Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Real-World Clinical Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mkmoon@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2460953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0134
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in Korean patients who had inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in real-world clinical practice.
METHODS
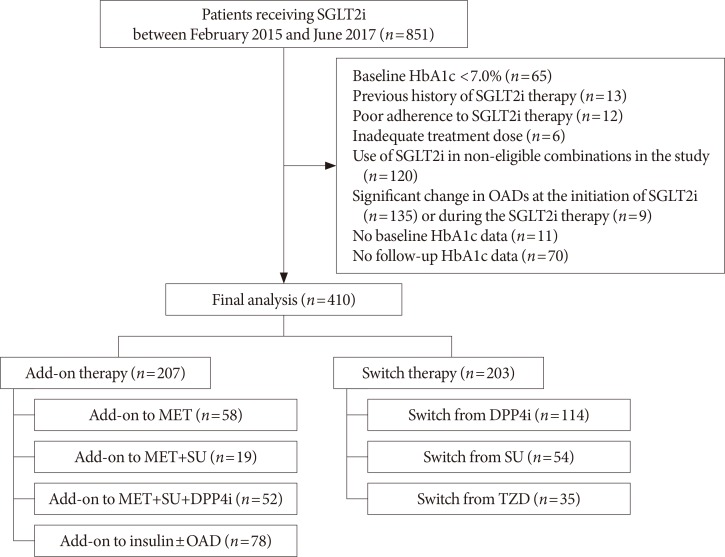
We included 410 patients who started SGLT2 inhibitors (empagliflozin or dapagliflozin) as add-on therapy or switch therapy between February 2015 and June 2017. The primary efficacy endpoint was a change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline to week 12. The secondary endpoints were patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% and changes in the fasting plasma glucose (FPG), lipid profiles, body weight, and blood pressure (BP).
RESULTS
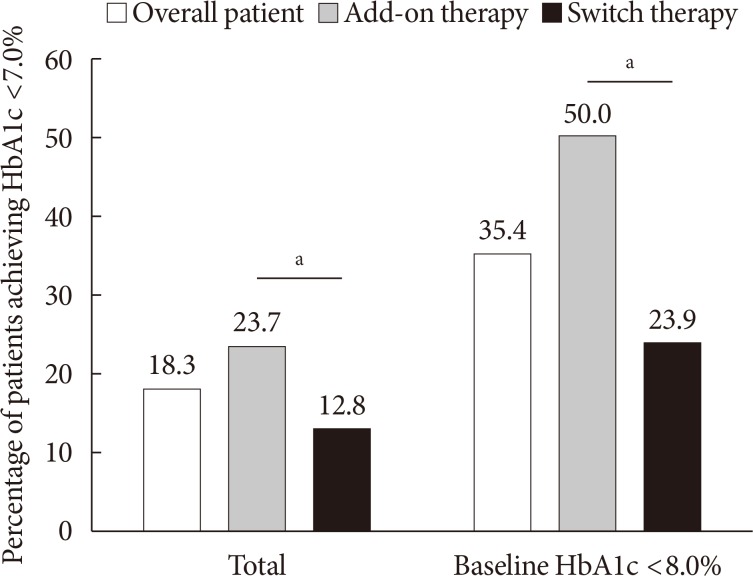
The mean HbA1c at baseline was 8.5% (8.6% in the add-on group and 8.4% in the switch group). At week 12, the mean adjusted HbA1c decreased by −0.68% in the overall patients (P<0.001), by −0.94% in the add-on group, and by −0.42% in the switch group. Significant reductions in FPG were also observed both in the add-on group and switch group (−30.3 and −19.8 mg/dL, respectively). Serum triglyceride (−16.5 mg/dL), body weight (−2.1 kg), systolic BP (−4.7 mm Hg), and diastolic BP (−1.3 mm Hg) were significantly improved in the overall patients. Approximately 18.3% of the patients achieved HbA1c <7.0% at week 12. A low incidence of hypoglycemia and genital tract infection was observed (6.3% and 2.2%, respectively).
CONCLUSION
SGLT2 inhibitors can be a suitable option as either add-on or switch therapy for Korean patients with inadequately controlled T2DM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon, ,
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):489-497. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0172.Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):808-817. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0387.
Reference
-
1. NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016; 387:1513–1530. PMID: 27061677.2. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2018. cited 2019 Jan 12. http://www.diabetes.or.kr/bbs/skin/dianews/download.php?code=admin&number=1694.3. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015; 58:429–442. PMID: 25583541.
