Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2019 Sep;23(5):317-328. 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.5.317.
Layer-specific cholinergic modulation of synaptic transmission in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of rat visual cortex
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea. djrhie@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Catholic Neuroscience Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- KMID: 2455808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.5.317
Abstract
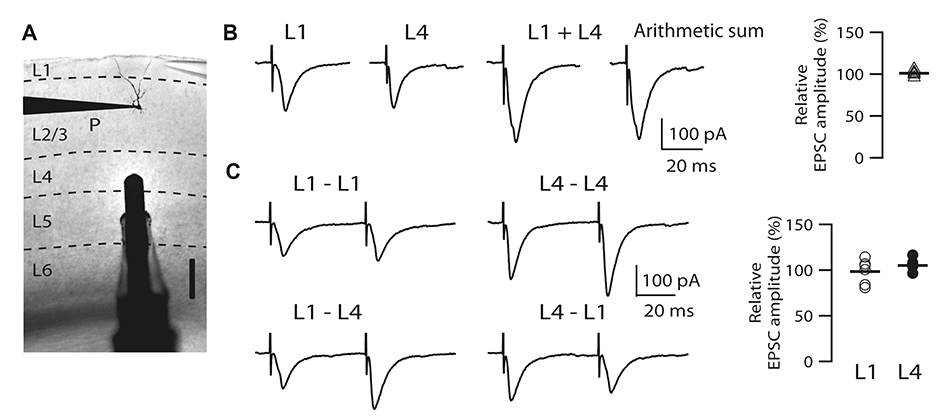
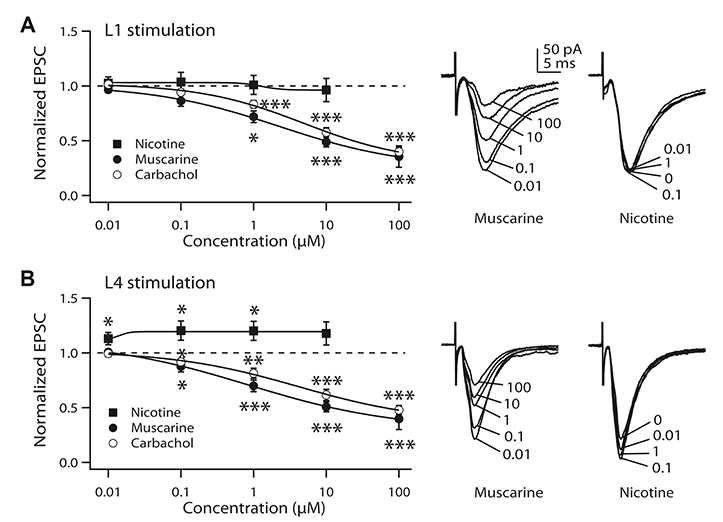
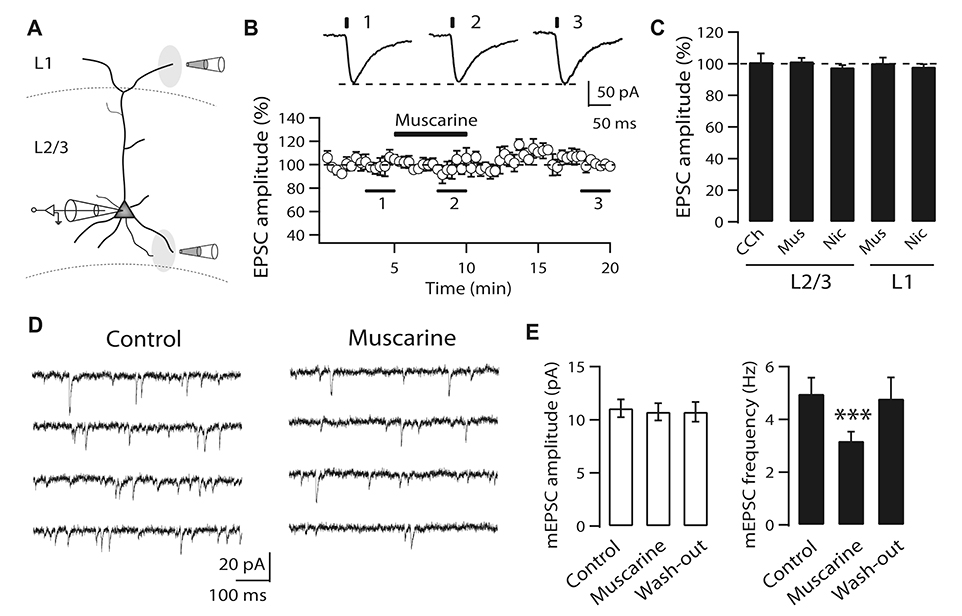
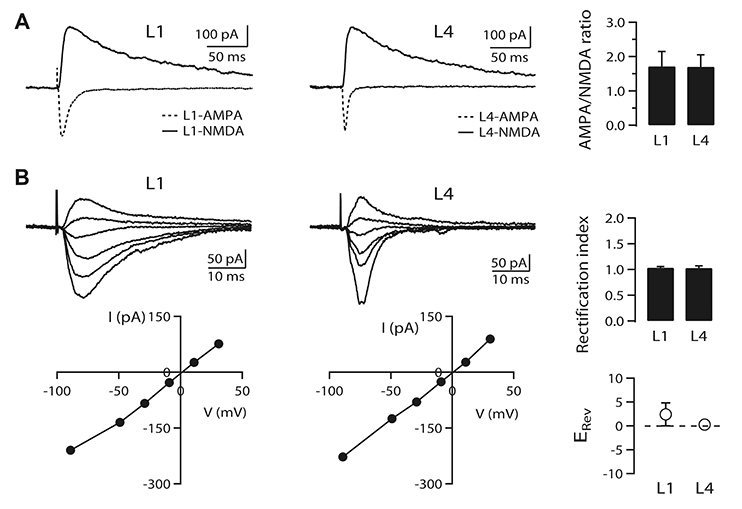
- It is known that top-down associative inputs terminate on distal apical dendrites in layer 1 while bottom-up sensory inputs terminate on perisomatic dendrites of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons (L2/3 PyNs) in primary sensory cortex. Since studies on synaptic transmission in layer 1 are sparse, we investigated the basic properties and cholinergic modulation of synaptic transmission in layer 1 and compared them to those in perisomatic dendrites of L2/3 PyNs of rat primary visual cortex. Using extracellular stimulations of layer 1 and layer 4, we evoked excitatory postsynaptic current/potential in synapses in distal apical dendrites (L1-EPSC/L1-EPSP) and those in perisomatic dendrites (L4-EPSC/L4-EPSP), respectively. Kinetics of L1-EPSC was slower than that of L4-EPSC. L1-EPSC showed presynaptic depression while L4-EPSC was facilitating. In contrast, inhibitory