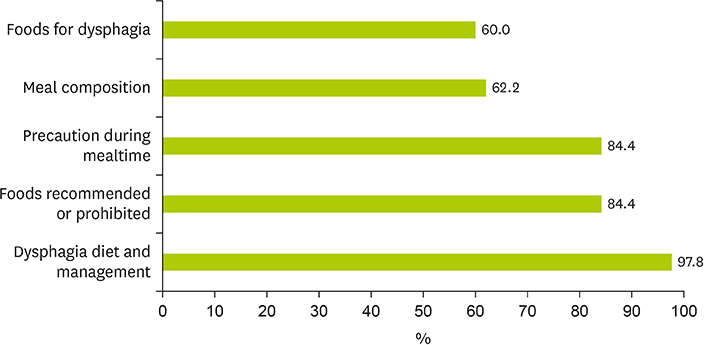
- This study aimed to examine nutrition care management for in-patients with dysphagia and to evaluate knowledge on nutrition care related to dysphagia among dietitians in clinical settings. A total of 554 questionnaires were distributed to dietitians at hospitals located in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province in Korea, and 147 responses were used for data analysis after excluding responses with significant missing data. Study participants worked at general hospitals (37.2%), long-term care hospitals (24.3%), hospitals (19.2%), and tertiary hospitals (11.5%). Prior education and training related to dysphagia was received by 69.9% of the respondents. The percentage of hospitals that had diet guidelines for dysphagia was 68.0%. Dysphagia diets of 2 levels and 3 levels were provided in 55.1% and 34.7% of the hospitals, respectively. Overall 74.7% of the dietitians responded that they provided information on dysphagia diets to in-patients and caregivers, but only 45.7% of dietitians did so in the long-term care hospitals. Among the respondents who used commercial thickening agents, 77.2% used only one type of commercial thickening agent. Patients or caregivers (75.7%) or nurses (34.5%) were reported to modify viscosity of liquid. Dietitians showed low levels of knowledge on nutrition care related to dysphagia (a mean of 5.14 based on possible scores from 0 to 10 points). To promote nutritional consumption and prevent malnutrition and aspiration, hospitals need the standardized diet guidelines, and dietitians should improve their expertise in nutritional care for patients with dysphagia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Taylor KA, Barr SI. Provision of small, frequent meals does not improve energy intake of elderly residents with dysphagia who live in an extended-care facility. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006; 106:1115–1118.
Article2. Kawashima K, Motohashi Y, Fujishima I. Prevalence of dysphagia among community-dwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening. Dysphagia. 2004; 19:266–271.
Article3. Madhavan A, LaGorio LA, Crary MA, Dahl WJ, Carnaby GD. Prevalence and risk factors for dysphagia in the community dwelling elderly: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging. 2016; 20:806–815.
Article4. Kim MS, Park YH. The risk of dysphagia and dysphagia-specific quality of life among community dwelling older adults in senior center. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2014; 26:393–402.
Article5. Park YH, Han HR, Oh BM, Lee J, Park JA, Yu SJ, Chang H. Prevalence and associated factors of dysphagia in nursing home residents. Geriatr Nurs. 2013; 34:212–217.
Article6. Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D, Cameron D. Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke. 1999; 30:744–748.7. Sura L, Madhavan A, Carnaby G, Crary MA. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin Interv Aging. 2012; 7:287–298.8. Ekberg O, Hamdy S, Woisard V, Wuttge-Hannig A, Ortega P. Social and psychological burden of dysphagia: its impact on diagnosis and treatment. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:139–146.
Article9. Takeuchi K, Aida J, Ito K, Furuta M, Yamashita Y, Osaka K. Nutritional status and dysphagia risk among community-dwelling frail older adults. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014; 18:352–357.
Article10. Foley NC, Martin RE, Salter KL, Teasell RW. A review of the relationship between dysphagia and malnutrition following stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2009; 41:707–713.
Article11. Runions S, Rodrigue N, White C. Practice on an acute stroke unit after implementation of a decision-making algorithm for dietary management of dysphagia. J Neurosci Nurs. 2004; 36:200–207.
Article12. Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005; 36:2756–2763.13. Garcia JM, Chambers E 4th. Managing dysphagia through diet modifications. Am J Nurs. 2010; 110:26–33.
Article14. Lotong V, Chun SS, Chambers E, Garcia JM. Texture and flavor characteristics of beverages containing commercial thickening agents for dysphagia diets. J Food Sci. 2003; 68:1537–1541.