Article4. American Diabetes Association. 8. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40(Suppl 1):S64–S74. PMID: 27979895.5. Abdul-Ghani MA, DeFronzo RA. Lowering plasma glucose concentration by inhibiting renal sodium-glucose cotransport. J Intern Med. 2014; 276:352–363. PMID: 24690096.
Article6. Ferrannini E, Solini A. SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes mellitus: rationale and clinical prospects. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012; 8:495–502. PMID: 22310849.
Article7. Zaccardi F, Webb DR, Htike ZZ, Youssef D, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:783–794. PMID: 27059700.
Article8. Vasilakou D, Karagiannis T, Athanasiadou E, Mainou M, Liakos A, Bekiari E, Sarigianni M, Matthews DR, Tsapas A. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013; 159:262–274. PMID: 24026259.9. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE. EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–2128. PMID: 26378978.
Article10. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Law G, Desai M, Matthews DR. CANVAS Program Collaborative Group. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:644–657. PMID: 28605608.
Article11. Singh AK, Singh R. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as add-on therapy to insulin: rationale and evidences. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 9:409–418. PMID: 26732230.
Article12. Tang H, Cui W, Li D, Wang T, Zhang J, Zhai S, Song Y. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in addition to insulin therapy for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017; 19:142–147. PMID: 27598833.
Article13. Tamez-Perez HE, Delgadillo-Esteban E, Soni-Duque D, Hernandez-Coria MI, Tamez-Pena AL. SGLT2 inhibitors as add on therapy in type 2 diabetes: a real world study. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2017; 16:27. PMID: 28680862.
Article14. Brown RE, Gupta N, Aronson R. Effect of dapagliflozin on glycemic control, weight, and blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes attending a specialist endocrinology practice in Canada: a retrospective cohort analysis. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017; 19:685–691. PMID: 28829163.
Article15. Blonde L, Patel C, Bookhart B, Pfeifer M, Chen YW, Wu B. A real-world analysis of glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes treated with canagliflozin versus dapagliflozin. Curr Med Res Opin. 2018; 34:1143–1152. PMID: 29595326.
Article16. Han E, Kim A, Lee SJ, Kim JY, Kim JH, Lee WJ, Lee BW. Characteristics of dapagliflozin responders: a longitudinal, prospective, nationwide dapagliflozin surveillance study in Korea. Diabetes Ther. 2018; 9:1689–1701. PMID: 29998370.
Article17. Ku EJ, Lee DH, Jeon HJ, Oh TK. Effectiveness and safety of empagliflozin-based quadruple therapy compared with insulin glargine-based therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: an observational study in clinical practice. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019; 21:173–177. PMID: 30039538.
Article18. Jeon HJ, Ku EJ, Oh TK. Dapagliflozin improves blood glucose in diabetes on triple oral hypoglycemic agents having inadequate glucose control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 142:188–194. PMID: 29807104.
Article19. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2017. Summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40(Suppl 1):S4–S5. PMID: 27979887.20. Horie I, Haraguchi A, Sako A, Akeshima J, Niri T, Shigeno R, Ito A, Nozaki A, Natsuda S, Akazawa S, Mori Y, Ando T, Kawakami A, Abiru N. Predictive factors of efficacy of combination therapy with basal insulin and liraglutide in type 2 diabetes when switched from longstanding basal-bolus insulin: association between the responses of β- and α-cells to GLP-1 stimulation and the glycaemic control at 6 months after switching therapy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 144:161–170. PMID: 30194951.21. Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:461–470. PMID: 10075613.22. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419. PMID: 3899825.23. World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. cited 2019 Jan 12. Available from: http://www.wpro.who.int/nutrition/documents/docs/Redefiningobesity.pdf.24. Wilding JP, Woo V, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Parikh S. Dapagliflozin 006 Study Group. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:124–136. PMID: 23911013.
Article25. Chow W, Miyasato G, Kokkotos FK, Bailey RA, Buysman EK, Henk HJ. Real-world canagliflozin utilization: glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multi-database synthesis. Clin Ther. 2016; 38:2071–2082. PMID: 27596020.26. Scheerer MF, Rist R, Proske O, Meng A, Kostev K. Changes in HbA1c, body weight, and systolic blood pressure in type 2 diabetes patients initiating dapagliflozin therapy: a primary care database study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2016; 9:337–345. PMID: 27822077.