postsynaptic currents showed similar paired-pulse ratio between layer 1 and layer 4 stimulations with depression only at 100 Hz. Cholinergic stimulation induced presynaptic depression by activating muscarinic receptors in excitatory and inhibitory synapses to similar extents in both inputs. However, nicotinic stimulation enhanced excitatory synaptic transmission by ~20% in L4-EPSC. Rectification index of AMPA receptors and AMPA/NMDA ratio were similar between synapses in distal apical and perisomatic dendrites. These results provide basic properties and cholinergic modulation of synaptic transmission between distal apical and perisomatic dendrites in L2/3 PyNs of the visual cortex, which might be important for controlling information processing balance depending on attentional state.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Somogyi P, Tamás G, Lujan R, Buhl EH. Salient features of synaptic organisation in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998; 26:113–135.2. Williams SR, Stuart GJ. Role of dendritic synapse location in the control of action potential output. Trends Neurosci. 2003; 26:147–154.
Article3. Sjöström PJ, Rancz EA, Roth A, Häusser M. Dendritic excitability and synaptic plasticity. Physiol Rev. 2008; 88:769–840.
Article4. Spruston N. Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008; 9:206–221.
Article5. Larkum M. A cellular mechanism for cortical associations: an organizing principle for the cerebral cortex. Trends Neurosci. 2013; 36:141–151.
Article6. Shipp S. Structure and function of the cerebral cortex. Curr Biol. 2007; 17:R443–R449.
