Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Apr;48(2):518-526. 10.4143/crt.2015.093.
VEGF and Ki-67 Overexpression in Predicting Poor Overall Survival in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bhumsuk@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3The Tumor Immunity Medical Research Center, Cancer Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2454328
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.093
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate potential prognostic factors in patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
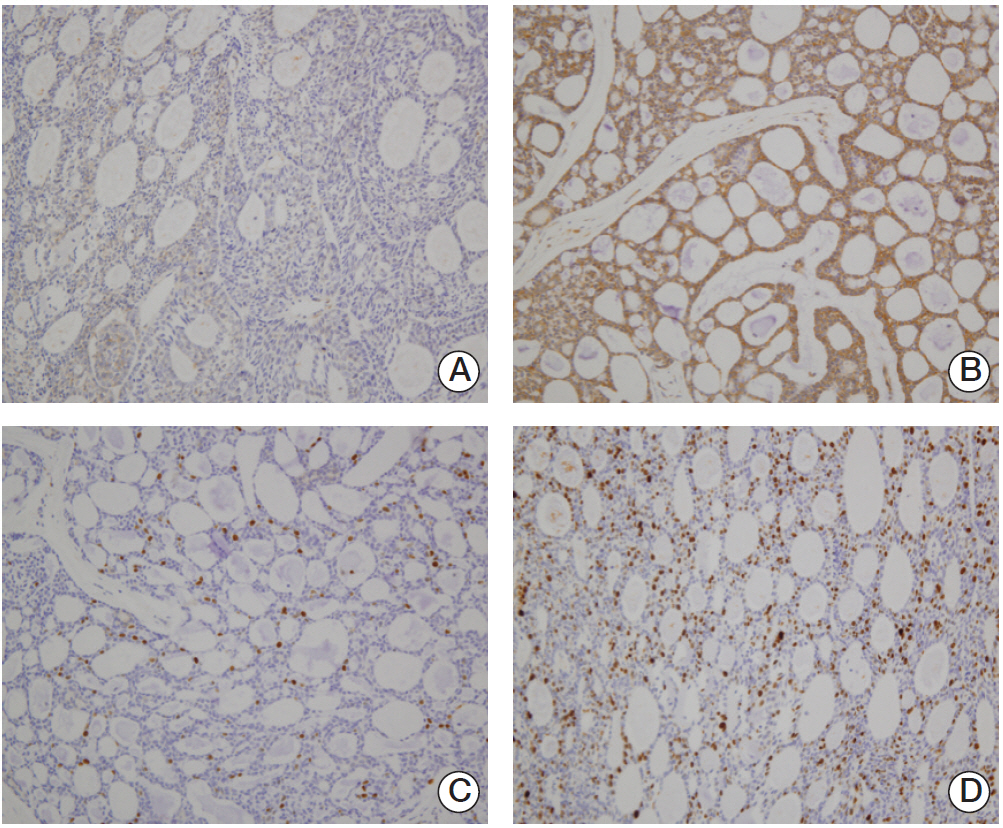
A total of 68 patients who underwent curative surgery and had available tissue were enrolled in this study. Their medical records and pathologic slides were reviewed and immunohistochemistry for basic fibroblast growth factor, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2, FGFR3, c-kit, Myb proto-oncogene protein, platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and Ki-67 was performed. Univariate and multivariate analysis was performed for determination of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
RESULTS
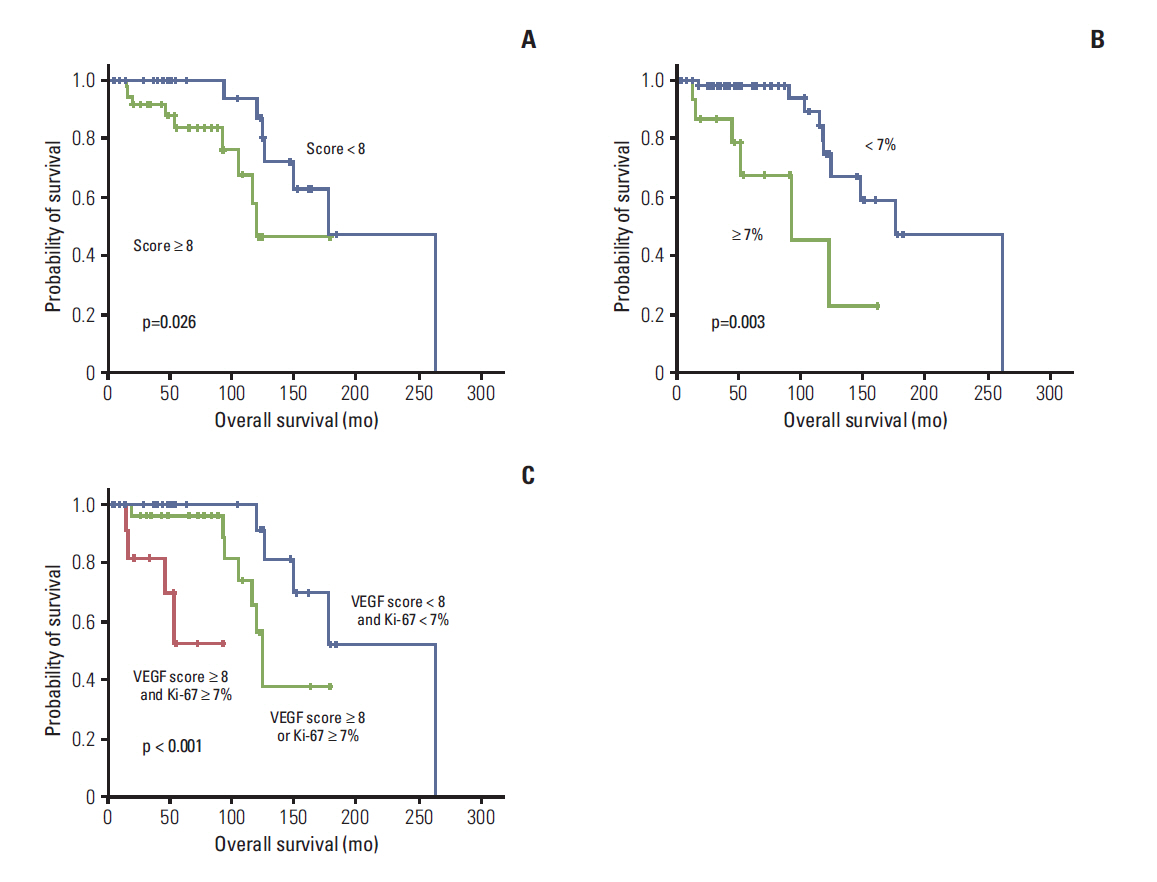
In univariate analyses, primary site of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus (p=0.022) and Ki-67 expression of more than 7% (p=0.001) were statistically significant factors for poor DFS. Regarding OS, perineural invasion (p=0.032), high expression of VEGF (p=0.033), and high expression of Ki-67 (p=0.007) were poor prognostic factors. In multivariate analyses, primary site of nasal cavity and paranasal sinus (p=0.028) and high expression of Ki-67 (p=0.004) were independent risk factors for poor DFS, and high expression of VEGF (p=0.011) and Ki-67 (p=0.011) showed independent association with poor OS.
