Lab Anim Res.
2018 Dec;34(4):248-256. 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.248.
[¹â¸F]FET PET is a useful tool for treatment evaluation and prognosis prediction of anti-angiogenic drug in an orthotopic glioblastoma mouse model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea Drug Development Platform using Radio-isotope, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea. hkchung@kirams.re.kr
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Division of Applied RI, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2459302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.248
Abstract
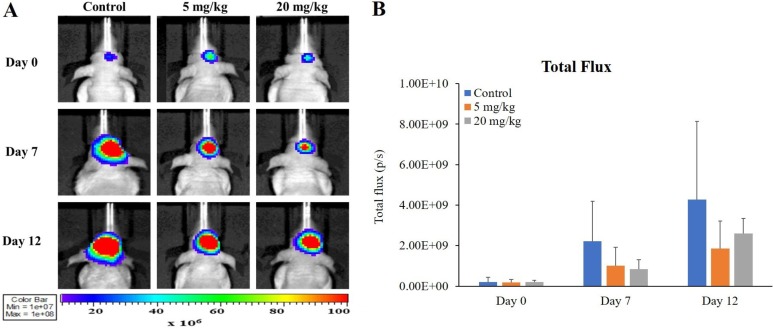
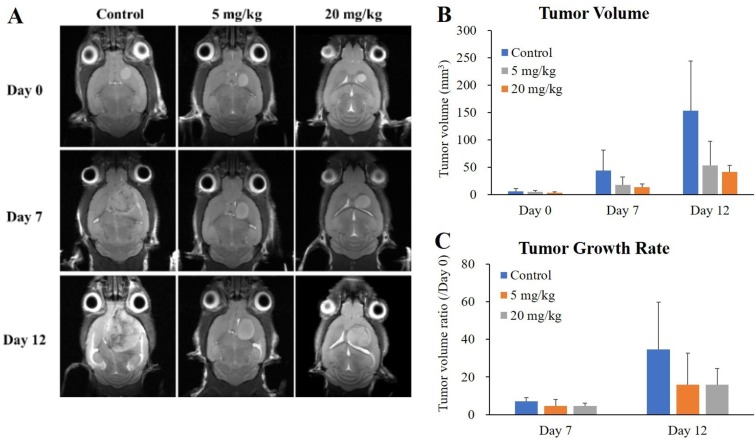
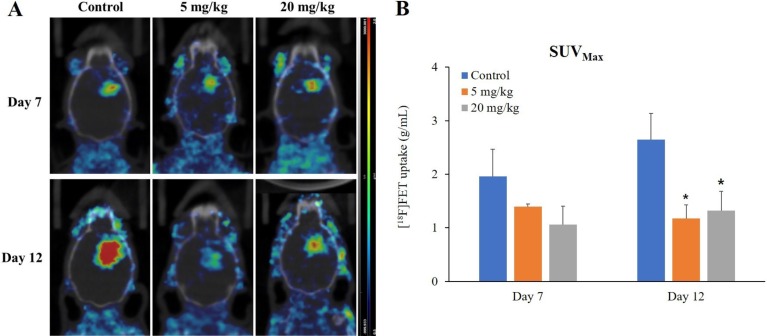
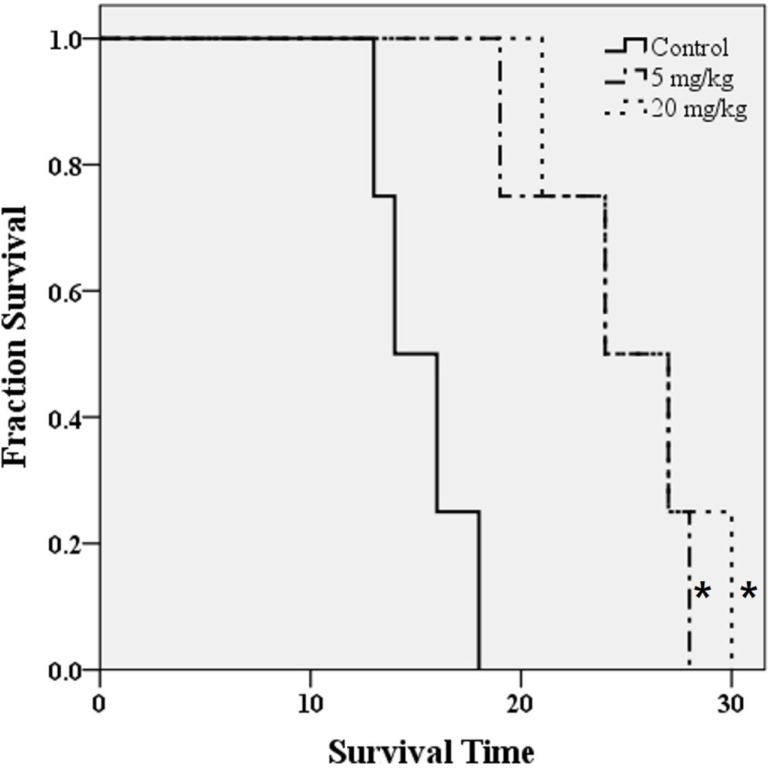
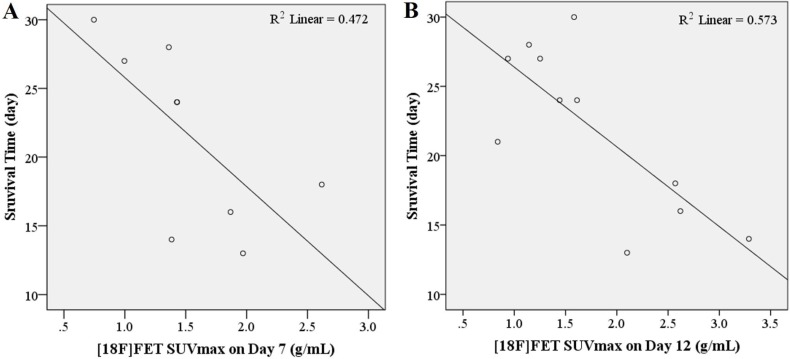
- O-2-¹â¸F-fluoroethyl-l-tyrosine ([¹â¸F]FET) has been widely used for glioblastomas (GBM) in clinical practice, although evaluation of its applicability in non-clinical research is still lacking. The objective of this study was to examine the value of [¹â¸F]FET for treatment evaluation and prognosis prediction of anti-angiogenic drug in an orthotopic mouse model of GBM. Human U87MG cells were implanted into nude mice and then bevacizumab, a representative anti-angiogenic drug, was administered. We monitored the effect of anti-angiogenic agents using multiple imaging modalities, including bioluminescence imaging (BLI), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT). Among these imaging methods analyzed, only [¹â¸F]FET uptake showed a statistically significant decrease in the treatment group compared to the control group (P=0.02 and P=0.03 at 5 and 20 mg/kg, respectively). This indicates that [¹â¸F]FET PET is a sensitive method to monitor the response of GBM bearing mice to anti-angiogenic drug. Moreover, [¹â¸F]FET uptake was confirmed to be a significant parameter for predicting the prognosis of anti-angiogenic drug (P=0.041 and P=0.007, on Days 7 and 12, respectively, on Pearson's correlation; P=0.048 and P=0.030, on Days 7 and 12, respectively, on Cox regression analysis). However, results of BLI or MRI were not significantly associated with survival time. In conclusion, this study suggests that [¹â¸F]FET PET imaging is a pertinent imaging modality for sensitive monitoring and accurate prediction of treatment response to anti-angiogenic agents in an orthotopic model of GBM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gallego O. Nonsurgical treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. Curr Oncol. 2015; 22(4):e273–e281. PMID: 26300678.
