Lab Anim Res.
2018 Dec;34(4):133-139. 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.133.
The role of hepatic macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, GAIHST, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Gachon Medical Research Institute, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khchun@yuhs.ac
- 4Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2459288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.133
Abstract
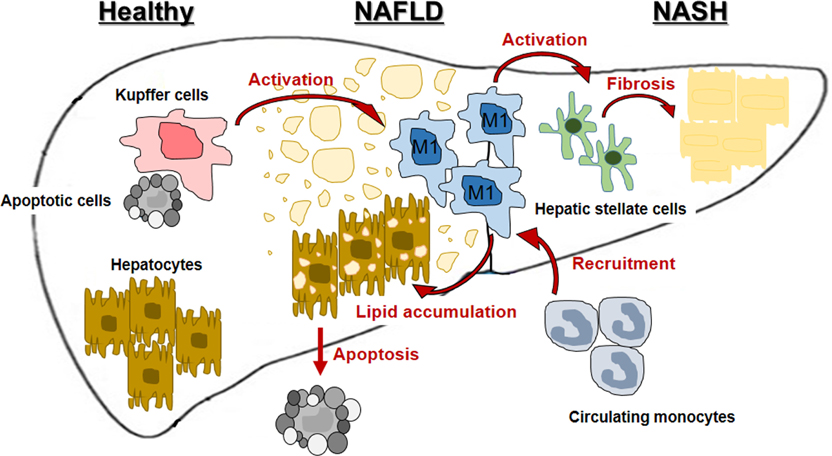
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is becoming common chronic liver disease because of the increasing global prevalence of obesity and consequently Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, the mechanism for progression of NAFLD to NASH and then cirrhosis is not completely understood, yet. The triggering of these hepatic diseases is thought from hepatocyte injury caused by over-accumulated lipid toxicity. Injured hepatocytes release damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which can stimulate the Kupffer cells (KCs), liver-resident macrophages, to release pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and recruit monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). The increased activation of KCs and recruitment of MDMs accelerate the progression of NAFLD to NASH and cirrhosis. Therefore, characterization for activation of hepatic macrophages, both KCs and MDMs, is a baseline to figure out the progression of hepatic diseases. The purpose of this review is to discuss the current understanding of mechanisms of NAFLD and NASH, mainly focusing on characterization and function of hepatic macrophages and suggests the regulators of hepatic macrophages as the therapeutic target in hepatic diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carr RM, Oranu A, Khungar V. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathophysiology and Management. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2016; 45(4):639–652.2. Liu W, Baker RD, Bhatia T, Zhu L, Baker SS. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016; 73(10):1969–1987.
Article3. Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Marra F. Molecular Pathogenesis of NASH. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17(9):
Article4. Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998; 114(4):842–845.
Article5. Lopez BG, Tsai MS, Baratta JL, Longmuir KJ, Robertson RT. Characterization of Kupffer cells in livers of developing mice. Comp Hepatol. 2011; 10(1):2.
Article6. Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 14(7):397–411.
Article7. Krenkel O, Tacke F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017; 17(5):306–321.
Article8. Grunhut J, Wang W, Aykut B, Gakhal I, Torres-Hernandez A, Miller G. Macrophages in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Friend or Foe? Eur Med J Hepatol. 2018; 6(1):100–109.9. Ju C, Tacke F. Hepatic macrophages in homeostasis and liver diseases: from pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016; 13(3):316–327.
Article10. Tacke F, Zimmermann HW. Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2014; 60(5):1090–1096.
Article11. Devisscher L, Verhelst X, Colle I, Van Vlierberghe H, Geerts A. The role of macrophages in obesity-driven chronic liver disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2016; 99(5):693–698.
Article12. Scott CL, Zheng F, De Baetselier P, Martens L, Saeys Y, De Prijck S, Lippens S, Abels C, Schoonooghe S, Raes G, Devoogdt N, Lambrecht BN, Beschin A, Guilliams M. Bone marrow-derived monocytes give rise to self-renewing and fully differentiated Kupffer cells. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:10321.
Article13. Zhou D, Yang K, Chen L, Wang Y, Zhang W, Xu Z, Zuo J, Jiang H, Luan J. Macrophage polarization and function: new prospects for fibrotic disease. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017; 95(10):864–869.
Article14. Murray PJ, Wynn TA. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011; 11(11):723–737.
Article15. Abdullah Z, Knolle PA. Liver macrophages in healthy and diseased liver. Pflugers Arch. 2017; 469(3-4):553–560.
Article16. Sun YY, Li XF, Meng XM, Huang C, Zhang L, Li J. Macrophage Phenotype in Liver Injury and Repair. Scand J Immunol. 2017; 85(3):166–174.
Article17. Duarte N, Coelho IC, Patarrão RS, Almeida JI, Penha-Gonçalves C, Macedo MP. How Inflammation Impinges on NAFLD: A Role for Kupffer Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:984578.
Article18. Thomson AW, Knolle PA. Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010; 10(11):753–766.