CONCLUSION
High expression of VEGF and Ki-67 were independent poor prognostic factors for OS in ACC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoids*
Carcinoma, Adenoid Cystic*
Disease-Free Survival
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Medical Records
Multivariate Analysis
Nasal Cavity
Prognosis
Proto-Oncogenes
Receptors, Fibroblast Growth Factor
Receptors, Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Risk Factors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A*
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2
Receptors, Fibroblast Growth Factor
Receptors, Platelet-Derived Growth Factor
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Analysis of Response and Progression Patterns of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Recurrent or Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: A
Post Hoc Analysis of Two KCSG Phase II Trials
Youjin Kim, Bhumsuk Keam, Eun Joo Kang, Jin-Soo Kim, Hye Ryun Kim, Keun-Wook Lee, Jung Hye Kwon, Kyoung Eun Lee, Yaewon Yang, Yoon Hee Choi, Min Kyoung Kim, Jun Ho Ji, Tak Yun, Moon Young Choi, Ki Hyeong Lee, Sung-Bae Kim, Myung-Ju Ahn
Cancer Res Treat. 2024;56(4):1068-1076. doi: 10.4143/crt.2024.008.
Reference
-
References
1. Renehan A, Gleave EN, Hancock BD, Smith P, McGurk M. Long-term follow-up of over 1000 patients with salivary gland tumours treated in a single centre. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:1750–4.
Article2. Gondivkar SM, Gadbail AR, Chole R, Parikh RV. Adenoid cystic carcinoma: a rare clinical entity and literature review. Oral Oncol. 2011; 47:231–6.
Article3. Spiro RH. Salivary neoplasms: overview of a 35-year experience with 2,807 patients. Head Neck Surg. 1986; 8:177–84.