Article2. Cao Y. Future options of anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Chin J Cancer. 2016; 35(2):21. PMID: 26879126.
Article3. Kuusk T, Albiges L, Escudier B, Grivas N, Haanen J, Powles T, Bex A. Antiangiogenic therapy combined with immune checkpoint blockade in renal cancer. Angiogenesis. 2017; 20(2):205–215. PMID: 28401381.
Article4. Eisermann K, Fraizer G. The Androgen Receptor and VEGF: Mechanisms of Androgen-Regulated Angiogenesis in Prostate Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2017; 9(4):32.
Article5. Hardee ME, Zagzag D. Mechanisms of glioma-associated neovascularization. Am J Pathol. 2012; 181(4):1126–1141. PMID: 22858156.
Article6. Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Holy R, Pinkawa M, Stoffels G, Nolte KW, Kaiser HJ, Filss CP, Fink GR, Coenen HH, Eble MJ, Piroth MD. Assessment of treatment response in patients with glioblastoma using O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in comparison to MRI. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53(7):1048–1057. PMID: 22645298.
Article7. Krcek R, Latzer P, Adamietz IA, Bühler H, Theiss C. Influence of vascular endothelial growth factor and radiation on gap junctional intercellular communication in glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(11):1816–1822. PMID: 29239327.
Article8. Fu P, He YS, Huang Q, Ding T, Cen YC, Zhao HY, Wei X. Bevacizumab treatment for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016; 4(5):833–838. PMID: 27123291.
Article9. Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science. 2005; 307(5706):58–62. PMID: 15637262.
Article10. Tobelem G. VEGF: a key therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer-insights into its role and pharmacological inhibition. Target Oncol. 2007; 2(3):153–164.11. Yanagisawa M, Yorozu K, Kurasawa M, Nakano K, Furugaki K, Yamashita Y, Mori K, Fujimoto-Ouchi K. Bevacizumab improves the delivery and efficacy of paclitaxel. Anticancer Drugs. 2010; 21(7):687–694. PMID: 20559127.
Article12. Borgström P, Bourdon MA, Hillan KJ, Sriramarao P, Ferrara N. Neutralizing anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody completely inhibits angiogenesis and growth of human prostate carcinoma micro tumors in vivo. Prostate. 1998; 35(1):1–10. PMID: 9537593.
Article13. Bagri A, Berry L, Gunter B, Singh M, Kasman I, Damico LA, Xiang H, Schmidt M, Fuh G, Hollister B, Rosen O, Plowman GD. Effects of anti-VEGF treatment duration on tumor growth, tumor regrowth, and treatment efficacy. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16(15):3887–3900. PMID: 20554752.
Article14. Warren RS, Yuan H, Matli MR, Gillett NA, Ferrara N. Regulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of human colon cancer tumorigenesis in a mouse model of experimental liver metastasis. J Clin Invest. 1995; 95(4):1789–1797. PMID: 7535799.
Article15. Mabuchi S, Terai Y, Morishige K, Tanabe-Kimura A, Sasaki H, Kanemura M, Tsunetoh S, Tanaka Y, Sakata M, Burger RA, Kimura T, Ohmichi M. Maintenance treatment with bevacizumab prolongs survival in an in vivo ovarian cancer model. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14(23):7781–7789. PMID: 19047105.
Article16. Zhang J, Wang S, Liu H, Du X, Chen X, Guo Y, Zhang J, Fang J, Zhang W. Quantitative MRI assessment of glioma response to bevacizumab in a mouse model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017; 10(10):14232–14243.17. Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27(28):4733–4740. PMID: 19720927.
Article18. Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE 2nd, Dowell JM, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Wagner M, Bigner DD, Friedman AH, Friedman HS. Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13(4):1253–1259. PMID: 17317837.
Article19. Jakobsen JN, Hasselbalch B, Stockhausen MT, Lassen U, Poulsen HS. Irinotecan and bevacizumab in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011; 12(5):825–833. PMID: 21385110.
