Yonsei Med J.
2019 Nov;60(11):1021-1027. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1021.
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Pathological Renal Sinus Fat Invasion in Renal Cell Carcinomas of ≤7 cm with Presumed Renal Sinus Fat Invasion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. uroham@yuhs.ac
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt.
- KMID: 2460218
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1021
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Computed tomography (CT) is the most useful diagnostic modality for staging renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, CT is limited in its ability to predict renal sinus fat invasion (SFI). Here, we aimed to evaluate whether preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) could predict pathological SFI in patients with RCC of ≤7 cm for whom preoperative imaging reveals potential renal SFI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of 1311 patients who underwent extirpative renal surgery for non-metastatic RCC of ≤7 cm between November 2005 and December 2014. After excluding patients with no SFI in preoperative imaging, unavailable preoperative data, and morbidity affecting inflammatory markers, a total of 476 patients were included in this study. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate predictors of pathological SFI.
RESULTS
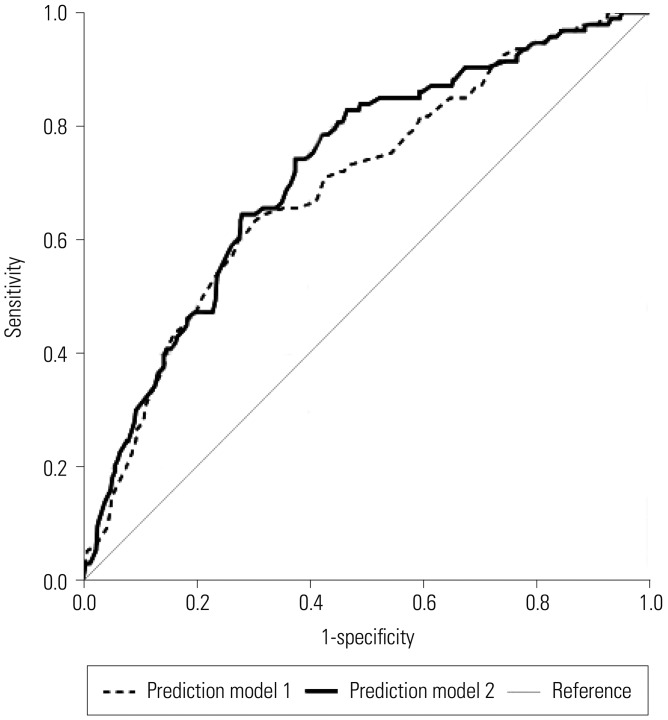
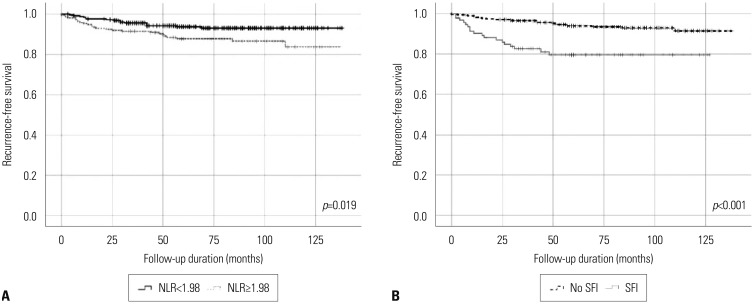
We implemented a cut-off value of 1.98, which was calculated by ROC analysis to obtain high (≥1.98) and low (<1.98) NLR groups. A total of 93 patients with pathological SFI had larger clinical tumor size, higher preoperative NLR, larger pathological tumor size, more frequent renal vein involvement, and higher Fuhrman nuclear grade. Multivariate analysis indicated that high NLR [odds ratio (OR) 2.032, p=0.004], clinical tumor size (OR 1.586, p<0.001), and collecting system involvement on preoperative imaging (OR 3.957, p=0.011) were significantly associated with pathological SFI in these tumors.
CONCLUSION
Preoperative high NLR was associated with pathological SFI in patients with RCC of ≤7 cm and presumed SFI on preoperative imaging. Greater surgical attention is needed to obtain negative margins during partial nephrectomy in these patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hollingsworth JM, Miller DC, Daignault S, Hollenbeck BK. Rising incidence of small renal masses: a need to reassess treatment effect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:1331–1334. PMID: 16985252.
Article3. Edge BE, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A 3rd. AJCC cancer staging handbook: from the AJCC cancer staging mannual. 7th ed. Chicago (IL): Springer;2011.4. Ramaswamy K, Kheterpal E, Pham H, Mohan S, Stifelman M, Taneja S, et al. Significance of pathologic T3a upstaging in clinical T1 renal masses undergoing nephrectomy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015; 13:344–349. PMID: 25680295.
Article5. Nayak JG, Patel P, Saarela O, Liu Z, Kapoor A, Finelli A, et al. Pathological upstaging of clinical T1 to pathological T3a renal cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional analysis of short-term outcomes. Urology. 2016; 94:154–160. PMID: 27041471.