Article7. Petreanu L, Mao T, Sternson SM, Svoboda K. The subcellular organization of neocortical excitatory connections. Nature. 2009; 457:1142–1145.
Article8. Larkman AU. Dendritic morphology of pyramidal neurones of the visual cortex of the rat: III. Spine distributions. J Comp Neurol. 1991; 306:332–343.
Article9. Larkum ME, Senn W, Lüscher HR. Top-down dendritic input increases the gain of layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Cereb Cortex. 2004; 14:1059–1070.
Article10. Katz LC, Shatz CJ. Synaptic activity and the construction of cortical circuits. Science. 1996; 274:1133–1138.
Article11. Bear MF, Rittenhouse CD. Molecular basis for induction of ocular dominance plasticity. J Neurobiol. 1999; 41:83–91.
Article12. Cho KH, Jang HJ, Jo YH, Singer W, Rhie DJ. Cholinergic induction of input-specific late-phase LTP via localized Ca2+ release in the visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2012; 32:4520–4530.13. Salgado H, Garcia-Oscos F, Patel A, Martinolich L, Nichols JA, Dinh L, Roychowdhury S, Tseng KY, Atzori M. Layer-specific noradrenergic modulation of inhibition in cortical layer II/III. Cereb Cortex. 2011; 21:212–221.
Article14. Joo K, Cho KH, Youn SH, Jang HJ, Rhie DJ. Layer-specific involvement of endocannabinoid signaling in muscarinic-induced long-term depression in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons of rat visual cortex. Brain Res. 2019; 1712:124–131.
Article15. Hasselmo ME. Neuromodulation: acetylcholine and memory consolidation. Trends Cogn Sci. 1999; 3:351–359.
Article16. Wen JA, Barth AL. Input-specific critical periods for experience-dependent plasticity in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:4456–4465.
Article17. Sarter M, Hasselmo ME, Bruno JP, Givens B. Unraveling the attentional functions of cortical cholinergic inputs: interactions between signal-driven and cognitive modulation of signal detection. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005; 48:98–111.
Article18. Gonchar Y, Burkhalter A. Three distinct families of GABAergic neurons in rat visual cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1997; 7:347–358.
Article19. Brill J, Huguenard JR. Sequential changes in AMPA receptor targeting in the developing neocortical excitatory circuit. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:13918–13928.
Article20. Quinlan EM, Olstein DH, Bear MF. Bidirectional, experience-dependent regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit composition in the rat visual cortex during postnatal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:12876–12880.
Article21. Lee C, Joo K, Kim MJ, Rhie DJ, Jang HJ. GluN2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors compensate for the inhibitory control of synaptic plasticity during the early critical period in the rat visual cortex. J Neurosci Res. 2015; 93:1405–1412.
Article22. Rhie DJ, Kang HY, Ryu GR, Kim MJ, Yoon SH, Hahn SJ, Min DS, Jo YH, Kim MS. Electrophysiological and morphological classification of inhibitory interneurons in layer II/III of the rat visual cortex. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003; 7:317–323.23. Dobrunz LE, Stevens CF. Heterogeneity of release probability, facilitation, and depletion at central synapses. Neuron. 1997; 18:995–1008.
Article24. Gil Z, Connors BW, Amitai Y. Differential regulation of neocortical synapses by neuromodulators and activity. Neuron. 1997; 19:679–686.
Article25. Cruikshank SJ, Urabe H, Nurmikko AV, Connors BW. Pathway-specific feedforward circuits between thalamus and neocortex revealed by selective optical stimulation of axons. Neuron. 2010; 65:230–245.
Article26. Rose HJ, Metherate R. Auditory thalamocortical transmission is reliable and temporally precise. J Neurophysiol. 2005; 94:2019–2030.
Article27. Amitai Y. Thalamocortical synaptic connections: efficacy, modulation, inhibition and plasticity. Rev Neurosci. 2001; 12:159–173.
Article28. Volpicelli LA, Levey AI. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Prog Brain Res. 2004; 145:59–66.
Article29. Lee SH, Dan Y. Neuromodulation of brain states. Neuron. 2012; 76:209–222.
Article30. Hasselmo ME, McGaughy J. High acetylcholine levels set circuit dynamics for attention and encoding and low acetylcholine levels set dynamics for consolidation. Prog Brain Res. 2004; 145:207–231.
