Brain Neurorehabil.
2015 Sep;8(2):104-108. 10.12786/bn.2015.8.2.104.
Dose-dependent Changes in Gait Pattern after Intrathecal Baclofen Bolus Injection in Adult Ambulatory Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. srcho918@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery and Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 4Avison Biomedical Research Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 5Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2165198
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12786/bn.2015.8.2.104
Abstract
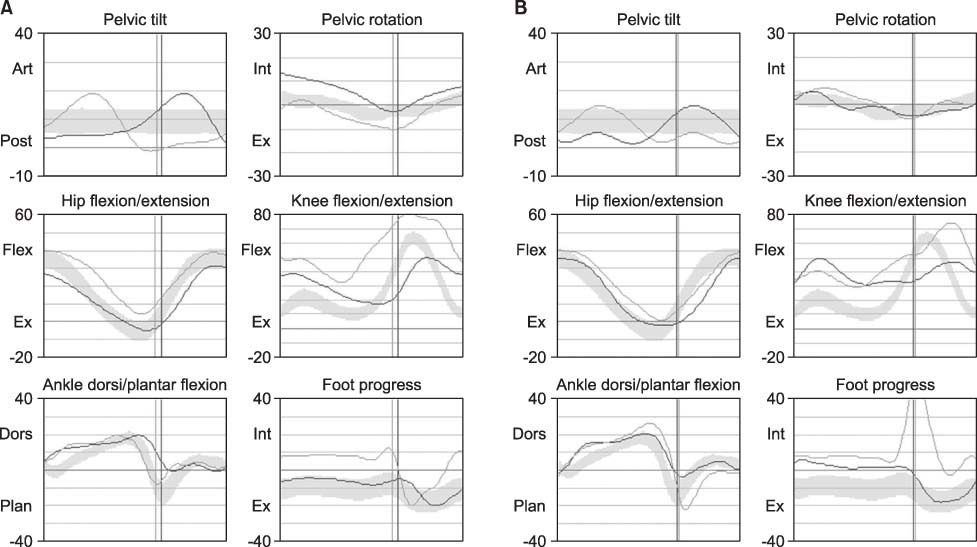
- Intrathecal baclofen (ITB) therapy has been proven to reduce severe spasticity in cerebral palsy (CP). However, few results reported the objective gait pattern change after ITB bolus injection in adult ambulatory CP. We therefore evaluated observational and kinematic gait patterns at different ITB bolus injection doses. We performed a test trial of 3-day ITB bolus injections at doses of 12.5 microg, 25 microg, and 50 microg in ambulatory CP. We evaluated modified Ashworth scale, visual analogue scale, observational gait scale, and kinematic gait analysis after ITB bolus injection. Intrathecal administration of low-dose baclofen 25 microg was successfully used not only for the treatment of spasticity but also for the treatment of gait disturbance, whereas the higher dose baclofen 50 microg induced foot drop and deteriorated gait pattern. We experienced dose-dependent changes in gait pattern confirmed by the observational and kinematic gait assessments after ITB bolus injection in adult ambulatory CP.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ross SA, Engsberg JR. Relationships between spasticity, strength, gait, and the GMFM-66 in persons with spastic diplegia cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:1114–1120.2. Lynn AK, Turner M, Chambers HG. Surgical management of spasticity in persons with cerebral palsy. PM R. 2009; 1:834–838.3. Penn RD, Kroin JS. Continuous intrathecal baclofen for severe spasticity. Lancet. 1985; 326:125–127.4. Walter M, Altermatt S, Furrer C, Meyer-Heim A. Intrathecal bacolfen therapy in children with severe spasticity: Outcome and complications. Dev Neurorehabil. 2014; 17(6):368–374.5. Horn TS, Yablon SA, Chow JW, Lee JE, Stokic DS. Effect of intrathecal baclofen bolus injection on lower extremity joint range of motion during gait in patients with acquired brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:30–34.6. Hoving MA, van Raak EPM, Spincemaille GHJJ, van Kranen-Mastenbroek VHJM, van Kleef M, Gorter JW, Vles JSH. Safety and one-year efficacy of intrathecal baclofen therapy in children with intractable spastic cerebral palsy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2009; 13:247–256.7. Boyd RN, Graham HK. Objective measurement of clinical findings in the use of botulinum toxin type A for the management of children with cerebral palsy. Eur J Neurol. 1999; 6:supple 4. S23–S35.8. Bleyenheuft C, Filipetti P, Caldas C, Lejeune T. Experience with external pump trial prior to implantation for intrathecal baclofen in ambulatory patients with spastic cerebral palsy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 37:23–28.9. Pin TW, Mccartney L, Lewis J, Waugh MC. Use of intrathecal baclofen therapy in ambulant children and adolescents with spasticity and dystonia of cerebral origin: A systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001; 53:885–895.10. Jasmin L, Rabkin SD, Granato A, Boudah A, Ohara PT. Analgesia and hyperalgesia from GABA-mediated modulation of the cerebral cortex. Nature. 2003; 424:316–320.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intrathecal Baclofen for Spasticity: Changes in Clinical Feature and Gait
- Effect of Intrathecal Baclofen Pump on Scoliosis in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-Analysis
- Effects of Intrathecal Baclofen on Spasticity
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Therapy on Gastrocnemius in Spastic Cerebral Palsied Children
- Outcomes of Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy Compared With Deep Brain Stimulation in a Patient With Dystonic Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report