Article6. Mouracade P, Kara O, Dagenais J, Maurice MJ, Nelson RJ, Malkoc E, et al. Perioperative morbidity, oncological outcomes and predictors of pT3a upstaging for patients undergoing partial nephrectomy for cT1 tumors. World J Urol. 2017; 35:1425–1433. PMID: 28197727.
Article7. Thompson RH, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Webster WS, Zincke H, Kwon ED, et al. Reclassification of patients with pT3 and pT4 renal cell carcinoma improves prognostic accuracy. Cancer. 2005; 104:53–60. PMID: 15895375.
Article8. Bonsib SM, Gibson D, Mhoon M, Greene GF. Renal sinus involvement in renal cell carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000; 24:451–458. PMID: 10716160.
Article9. Kim C, Choi HJ, Cho KS. Diagnostic value of multidetector computed tomography for renal sinus fat invasion in renal cell carcinoma patients. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:914–918. PMID: 24713489.
Article10. Ramsey S, Lamb GW, Aitchison M, McMillan DC. Prospective study of the relationship between the systemic inflammatory response, prognostic scoring systems and relapse-free and cancer-specific survival in patients undergoing potentially curative resection for renal cancer. BJU Int. 2008; 101:959–963. PMID: 18190639.
Article11. Saito K, Kihara K. Role of C-reactive protein in urological cancers: a useful biomarker for predicting outcomes. Int J Urol. 2013; 20:161–171. PMID: 22897628.
Article12. Han JH, Yoon YE, Kim SY, Cho YI, Rha KH, Choi YD, et al. Preoperative lymphocyte-monocyte ratio ameliorates the accuracy of differential diagnosis in non-metastatic infiltrative renal masses. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:388–394. PMID: 28120570.
Article13. Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Ohori M, Hatano T, Tachibana M. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010; 184:873–878. PMID: 20643463.
Article14. de Martino M, Pantuck AJ, Hofbauer S, Waldert M, Shariat SF, Belldegrun AS, et al. Prognostic impact of preoperative neutrophilto-lymphocyte ratio in localized nonclear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2013; 190:1999–2004. PMID: 23831313.
Article15. Viers BR, Houston Thompson R, Boorjian SA, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Tollefson MK. Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts death among patients with localized clear cell renal carcinoma undergoing nephrectomy. Urol Oncol. 2014; 32:1277–1284. PMID: 25017696.
Article16. Ficarra V, Novara G, Secco S, Macchi V, Porzionato A, De Caro R, et al. Preoperative aspects and dimensions used for an anatomical (PADUA) classification of renal tumors in patients who are candidates for nephron-sparing surgery. Eur Urol. 2009; 56:786–793. PMID: 19665284.17. Bertini R, Roscigno M, Freschi M, Strada E, Petralia G, Pasta A, et al. Renal sinus fat invasion in pT3a clear cell renal cell carcinoma affects outcomes of patients without nodal involvement or distant metastases. J Urol. 2009; 181:2027–2032. PMID: 19286201.
Article18. Koo KC, Kim JC, Cho KS, Choi YD, Hong SJ, Yang SC, et al. Oncological outcomes after partial vs radical nephrectomy in renal cell carcinomas of ≤7 cm with presumed renal sinus fat invasion on preoperative imaging. BJU Int. 2016; 117:87–93. PMID: 25099267.19. Sokhi HK, Mok WY, Patel U. Stage T3a renal cell carcinoma: staging accuracy of CT for sinus fat, perinephric fat or renal vein invasion. Br J Radiol. 2015; 88:20140504. PMID: 25410425.
Article20. Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010; 140:883–899. PMID: 20303878.
Article21. Liang W, Ferrara N. The complex role of neutrophils in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016; 4:83–91. PMID: 26839309.
Article22. Speiser DE, Ho PC, Verdeil G. Regulatory circuits of T cell function in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016; 16:599–611. PMID: 27526640.
Article23. Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Bronte V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012; 12:253–268. PMID: 22437938.24. Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:e493–e503. PMID: 25281468.
Article25. Sejima T, Iwamoto H, Morizane S, Hinata N, Yao A, Isoyama T, et al. The significant immunological characteristics of peripheral blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and Fas ligand expression incidence in nephrectomized tumor in late recurrence from renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2013; 31:1343–1349. PMID: 22153754.
Article26. Fox P, Hudson M, Brown C, Lord S, Gebski V, De Souza P, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation predict survival in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:147–153. PMID: 23778526.
Article27. Koo KC, Lee KS, Cho KS, Rha KH, Hong SJ, Chung BH. Comprehensive analysis and validation of contemporary survival prognosticators in Korean patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy: prognostic impact of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016; 48:985–992. PMID: 26946137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perirenal Fat Invasion (pT3a) in Renal Cell Carcinoma Less Than 4cm in Size (cT1a): Analysis of the Prognostic and Pathological Implications
- The Frequency of Perirenal Fat Invasion according to Size and Protrusion Shape of Renal Cell Carcinomas
- Reliability of CT finding of the pararenal muscle invasion in renal cell carcinoma
- Hemangiopericytoma of renal sinus expanding to the renal hilum: an unusual presentation causes misinterpretation as transitional cell carcinoma
- Prognostic parameters in Renal Cell Carcinoma