Article20. Odia Y, Iwamoto FM, Moustakas A, Fraum TJ, Salgado CA, Li A, Kreisl TN, Sul J, Butman JA, Fine HA. A phase II trial of enzastaurin (LY317615) in combination with bevacizumab in adults with recurrent malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2016; 127(1):127–135. PMID: 26643807.
Article21. Heiland DH, Masalha W, Franco P, Machein MR, Weyerbrock A. Progression-free and overall survival in patients with recurrent Glioblastoma multiforme treated with last-line bevacizumab versus bevacizumab/lomustine. J Neurooncol. 2016; 126(3):567–575. PMID: 26614518.
Article22. Al-Abd AM, Alamoudi AJ, Abdel-Naim AB, Neamatallah TA, Ashour OM. Anti-angiogenic agents for the treatment of solid tumors: Potential pathways, therapy and current strategies - A review. J Adv Res. 2017; 8(6):591–605. PMID: 28808589.
Article23. Ozel O, Kurt M, Ozdemir O, Bayram J, Akdeniz H, Koca D. Complete response to bevacizumab plus irinotecan in patients with rapidly progressive GBM: Cases report and literature review. J Oncol Sci. 2016; 2(2-3):87–94.
Article24. Huang RY, Neagu MR, Reardon DA, Wen PY. Pitfalls in the neuroimaging of glioblastoma in the era of antiangiogenic and immuno/targeted therapy - detecting illusive disease, defining response. Front Neurol. 2015; 6:33. PMID: 25755649.
Article25. Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM. Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28(11):1963–1972. PMID: 20231676.
Article26. Norden AD, Drappatz J, Muzikansky A, David K, Gerard M, McNamara MB, Phan P, Ross A, Kesari S, Wen PY. An exploratory survival analysis of anti-angiogenic therapy for recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol. 2009; 92(2):149–155. PMID: 19043778.
Article27. Nedergaard MK, Michaelsen SR, Perryman L, Erler J, Poulsen HS, Stockhausen MT, Lassen U, Kjaer A. FFET and (18)F-FLT small animal PET for the assessment of anti-VEGF treatment response in an orthotopic model of glioblastoma. Nucl Med Biol. 2016; 43(3):198–205. PMID: 26924500.28. Hutterer M, Nowosielski M, Putzer D, Waitz D, Tinkhauser G, Kostron H, Muigg A, Virgolini IJ, Staffen W, Trinka E, Gotwald T, Jacobs AH, Stockhammer G. O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET predicts failure of antiangiogenic treatment in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. J Nucl Med. 2011; 52(6):856–864. PMID: 21622893.
Article29. Schwarzenberg J, Czernin J, Cloughesy TF, Ellingson BM, Pope WB, Geist C, Dahlbom M, Silverman DH, Satyamurthy N, Phelps ME, Chen W. 3′-deoxy-3′-18F-fluorothymidine PET and MRI for early survival predictions in patients with recurrent malignant glioma treated with bevacizumab. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53(1):29–36. PMID: 22159180.
Article30. Gulyás B, Halldin C. New PET radiopharmaceuticals beyond FDG for brain tumor imaging. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012; 56(2):173–190. PMID: 22617239.31. Isselbacher KJ. Sugar and amino acid transport by cells in culture--differences between normal and malignant cells. N Engl J Med. 1972; 286(17):929–933. PMID: 4335317.32. BUSCH H, DAVIS JR, HONIG GR, ANDERSON DC, NAIR PV, NYHAN WL. The uptake of a variety of amino acids into nuclear proteins of tumors and other tissues. Cancer Res. 1959; 19(10):1030–1039. PMID: 13806375.33. Holzgreve A, Brendel M, Gu S, Carlsen J, Mille E, Böning G, Mastrella G, Unterrainer M, Gildehaus FJ, Rominger A, Bartenstein P, Kälin RE, Glass R, Albert NL. Monitoring of Tumor Growth with [(18)F]-FET PET in a Mouse Model of Glioblastoma: SUV Measurements and Volumetric Approaches. Front Neurosci. 2016; 10:260. PMID: 27378835.