Article15. Matta Z, Chambers E 4th, Mertz Garcia J, McGowan Helverson JM. Sensory characteristics of beverages prepared with commercial thickeners used for dysphagia diets. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006; 106:1049–1054.
Article16. Garcia JM, Chambers E 4th, Clark M, Helverson J, Matta Z. Quality of care issues for dysphagia: modifications involving oral fluids. J Clin Nurs. 2010; 19:1618–1624.
Article17. Korea Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. 2019 A guide to food preparation for people with difficulties in chewing and swallowing. Sejong: Korea Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2019.18. Johnson S, Broady R, Marcus A, Touger-Decker R. Knowledge and performance of dysphagia risk screening among registered dietitians in clinical practice. Top Clin Nutr. 2015; 30:302–313.
Article19. Kim HJ, Kim EM, Kee GJ, Lee JJ, Lim JH, Lee JM, Leon HJ, Lee HY. Clinical nutrition service at medical centers in Seoul. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2011; 17:176–189.20. Lee SJ, Park EJ. Importance-performance analysis of clinical nutrition management in convalescent hospitals in the Gyeongnam area. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2016; 22:53–69.
Article21. Yi JR, Son EJ, Lyu ES. Perception and satisfaction on nutrition counseling service for patients consuming a therapeutic diet at hospitals in Busan. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2010; 39:1305–1312.
Article22. Park MS, Lyu ES. Importance and performance of dietitian’s task at long term care hospital foodservice in Busan·Kyungnam area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16:602–612.
Article23. McCallum SL. The national dysphagia diet: implementation at a regional rehabilitation center and hospital system. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003; 103:381–384.
Article24. Seo JS, Kim EM, Park MS, Son JM, Woo MH, Wie KA, Lee SM, Ju DL, Cha JA. Job standards and practice toolkits for clinical nutrition therapy: diabetes mellitus cancer dyslipidemia. Sejong: Ministry of Health & Welfare;2014.25. Castellanos VH, Butler E, Gluch L, Burke B. Use of thickened liquids in skilled nursing facilities. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004; 104:1222–1226.
Article26. Groher ME, McKaig TN. Dysphagia and dietary levels in skilled nursing facilities. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1995; 43:528–532.
Article27. Um MH, Lyu ES, Lee SM, Lee SM, Lee E, Cha JA, Park MS, Lee HS, Rha MY, Park YK. Clinical nutrition services of a long-term care hospital in Korea. Korean J Community Nutr. 2015; 20:220–235.
Article28. Kim HJ, Kim EM, Lee GJ, Lee JJ, Lim JH, Lee JM, Jeon HJ, Lee HY. Clinical nutrition service at medical centers in Seoul. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2011; 17:176–189.29. Choi KB, Lee SM, Lee SM, Lee E, Park MS, Park YK, Cha JA, Lyu ES. Patient satisfaction and perception on nutritional counseling services quality. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2017; 46:251–258.
Article30. Um MH, Park YK, Lee SO, Lee SM, Lee E, Cha JA, Park MS, Lee HS, Rha MY, Lyu ES. Clinical nutrition service in Korean tertiary hospitals and general hospitals: result of nationwide cross-sectional survey. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2014; 20:183–198.
Article31. Hong SY, Seo S. Job performance frequency and the training needs of dietitians in elderly healthcare facilities. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2010; 16:160–177.32. Clavé P, de Kraa M, Arreola V, Girvent M, Farré R, Palomera E, Serra-Prat M. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 24:1385–1394.
Article33. Garcia JM, Chambers E 4th, Matta Z, Clark M. Viscosity measurements of nectar- and honey-thick liquids: product, liquid, and time comparisons. Dysphagia. 2005; 20:325–335.
Article34. Garcia JM, Chambers E 4th, Molander M. Thickened liquids: practice patterns of speech-language pathologists. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2005; 14:4–13.35. Langmore SE, Terpenning MS, Schork A, Chen Y, Murray JT, Lopatin D, Loesche WJ. Predictors of aspiration pneumonia: how important is dysphagia? Dysphagia. 1998; 13:69–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nursing Care of Patients with Dysphagia
- Sarcopenic Dysphagia and Simplified Rehabilitation Nutrition Care Process: An Update
- Meal Service and Nutritional Management for Dysphagia: A Nationwide Hospital Survey
- Assessment and Management of Dysphagia during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Nutrition Support and Transition to Oral Intake in Cancer Patients with Dysphagia