Article19. You Q, Cheng L, Kedl RM, Ju C. Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer cells. Hepatology. 2008; 48(3):978–990.
Article20. Lang PA, Recher M, Honke N, Scheu S, Borkens S, Gailus N, Krings C, Meryk A, Kulawik A, Cervantes-Barragan L, Van Rooijen N, Kalinke U, Ludewig B, Hengartner H, Harris N, Häussinger D, Ohashi PS, Zinkernagel RM, Lang KS. Tissue macrophages suppress viral replication and prevent severe immunopathology in an interferon-I-dependent manner in mice. Hepatology. 2010; 52(1):25–32.
Article21. Breous E, Somanathan S, Vandenberghe LH, Wilson JM. Hepatic regulatory T cells and Kupffer cells are crucial mediators of systemic T cell tolerance to antigens targeting murine liver. Hepatology. 2009; 50(2):612–621.
Article22. Bissell DM, Wang SS, Jarnagin WR, Roll FJ. Cell-specific expression of transforming growth factor-beta in rat liver. Evidence for autocrine regulation of hepatocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest. 1995; 96(1):447–455.
Article23. Knolle P, Schlaak J, Uhrig A, Kempf P, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH, Gerken G. Human Kupffer cells secrete IL-10 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. J Hepatol. 1995; 22(2):226–229.24. Fujimoto M, Uemura M, Nakatani Y, Tsujita S, Hoppo K, Tamagawa T, Kitano H, Kikukawa M, Ann T, Ishii Y, Kojima H, Sakurai S, Tanaka R, Namisaki T, Noguchi R, Higashino T, Kikuchi E, Nishimura K, Takaya A, Fukui H. Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of liver disturbance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000; 24:4 Suppl. 48s–54s.
Article25. Harte AL, da Silva NF, Creely SJ, McGee KC, Billyard T, Youssef-Elabd EM, Tripathi G, Ashour E, Abdalla MS, Sharada HM, Amin AI, Burt AD, Kumar S, Day CP, McTernan PG. Elevated endotoxin levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 2010; 7:15.
Article26. Marí M, Caballero F, Colell A, Morales A, Caballeria J, Fernandez A, Enrich C, Fernandez-Checa JC, García-Ruiz C. Mitochondrial free cholesterol loading sensitizes to TNF- and Fas-mediated steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006; 4(3):185–198.
Article27. Adkins Y, Schie IW, Fedor D, Reddy A, Nguyen S, Zhou P, Kelley DS, Wu J. A novel mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with significant insulin resistance. Lab Invest. 2013; 93(12):1313–1322.
Article28. Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C, Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, Garner H, Trouillet C, de Bruijn MF, Geissmann F, Rodewald HR. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolksac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. 2015; 518(7540):547–551.
Article29. Antoniades CG, Quaglia A, Taams LS, Mitry RR, Hussain M, Abeles R, Possamai LA, Bruce M, McPhail M, Starling C, Wagner B, Barnardo A, Pomplun S, Auzinger G, Bernal W, Heaton N, Vergani D, Thursz MR, Wendon J. Source and characterization of hepatic macrophages in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in humans. Hepatology. 2012; 56(2):735–746.
Article30. González-Domínguez É, Samaniego R, Flores-Sevilla JL, Campos-Campos SF, Gómez-Campos G, Salas A, Campos-Peña V, Corbí ÁL, Sánchez-Mateos P, Sánchez-Torres C. CD163L1 and CLEC5A discriminate subsets of human resident and inflammatory macrophages in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 2015; 98(4):453–466.31. Tacke F, Randolph GJ. Migratory fate and differentiation of blood monocyte subsets. Immunobiology. 2006; 211(6-8):609–618.
Article32. Ingersoll MA, Spanbroek R, Lottaz C, Gautier EL, Frankenberger M, Hoffmann R, Lang R, Haniffa M, Collin M, Tacke F, Habenicht AJ, Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Randolph GJ. Comparison of gene expression profiles between human and mouse monocyte subsets. Blood. 2010; 115(3):e10–e19.
Article33. Karlmark KR, Weiskirchen R, Zimmermann HW, Gassler N, Ginhoux F, Weber C, Merad M, Luedde T, Trautwein C, Tacke F. Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2009; 50(1):261–274.34. Liaskou E, Zimmermann HW, Li KK, Oo YH, Suresh S, Stamataki Z, Qureshi O, Lalor PF, Shaw J, Syn WK, Curbishley SM, Adams DH. Monocyte subsets in human liver disease show distinct phenotypic and functional characteristics. Hepatology. 2013; 57(1):385–398.
Article35. Marra F, Tacke F. Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2014; 147(3):577–594.
Article36. Wang M, You Q, Lor K, Chen F, Gao B, Ju C. Chronic alcohol ingestion modulates hepatic macrophage populations and functions in mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2014; 96(4):657–665.
Article37. Duffield JS, Forbes SJ, Constandinou CM, Clay S, Partolina M, Vuthoori S, Wu S, Lang R, Iredale JP. Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct, opposing roles during liver injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(1):56–65.
