Lab Med Online.
2019 Oct;9(4):254-257. 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.4.254.
A Case of Anti-Le(bH) Antibody Identified in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. daehyuni1118@gmail.com
- 2Seegene Medical Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2458688
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2019.9.4.254
Abstract
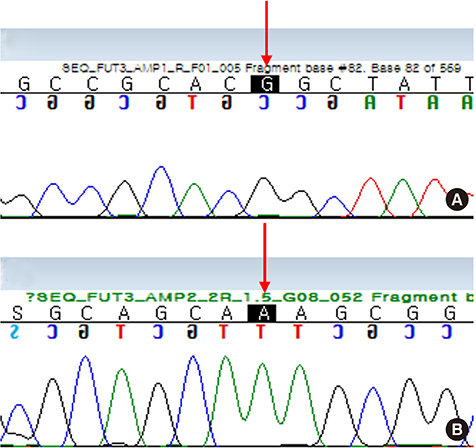
- A 67-year-old man previously diagnosed with ulcerative colitis complained of difficulty in defecation and underwent balloon dilatation of rectum, but the procedure failed. The patient was transferred to a surgical department for further treatment. Before surgery, his red cells were typed A, Rh(D) positive. The antibody screening test was positive and the results of the identification tests were atypical. The reactivity was similar to anti-Le(b) antibody; however, the antibody showed panreactivity against papainized red cells. It showed stronger reactivity against O red cells than A Le(a−b+) red cells, and we concluded that the antibody was anti-Le(bH). After reexamination, his Lewis phenotype was found to be Le(a−b−). His FUT2 and FUT3 were analyzed to confirm his Lewis blood type, and c.59T>G and c.1067T>A variants were found on the FUT3. Therefore, the patient's Lewis blood type was concluded as Le(a−b−).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mourant AE. A new human blood group antigen of frequent occurrence. Nature. 1946; 158:237.
Article2. Andresen PH. The blood group system L. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1948; 25:728–731.
Article3. Han KS, Park KU, editors. Transfusion medicine. 4th ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publishing Company;2014. p. 215–217.4. Bharucha ZS, Joshi SR, Bhatia HM. Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to anti-Le. Vox Sang. 1981; 41:36–39.
Article5. Weir AB 3rd, Woods LL, Chesney C, Neitzer G. Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction caused by anti-LebH antibody. Vox Sang. 1987; 53:105–107.6. Reid ME, Lomas-Francis C, editors. The blood group antigen Facts-Book. 3rd ed. Waltham: Academic Press;2012. p. 347–359.7. Henry S, Oriol R, Samuelsson B. Lewis histo-blood group system and associated secretory phenotypes. Vox Sang. 1995; 69:166–182.
Article8. Han KS, Cho HI, Kim SI. A study on the hemolytic transfusion reactions due to irregular antibodies. Korean J Hematol. 1989; 24:27–33.9. Mollicone R, Reguigne I, Kelly RJ, Fletcher A, Watt J, Chatfield S, et al. Molecular basis for Lewis alpha(1,3/1,4)-fucosyltransferase gene deficiency (FUT3) found in Lewis-negative Indonesian pedigrees. J Biol Chem. 1994; 269:20987–20994.
Article10. Salmon C, Cartron JP, Rouger P. The human blood groups. NY: Masson Pub;1984. p. 174.11. Good AH, Yau O, Lamontagne LR, Oriol R. Serological and chemical specificities of twelve monoclonal anti-Lea and anti-Leb antibodies. Vox Sang. 1992; 62:180–189.
Article12. Cho SG, Lim J, Kim Y, Han K, Han CH, Lee AH, et al. A case of anti-LebH antibody concurrent Leb antigen suppression during pregnancy in a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1998; 9:283–287.13. Contreras M, Mollison PL. Delayed haemolytic transfusion reaction caused by anti-LebH Antibody. Vox Sang. 1989; 56:290.14. Kim MJ, Kim HO, Kim HS, Song KS. Influence of Lewis phenotype and genotype on serum CA19-9 and DUPAN-2 level in gastric cancer patients. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2000; 11:115–123.15. Previato M, Borim MP, Liberatore RD Jr, Pires AC, Dias MA, Brandão de Mattos CC, et al. Lewis histo-blood group system phenotyping and genotyping reveal divergence in the association of Le(a−b−) phenotype and type 1 diabetes. Vox Sang. 2015; 108:281–286.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cytomegalvirus Colitis Developed during the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
- A Case of Malignant Lymphoma in Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- A case of ulcerative colitis
- Malignant change of chronic ulcerative colitis : report of a case
- A Case of Simultaneous Presentation of Bullous and Ulcerative Types of Pyoderma Gangrenosum in an Ulcerative Colitis Patient