Article34. Ramasawmy R, Johnson SP, Roberts TA, Stuckey DJ, David AL, Pedley RB, Lythgoe MF, Siow B, Walker-Samuel S. Monitoring the Growth of an Orthotopic Tumour Xenograft Model: Multi-Modal Imaging Assessment with Benchtop MRI (1T), High-Field MRI (9.4T), Ultrasound and Bioluminescence. PLoS One. 2016; 11(5):e0156162. PMID: 27223614.
Article35. Jarzabek MA, Sweeney KJ, Evans RL, Jacobs AH, Stupp R, O'Brien D, Berger MS, Prehn JH, Byrne AT. Molecular imaging in the development of a novel treatment paradigm for glioblastoma (GBM): an integrated multidisciplinary commentary. Drug Discov Today. 2013; 18(21-22):1052–1066. PMID: 23792334.
Article36. Nedergaard MK, Michaelsen SR, Urup T, Broholm H, El Ali H, Poulsen HS, Stockhausen MT, Kjaer A, Lassen U. 18F-FET microPET and microMRI for anti-VEGF and anti-PlGF response assessment in an orthotopic murine model of human glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2015; 10(2):e0115315. PMID: 25680186.
Article37. Christoph S, Schlegel J, Alvarez-Calderon F, Kim YM, Brandao LN, DeRyckere D, Graham DK. Bioluminescence imaging of leukemia cell lines in vitro and in mouse xenografts: effects of monoclonal and polyclonal cell populations on intensity and kinetics of photon emission. J Hematol Oncol. 2013; 6(1):10. PMID: 23343252.
Article38. Khalil AA, Jameson MJ, Broaddus WC, Lin PS, Dever SM, Golding SE, Rosenberg E, Valerie K, Chung TD. The Influence of Hypoxia and pH on Bioluminescence Imaging of Luciferase-Transfected Tumor Cells and Xenografts. Int J Mol Imaging. 2013; 2013:287697. PMID: 23936647.
Article39. O'Farrell AC, Shnyder SD, Marston G, Coletta PL, Gill JH. Non-invasive molecular imaging for preclinical cancer therapeutic development. Br J Pharmacol. 2013; 169(4):719–735. PMID: 23488622.40. Galldiks N, Law I, Pope WB, Arbizu J, Langen KJ. The use of amino acid PET and conventional MRI for monitoring of brain tumor therapy. Neuroimage Clin. 2016; 13:386–394. PMID: 28116231.
Article41. Jalali S, Chung C, Foltz W, Burrell K, Singh S, Hill R, Zadeh G. MRI biomarkers identify the differential response of glioblastoma multiforme to anti-angiogenic therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2014; 16(6):868–879. PMID: 24759636.
Article42. Götz I, Grosu A-L, Spehl TS. Role of PET Imaging in Patients with High-Grade Gliomas Undergoing Anti-Angiogenic Therapy with Bevacizumab-Review of the Literature and Case Report. Eur Assoc NeuroOncology Mag. 2014; 4(3):102–108.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spectrum of Metabolic and Angiogenic Imaging with 18F-FDOPA and 18F-PSMA 1007 PET/CT in the Evaluation of Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Role of ¹â¸F-FDG PET-CT in Monitoring the Cyclophosphamide Induced Pulmonary Toxicity in Patients with Breast Cancer: 2 Case Reports
- ¹â¸F-FDG PET/MR Refines Evaluation in Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Urethral Adenocarcinoma
- Outcome in Patients with Fever of Unknown Origin whose ¹â¸Fluoro-Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computerized Tomography Finding is Non-Diagnostic
- Application of Quantitative Indexes of FDG PET to Treatment Response Evaluation in Indolent Lymphoma