Article31. Mesulam MM, Mufson EJ, Wainer BH, Levey AI. Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature (Ch1-Ch6). Neuroscience. 1983; 10:1185–1201.
Article32. Lysakowski A, Wainer BH, Bruce G, Hersh LB. An atlas of the regional and laminar distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience. 1989; 28:291–336.
Article33. van der Zee EA, Luiten PG. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the hippocampus, neocortex and amygdala: a review of immunocytochemical localization in relation to learning and memory. Prog Neurobiol. 1999; 58:409–471.
Article34. Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes and their function in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex. Prog Brain Res. 2004; 145:109–120.
Article35. Hasselmo ME, Bower JM. Cholinergic suppression specific to intrinsic not afferent fiber synapses in rat piriform (olfactory) cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1992; 67:1222–1229.
Article36. Hsieh CY, Cruikshank SJ, Metherate R. Differential modulation of auditory thalamocortical and intracortical synaptic transmission by cholinergic agonist. Brain Res. 2000; 880:51–64.
Article37. Oldford E, Castro-Alamancos MA. Input-specific effects of acetylcholine on sensory and intracortical evoked responses in the “barrel cortex” in vivo. Neuroscience. 2003; 117:769–778.38. Jang HJ, Cho KH, Kim MJ, Yoon SH, Rhie DJ. Layer- and cell-type-specific tonic GABAergic inhibition of pyramidal neurons in the rat visual cortex. Pflugers Arch. 2013; 465:1797–1810.
Article39. Liu G. Local structural balance and functional interaction of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in hippocampal dendrites. Nat Neurosci. 2004; 7:373–379.
Article40. Haider B, Duque A, Hasenstaub AR, McCormick DA. Neocortical network activity in vivo is generated through a dynamic balance of excitation and inhibition. J Neurosci. 2006; 26:4535–4545.41. Lucas-Meunier E, Monier C, Amar M, Baux G, Frégnac Y, Fossier P. Involvement of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the endogenous cholinergic modulation of the balance between excitation and inhibition in the young rat visual cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2009; 19:2411–2427.
Article42. Laezza F, Doherty JJ, Dingledine R. Long-term depression in hippocampal interneurons: joint requirement for pre- and postsynaptic events. Science. 1999; 285:1411–1414.
Article43. Kumar SS, Bacci A, Kharazia V, Huguenard JR. A developmental switch of AMPA receptor subunits in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:3005–3015.
Article44. Busetto G, Higley MJ, Sabatini BL. Developmental presence and disappearance of postsynaptically silent synapses on dendritic spines of rat layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons. J Physiol. 2008; 586:1519–1527.
Article45. Daw N, Rao Y, Wang XF, Fischer Q, Yang Y. LTP and LTD vary with layer in rodent visual cortex. Vision Res. 2004; 44:3377–3380.
Article46. Wang XF, Daw NW. Long term potentiation varies with layer in rat visual cortex. Brain Res. 2003; 989:26–34.
Article47. Jiang B, Treviño M, Kirkwood A. Sequential development of long-term potentiation and depression in different layers of the mouse visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2007; 27:9648–9652.
Article48. Jang HJ, Cho KH, Kim HS, Hahn SJ, Kim MS, Rhie DJ. Age-dependent decline in supragranular long-term synaptic plasticity by increased inhibition during the critical period in the rat primary visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2009; 101:269–275.
Article49. Cauller L. Layer I of primary sensory neocortex: where top-down converges upon bottom-up. Behav Brain Res. 1995; 71:163–170.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Layer-specific serotonergic induction of long-term depression in the prefrontal cortex of rats
- Distribution Pattern and Synaptic Circuitry of Cholinergic Neurons in the Rat Retina
- Global Cerebral Ischemia-induced Depression Accompanies Alteration of Neuronal Excitability in the Infralimbic Cortex Layer 2/3 Pyramidal Neurons
- Basal Forebrain Cholinergic-induced Activation of Cholecystokinin Inhibitory Neurons in the Basolateral Amygdala
- Electrophysiological and Morphological Classification of Inhibitory Interneurons in Layer II/III of the Rat Visual Cortex