Article27. Lavalle-Gonzalez FJ, Januszewicz A, Davidson J, Tong C, Qiu R, Canovatchel W, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin compared with placebo and sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes on background metformin monotherapy: a randomised trial. Diabetologia. 2013; 56:2582–2592. PMID: 24026211.
Article28. Rosenstock J, Seman LJ, Jelaska A, Hantel S, Pinnetti S, Hach T, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, as add-on to metformin in type 2 diabetes with mild hyperglycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:1154–1160. PMID: 23906374.
Article29. Haring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Broedl UC, Woerle HJ. EMPA-REG MET Trial Investigators. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1650–1659. PMID: 24722494.30. DeFronzo RA, Lewin A, Patel S, Liu D, Kaste R, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Erratum. Combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin as second-line therapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:384–393. 1173PMID: 25583754.31. Ross S, Thamer C, Cescutti J, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin twice daily versus once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 16-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:699–702. PMID: 25827441.
Article32. Haring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG METSU Trial Investigators. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3396–3404. PMID: 23963895.33. Matthaei S, Bowering K, Rohwedder K, Grohl A, Parikh S. Study 05 Group. Dapagliflozin improves glycemic control and reduces body weight as add-on therapy to metformin plus sulfonylurea: a 24-week randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:365–372. PMID: 25592197.
Article34. Wilding JP, Charpentier G, Hollander P, Gonzalez-Galvez G, Mathieu C, Vercruysse F, Usiskin K, Law G, Black S, Canovatchel W, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sulphonylurea: a randomised trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2013; 67:1267–1282. PMID: 24118688.
Article35. Kern M, Kloting N, Mark M, Mayoux E, Klein T, Bluher M. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice both as monotherapy and in combination with linagliptin. Metabolism. 2016; 65:114–123. PMID: 26773934.
Article36. Ahn CH, Oh TJ, Kwak SH, Cho YM. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition improves incretin sensitivity of pancreatic β-cells in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:370–377. PMID: 28786557.
Article37. Ma RC, Chan JC. Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013; 1281:64–91. PMID: 23551121.
Article38. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006; 368:1681–1688. PMID: 17098087.
Article39. Graefe-Mody U, Retlich S, Friedrich C. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of linagliptin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012; 51:411–427. PMID: 22568694.
Article40. Hu P, Yin Q, Deckert F, Jiang J, Liu D, Kjems L, Dole WP, He YL. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in healthy Chinese volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 49:39–49. PMID: 18832295.
Article41. Jabbour S, Seufert J, Scheen A, Bailey CJ, Karup C, Langkilde AM. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis of safety data from phase IIb/III clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:620–628. PMID: 28950419.
Article42. Ferrannini E, Seman L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Hantel S, Pinnetti S, Woerle HJ. A phase IIb, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:721–728. PMID: 23398530.
Article43. Søfteland E, Meier JJ, Vangen B, Toorawa R, Maldonado-Lutomirsky M, Broedl UC. Empagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with linagliptin and metformin: a 24-week randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40:201–209. PMID: 27913576.
Article44. Roden M, Weng J, Eilbracht J, Delafont B, Kim G, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG MONO trial investigators. Empagliflozin monotherapy with sitagliptin as an active comparator in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013; 1:208–219. PMID: 24622369.
Article45. Wilding JP, Norwood P, T'joen C, Bastien A, List JF, Fiedorek FT. A study of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin plus insulin sensitizers: applicability of a novel insulin-independent treatment. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1656–1662. PMID: 19528367.46. Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Mahaffey KW, Fulcher G, Ways K, Desai M, Shaw W, Capuano G, Alba M, Jiang J, Vercruysse F, Meininger G, Matthews D. CANVAS Trial Collaborative Group. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin, an inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2, when used in conjunction with insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:403–411. PMID: 25468945.
Article47. Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Frappin G, Salsali A, Kim G, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG MDI Trial Investigators. Improved glucose control with weight loss, lower insulin doses, and no increased hypoglycemia with empagliflozin added to titrated multiple daily injections of insulin in obese inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1815–1823. PMID: 24929430.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Emerging Safety Issues of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: How to Interpret and Apply in Clinical Practice
- The Side Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor
- Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for People with Type 1 Diabetes
- Glucose Lowering Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of Clinical Studies