Article38. Hirsova P, Ibrahim SH, Gores GJ, Malhi H. Lipotoxic lethal and sublethal stress signaling in hepatocytes: relevance to NASH pathogenesis. J Lipid Res. 2016; 57(10):1758–1770.
Article39. Ioannou GN, Subramanian S, Chait A, Haigh WG, Yeh MM, Farrell GC, Lee SP, Savard C. Cholesterol crystallization within hepatocyte lipid droplets and its role in murine NASH. J Lipid Res. 2017; 58(6):1067–1079.
Article40. Bieghs V, Wouters K, van Gorp PJ, Gijbels MJ, de Winther MP, Binder CJ, Lütjohann D, Febbraio M, Moore KJ, van Bilsen M, Hofker MH, Shiri-Sverdlov R. Role of scavenger receptor A and CD36 in diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in hyperlipidemic mice. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138(7):2477–2486.
Article41. Cai C, Zhu X, Li P, Li J, Gong J, Shen W, He K. NLRP3 Deletion Inhibits the Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Development and Inflammation in Kupffer Cells Induced by Palmitic Acid. Inflammation. 2017; 40(6):1875–1883.
Article42. Bieghs V, van Gorp PJ, Walenbergh SM, Gijbels MJ, Verheyen F, Buurman WA, Briles DE, Hofker MH, Binder CJ, Shiri-Sverdlov R. Specific immunization strategies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein: a novel way to reduce nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology. 2012; 56(3):894–903.
Article43. Hirsova P, Gores GJ. Death Receptor-Mediated Cell Death and Proinflammatory Signaling in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 1(1):17–27.
Article44. Brenner C, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol. 2013; 59(3):583–594.
Article45. Luedde T, Kaplowitz N, Schwabe RF. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology. 2014; 147(4):765–783.
Article46. Camell C, Goldberg E, Dixit VD. Regulation of Nlrp3 inflammasome by dietary metabolites. Semin Immunol. 2015; 27(5):334–342.
Article47. He K, Zhu X, Liu Y, Miao C, Wang T, Li P, Zhao L, Chen Y, Gong J, Cai C, Li J, Li S, Ruan XZ, Gong J. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome by thioredoxin-interacting protein in mouse Kupffer cells as a regulatory mechanism for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(23):37657–37672.
Article48. Szabo G, Iracheta-Vellve A. Inflammasome activation in the liver: Focus on alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2015; 39:Suppl 1. S18–S23.
Article49. Kanda T, Matsuoka S, Yamazaki M, Shibata T, Nirei K, Takahashi H, Kaneko T, Fujisawa M, Higuchi T, Nakamura H, Matsumoto N, Yamagami H, Ogawa M, Imazu H, Kuroda K, Moriyama M. Apoptosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2018; 24(25):2661–2672.
Article50. Akazawa Y, Nakao K. Lipotoxicity pathways intersect in hepatocytes: Endoplasmic reticulum stress, c-Jun N-terminal kinase-1, and death receptors. Hepatol Res. 2016; 46(10):977–984.
Article51. Wree A, Mehal WZ, Feldstein AE. Targeting Cell Death and Sterile Inflammation Loop for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 2016; 36(1):27–36.
Article52. Ashraf NU, Sheikh TA. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic Res. 2015; 49(12):1405–1418.
Article53. Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2017; 66(6):1300–1312.
Article54. Thomas P, Lazure DA, Moussa R, Bajenova O, Burke PA, Ganguly A, Forse RA. Identification of two novel LPS-binding proteins in Kupffer cells: implications in TNF-alpha production. J Endotoxin Res. 2006; 12(6):352–357.55. Farrell GC, van Rooyen D, Gan L, Chitturi S. NASH is an Inflammatory Disorder: Pathogenic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Gut Liver. 2012; 6(2):149–171.56. Rivera CA, Adegboyega P, van Rooijen N, Tagalicud A, Allman M, Wallace M. Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2007; 47(4):571–579.
Article57. Xu Z, Zhang X, Lau J, Yu J. C-X-C motif chemokine 10 in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: role as a pro-inflammatory factor and clinical implication. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2016; 18:e16.
Article58. Stojsavljeviæ S, Gomerèiæ Palèiæ M, Viroviæ Jukiæ L, Smirèiæ Duvnjak L, Duvnjak M. Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20(48):18070–18091.59. Nati M, Haddad D, Birkenfeld AL, Koch CA, Chavakis T, Chatzigeorgiou A. The role of immune cells in metabolism-related liver inflammation and development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016; 17(1):29–39.
Article60. Nakamoto N, Kanai T. Role of toll-like receptors in immune activation and tolerance in the liver. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:221.
Article61. Gao B, Tsukamoto H. Inflammation in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Friend or Foe? Gastroenterology. 2016; 150(8):1704–1709.
Article62. Heymann F, Tacke F. Immunology in the liver--from homeostasis to disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 13(2):88–110.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pathology of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- The Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Noninvasive serum biomarkers for liver steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current and future developments
- Clinical Predictors Reflecting the Pathologic Severity of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver