Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Jun;43(3):335-340. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.3.335.
Outcomes of Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy Compared With Deep Brain Stimulation in a Patient With Dystonic Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. srcho918@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurosurgery and Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- 4Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2453924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.3.335
Abstract
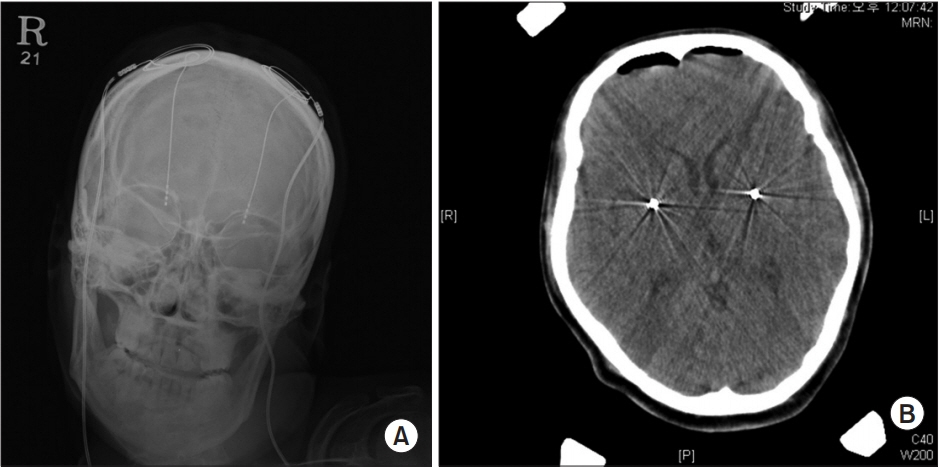
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS) in internal globus pallidus is considered to be a good option for controlling generalized dystonia in patients with this condition. In this relation, it is known that DBS has already been shown to have significant effects on primary dystonia, but is seen as controversial in secondary dystonia including cerebral palsy (CP). On the other hand, intrathecal baclofen (ITB) has been known to reduce spasticity and dystonia in patients who did not respond to oral medications or botulinum toxin treatment. Here, we report a patient with dystonic CP, who received the ITB pump implantation long after the DBS and who noted remarkable improvement in the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey, Dystonia Rating Scale, Modified Barthel Index, and visual analog scale scores for pain after an ITB pump implantation was used as compared with DBS. To our knowledge, the present case report is the first to demonstrate the effects of an ITB pump on reducing pain and dystonia and improving quality of life and satisfaction, compared with DBS in a patient with CP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kupsch A, Benecke R, Muller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, et al. Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1978–90.
Article2. Yoon YK, Lee KC, Cho HE, Chae M, Chang JW, Chang WS, et al. Outcomes of intrathecal baclofen therapy in patients with cerebral palsy and acquired brain injury. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e7472.
Article3. Eek MN, Olsson K, Lindh K, Askljung B, Pahlman M, Corneliusson O, et al. Intrathecal baclofen in dyskinetic cerebral palsy: effects on function and activity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018; 60:94–9.
Article4. Vidailhet M, Yelnik J, Lagrange C, Fraix V, Grabli D, Thobois S, et al. Bilateral pallidal deep brain stimulation for the treatment of patients with dystonia-choreoathetosis cerebral palsy: a prospective pilot study. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:709–17.
Article5. Kim AR, Chang JW, Chang WS, Park ES, Cho SR. Twoyear outcomes of deep brain stimulation in adults with cerebral palsy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014; 38:209–17.
Article6. Andrews C, Aviles-Olmos I, Hariz M, Foltynie T. Which patients with dystonia benefit from deep brain stimulation? A metaregression of individual patient outcomes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010; 81:1383–9.
Article7. Narayan RK, Loubser PG, Jankovic J, Donovan WH, Bontke CF. Intrathecal baclofen for intractable axial dystonia. Neurology. 1991; 41:1141–2.
Article8. Zieglgansberger W. Dorsal horn neuropharmacology: baclofen and morphine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988; 531:150–6.9. Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990; 13:266–71.
Article10. Albright AL, Barry MJ, Shafton DH, Ferson SS. Intrathecal baclofen for generalized dystonia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001; 43:652–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Area for Dystonic Tremor
- Dose-dependent Changes in Gait Pattern after Intrathecal Baclofen Bolus Injection in Adult Ambulatory Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
- Effect of Intrathecal Baclofen Pump on Scoliosis in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-Analysis
- Combined Therapy of Orthopedic Surgery after Deep Brain Stimulation in Cerebral Palsy Mixed Type: A Case Report
- Successful Control of Intractable Myoclonus in a Patient With Hypoxic Brain Injury After Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy: A Case Report