Article4. Sung MW, Kim KH, Kim JW, Min YG, Seong WJ, Roh JL, et al. Clinicopathologic predictors and impact of distant metastasis from adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 129:1193–7.
Article5. Huang M, Ma D, Sun K, Yu G, Guo C, Gao F. Factors influencing survival rate in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 26:435–9.
Article6. Spiro RH. Distant metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary origin. Am J Surg. 1997; 174:495–8.7. Laurie SA, Ho AL, Fury MG, Sherman E, Pfister DG. Systemic therapy in the management of metastatic or locally recurrent adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:815–24.
Article8. Liu J, Shao C, Tan ML, Mu D, Ferris RL, Ha PK. Molecular biology of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Head Neck. 2012; 34:1665–77.
Article9. da Cruz Perez DE, de Abreu Alves F, Nobuko Nishimoto I, de Almeida OP, Kowalski LP. Prognostic factors in head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2006; 42:139–46.
Article10. Khan AJ, DiGiovanna MP, Ross DA, Sasaki CT, Carter D, Son YH, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma: a retrospective clinical review. Int J Cancer. 2001; 96:149–58.11. Tang Y, Liang X, Zheng M, Zhu Z, Zhu G, Yang J, et al. Expression of c-kit and Slug correlates with invasion and metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2010; 46:311–6.
Article12. Yu F, Jiang XZ, Chen WT, Zhao YF, Zhou XJ. Microvessel density and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2003; 12:443–6.13. Lim JJ, Kang S, Lee MR, Pai HK, Yoon HJ, Lee JI, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in salivary gland carcinomas and its relation to p53, Ki-67 and prognosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2003; 32:552–61.
Article14. Ettl T, Schwarz S, Kleinsasser N, Hartmann A, Reichert TE, Driemel O. Overexpression of EGFR and absence of C-KIT expression correlate with poor prognosis in salivary gland carcinomas. Histopathology. 2008; 53:567–77.
Article15. Zhu QR, White FH, Tipoe GL. p53 oncoprotein accumulation in adenoid cystic carcinoma of parotid and palatine salivary glands. Pathology. 1997; 29:154–8.
Article16. Vekony H, Ylstra B, Wilting SM, Meijer GA, van de Wiel MA, Leemans CR, et al. DNA copy number gains at loci of growth factors and their receptors in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:3133–9.
Article17. Salehinejad J, Mohtasham N, Bagherpour A, Abbaszadeh-Bidokhty H, Ghazi A. Evaluation of c-kit protein (CD117) expression in common salivary gland neoplasms. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014; 18:177–82.
Article18. Ciccolallo L, Licitra L, Gatta G; EUROCARE Working Group. Gatta G. Survival from salivary glands adenoid cystic carcinoma in European populations. Oral Oncol. 2009; 45:669–74.19. Garden AS, Weber RS, Morrison WH, Ang KK, Peters LJ. The influence of positive margins and nerve invasion in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck treated with surgery and radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995; 32:619–26.
Article20. Li Z, Tang P, Xu Z. Clinico-pathological significance of microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001; 36:212–4.21. Nordgard S, Franzen G, Boysen M, Halvorsen TB. Ki-67 as a prognostic marker in adenoid cystic carcinoma assessed with the monoclonal antibody MIB1 in paraffin sections. Laryngoscope. 1997; 107:531–6.
Article22. West RB, Kong C, Clarke N, Gilks T, Lipsick JS, Cao H, et al. MYB expression and translocation in adenoid cystic carcinomas and other salivary gland tumors with clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011; 35:92–9.
Article23. Mitani Y, Li J, Rao PH, Zhao YJ, Bell D, Lippman SM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the MYB-NFIB gene fusion in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: incidence, variability, and clinicopathologic significance. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:4722–31.
Article24. Paulsson J, Sjoblom T, Micke P, Ponten F, Landberg G, Heldin CH, et al. Prognostic significance of stromal platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor expression in human breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2009; 175:334–41.25. Koo JS, Park S, Kim SI, Lee S, Park BW. The impact of caveolin protein expression in tumor stroma on prognosis of breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2011; 32:787–99.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- p27Kipl, K-67 and Bcl-2 Expression in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Head and Neck
- Palliative Radiotherapy in a Patient with Pulmonary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic CArcinoma of Unusually Located Lacrimal Gland
- A case of adenoid basal cell carcinoma in uterine cervix
- A Case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Bartholin's Gland